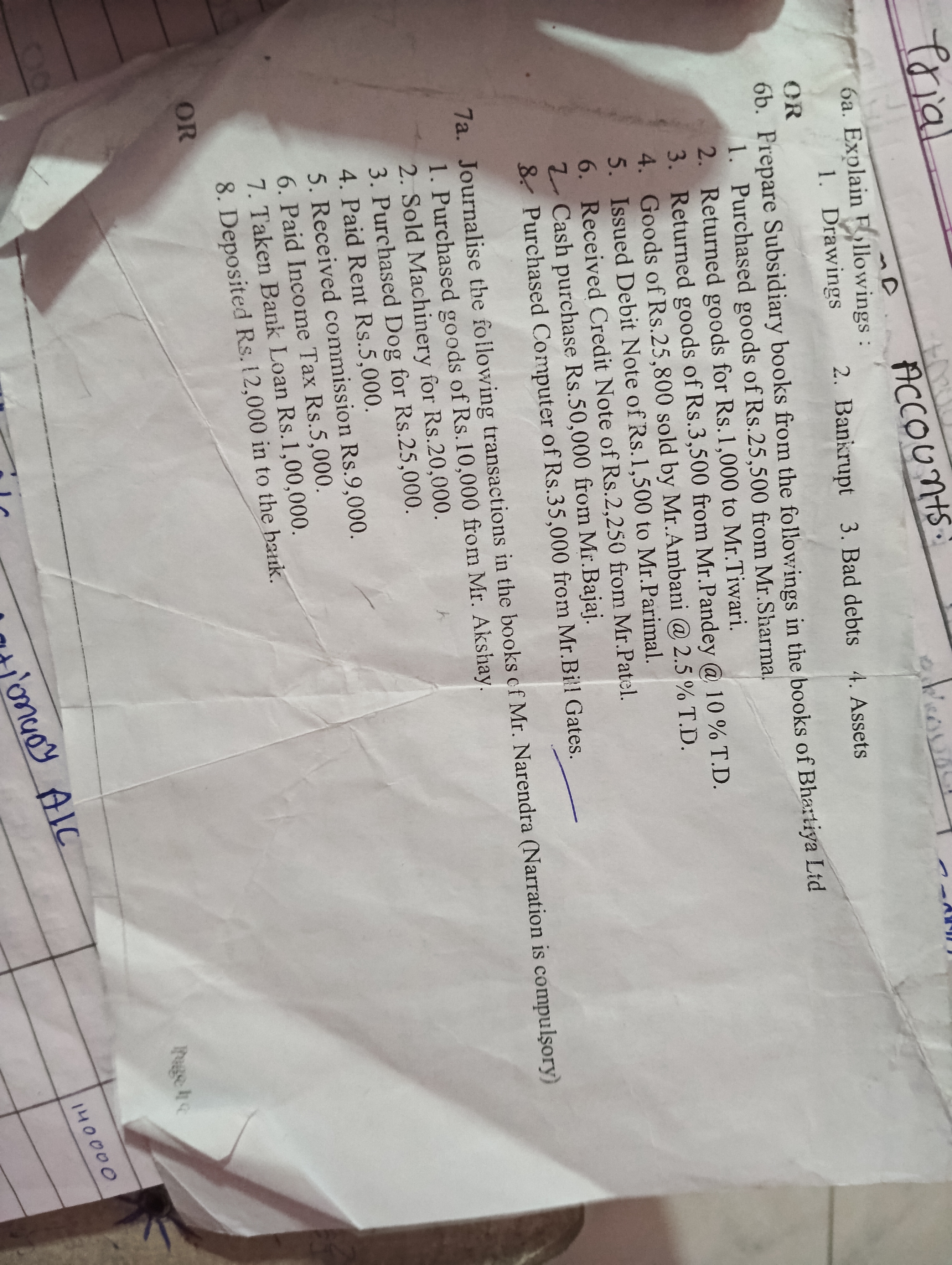
Journalize the following transactions in the books of M. A. B. I. T. 1. Purchased goods for Rs. 10,000 from Mr. A. 2. Sold Machinery for Rs. 25,000. 3. Purchased Rs. 5,000. 4. Paid... Journalize the following transactions in the books of M. A. B. I. T. 1. Purchased goods for Rs. 10,000 from Mr. A. 2. Sold Machinery for Rs. 25,000. 3. Purchased Rs. 5,000. 4. Paid Rs. 3,000. 5. Received commission Rs. 9,000. 6. Paid Income Tax Rs. 10,000. 7. Taken Bank Loan Rs. 1,00,000. 8. Deposited Rs. 12,000 in the bank.
