Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the anatomical structure that serves as the functional unit of the kidney?
What is the anatomical structure that serves as the functional unit of the kidney?
Which feature distinguishes the male urethra from the female urethra?
Which feature distinguishes the male urethra from the female urethra?
What is the primary function of the urinary bladder?
What is the primary function of the urinary bladder?
Which part of the nephron is involved in the reabsorption of water and solutes?
Which part of the nephron is involved in the reabsorption of water and solutes?
Signup and view all the answers
Where does the ureter transport urine from?
Where does the ureter transport urine from?
Signup and view all the answers
Study Notes
Urinary System Overview
- Composed of kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra.
- Functions include filtering blood, excreting waste, regulating fluid balance, and balancing electrolytes.
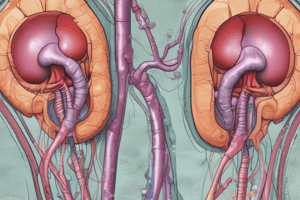
Kidneys
- Number: 2 (right and left).
- Shape: Bean-shaped.
- Location: Flank the vertebral column below the ribs.
- Size: Approximately 1 x 2 x 4 inches.
- Features two ends (upper with supra-renal gland, lower), two borders (outer convex, inner concave with hilum), and two surfaces (anterior and posterior).
- Nephrons:
- Functional units of the kidney, approximately one million per kidney.
- Consist of glomerulus and renal tubule.
- Tubule parts: proximal convoluted tubules, loop of Henle, distal convoluted tubule, and collecting duct.
Ureters
- Number: 2 (right and left) fibromuscular tubes.
- Length: Approximately 25 cm.
- Location: Upper abdomen to lower pelvis.
- Function: Transport urine from kidneys to urinary bladder.
Urinary Bladder
- Definition: Hollow muscular organ.
- Location: Pelvic cavity, behind the symphysis pubis.
- Function: Stores urine.
- Shape: Pyramidal, featuring:
- Apex (anteriorly) connected to umbilicus by median umbilical ligament.
- Base (posteriorly) where trigone area receives openings from both ureters.
- Inner base surface called trigone.
Ureters and Bladder Structure
- Bladder has three surfaces.
- Inferior angle known as the neck, encircled by the involuntary internal urethral sphincter.
Male Urethra
- Length: About 8 inches (20 cm).
- Begins at the neck of the urinary bladder.
- Comprises three parts:
- Prostatic: 1.5 inches long.
- Membranous: 0.5 inches long, surrounded by external sphincter.
- Penile (spongy): 6 inches long.
- Terminates at the tip of the glans penis.
Female Urethra
- Length: Approximately 1.5 inches (4 cm).
- Begins at the neck of the urinary bladder.
- Terminates in the vestibule anterior to the vaginal orifice.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Related Documents
Description
This quiz covers the components, anatomical structures, and functions of the urinary system. It aims to correlate the function of the urinary system with its anatomical features, specifically focusing on the kidneys and their attributes. Test your knowledge on these essential concepts of human anatomy!