What is the mechanism depicted in the provided reaction image?
Understand the Problem
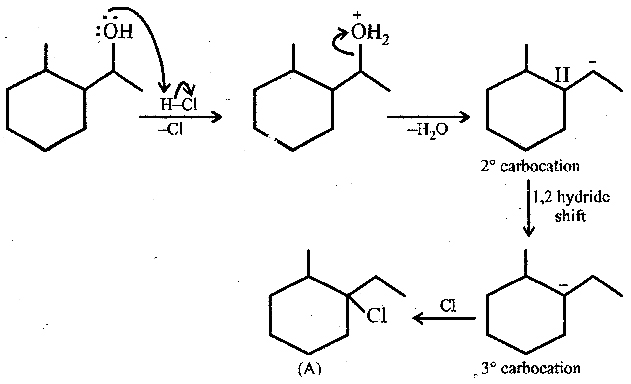
The question involves a chemical mechanism that outlines the steps of a reaction involving carbocations and hydride shifts. It seems to involve an organic chemistry topic related to stability and reactivity of carbocations as well as nucleophilic attack and rearrangement processes.
Answer
Protonation, water elimination, hydride shift, chloride capture.
The mechanism involves protonation of the alcohol by HCl, followed by elimination of water to form a 2° carbocation. This undergoes a 1,2-hydride shift to form a 3° carbocation, before capturing a chloride ion to form the alkyl chloride.
Answer for screen readers
The mechanism involves protonation of the alcohol by HCl, followed by elimination of water to form a 2° carbocation. This undergoes a 1,2-hydride shift to form a 3° carbocation, before capturing a chloride ion to form the alkyl chloride.
More Information
The reaction is an example of carbocation rearrangement to achieve a more stable intermediate, known as a hydride shift.
Tips
A common mistake is assuming direct attack by Cl-; remember that rearrangement can occur to stabilize carbocations.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information