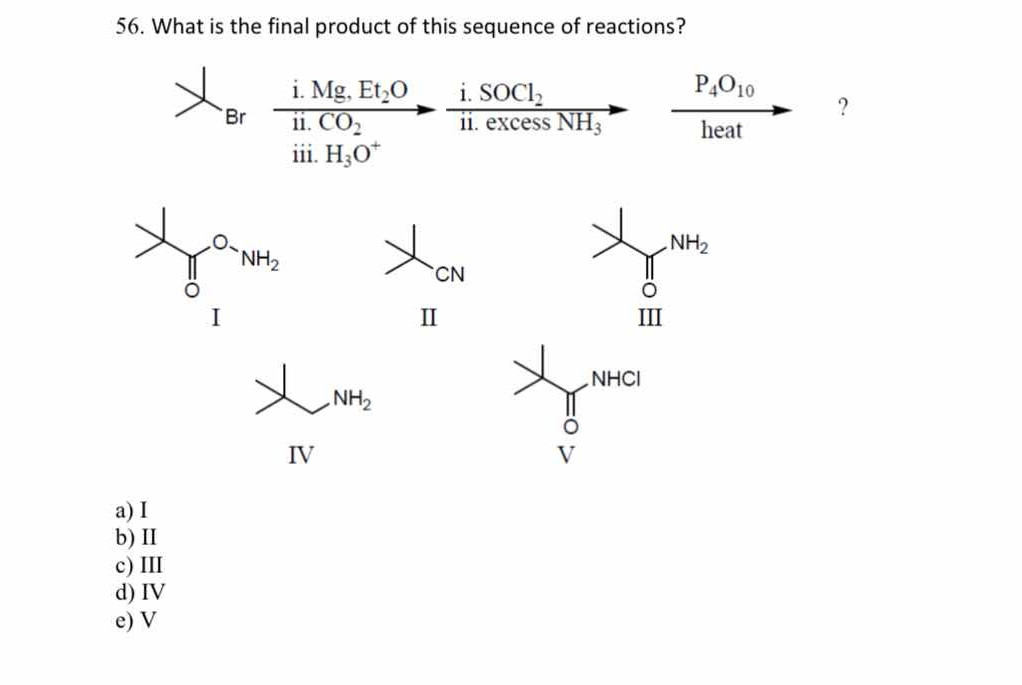
What is the final product of this sequence of reactions?
Understand the Problem
The question is asking to determine the final product of a given series of chemical reactions starting from a molecule with a bromine (Br) group. This involves identifying the transformations based on the provided reagents and conditions.
Answer
The final product is II ($\text{R-C}\equiv\text{N}$).
Answer for screen readers
The final product is likely option II, represented by the nitrile structure.
Steps to Solve
-
Formation of the Grignard Reagent Start by reacting the bromine compound with magnesium in diethyl ether ($\text{Et}_2\text{O}$). This forms a Grignard reagent: $$ \text{R-Br} + \text{Mg} \xrightarrow{\text{Et}_2\text{O}} \text{R-MgBr} $$
-
Carboxylation Reaction Next, introduce carbon dioxide ($\text{CO}_2$) to the Grignard reagent. This process transforms the Grignard reagent into a carboxylic acid: $$ \text{R-MgBr} + \text{CO}_2 \rightarrow \text{R-COOMgBr} $$
-
Acid Workup After the carboxylation, add $\text{H}_3\text{O}^+$ (acid) to obtain the carboxylic acid: $$ \text{R-COOMgBr} + \text{H}_3\text{O}^+ \rightarrow \text{R-COOH} $$
-
Conversion to Amide Next, the carboxylic acid is reacted with thionyl chloride ($\text{SOCl}_2$) to generate the acyl chloride: $$ \text{R-COOH} + \text{SOCl}_2 \rightarrow \text{R-COCl} + \text{SO}_2 + \text{HCl} $$
-
Amide Formation Introduce excess ammonia ($\text{NH}_3$) to the acyl chloride to form the amide: $$ \text{R-COCl} + \text{NH}_3 \rightarrow \text{R-CONH}_2 + \text{HCl} $$
-
Dehydration Reaction Finally, treat the amide with phosphorus pentoxide ($\text{P}4\text{O}{10}$) and heat, which may lead to the removal of water and possibly reforming the original amide: $$ \text{R-CONH}_2 \xrightarrow{\text{P}4\text{O}{10}, \text{heat}} \text{R-C}\equiv\text{N} $$
The final product is likely option II, represented by the nitrile structure.
More Information
This sequence of reactions starts from a bromoalkane and involves the formation of a Grignard reagent, carboxylation, conversion to acyl chloride, and lastly the formation of a nitrile after dehydration. This indicates a complex interplay of functional group transformations.
Tips
- Confusing the order of reactions, especially the transition from carboxylic acid to amide and then to a nitrile.
- Misidentifying the reagents’ roles, particularly the difference between acyl chlorides and carboxylic acids.
- Overlooking the effect of heat and dehydrating agents like $\text{P}4\text{O}{10}$, which can lead to structural changes in the final product.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information