Understand the Problem
The question is asking to journalize specific transactions based on the provided details. This involves recording financial transactions accurately in a journal format, likely for accounting purposes.
Answer
Each transaction is recorded with appropriate debits and credits as shown in the journal entries above.
Answer for screen readers
Purchases A/c Dr. 10,000
To Mr. A A/c 10,000
Cash/Bank A/c Dr. 25,000
To Machinery A/c 25,000
Purchases A/c Dr. 5,000
To Cash/Bank A/c 5,000
Expense/Liability A/c Dr. 3,000
To Cash/Bank A/c 3,000
Cash/Bank A/c Dr. 9,000
To Commission Income A/c 9,000
Income Tax Expense A/c Dr. 10,000
To Cash/Bank A/c 10,000
Cash/Bank A/c Dr. 1,00,000
To Bank Loan A/c 1,00,000
Bank A/c Dr. 12,000
To Cash A/c 12,000
Steps to Solve
-
Record Purchase of Goods
When goods are purchased, Debit the Purchases account and Credit the Supplier's account. Here, Rs. 10,000 is purchased from Mr. A.
- Debit Purchases Account: Rs. 10,000
- Credit Mr. A Account: Rs. 10,000
Journal Entry:
Purchases A/c Dr. 10,000 To Mr. A A/c 10,000 -
Record Sale of Machinery
When machinery is sold, Debit the Cash/Bank account and Credit the Machinery account.
- Debit Cash/Bank Account: Rs. 25,000
- Credit Machinery Account: Rs. 25,000
Journal Entry:
Cash/Bank A/c Dr. 25,000 To Machinery A/c 25,000 -
Record Purchase of Goods
For the next purchase of goods worth Rs. 5,000:
- Debit Purchases Account: Rs. 5,000
- Credit Cash/Bank Account: Rs. 5,000 (assuming it is paid immediately)
Journal Entry:
Purchases A/c Dr. 5,000 To Cash/Bank A/c 5,000 -
Record Payment Made
When payment of Rs. 3,000 is made, Debit the respective account (could be an expense or liability) and Credit Cash/Bank.
- Debit respective account: Rs. 3,000
- Credit Cash/Bank Account: Rs. 3,000
Journal Entry:
Expense/Liability A/c Dr. 3,000 To Cash/Bank A/c 3,000 -
Record Commission Received
For the commission received:
- Debit Cash/Bank Account: Rs. 9,000
- Credit Commission Income Account: Rs. 9,000
Journal Entry:
Cash/Bank A/c Dr. 9,000 To Commission Income A/c 9,000 -
Record Income Tax Paid
When Rs. 10,000 is paid as income tax:
- Debit Income Tax Expense Account: Rs. 10,000
- Credit Cash/Bank Account: Rs. 10,000
Journal Entry:
Income Tax Expense A/c Dr. 10,000 To Cash/Bank A/c 10,000 -
Record Bank Loan Taken
For a bank loan of Rs. 1,00,000:
- Debit Cash/Bank Account: Rs. 1,00,000
- Credit Bank Loan Account: Rs. 1,00,000
Journal Entry:
Cash/Bank A/c Dr. 1,00,000 To Bank Loan A/c 1,00,000 -
Record Bank Deposit
When Rs. 12,000 is deposited in the bank:
- Debit Bank Account: Rs. 12,000
- Credit Cash Account: Rs. 12,000
Journal Entry:
Bank A/c Dr. 12,000 To Cash A/c 12,000
Purchases A/c Dr. 10,000
To Mr. A A/c 10,000
Cash/Bank A/c Dr. 25,000
To Machinery A/c 25,000
Purchases A/c Dr. 5,000
To Cash/Bank A/c 5,000
Expense/Liability A/c Dr. 3,000
To Cash/Bank A/c 3,000
Cash/Bank A/c Dr. 9,000
To Commission Income A/c 9,000
Income Tax Expense A/c Dr. 10,000
To Cash/Bank A/c 10,000
Cash/Bank A/c Dr. 1,00,000
To Bank Loan A/c 1,00,000
Bank A/c Dr. 12,000
To Cash A/c 12,000
More Information
These journal entries reflect the basic accounting principles where each transaction is recorded in a double-entry system, ensuring that the accounting equation remains balanced.
Tips
- Forgetting to include both sides of the transaction (debit and credit).
- Misclassifying accounts, such as treating an expense as revenue.
- Not matching debits and credits correctly.