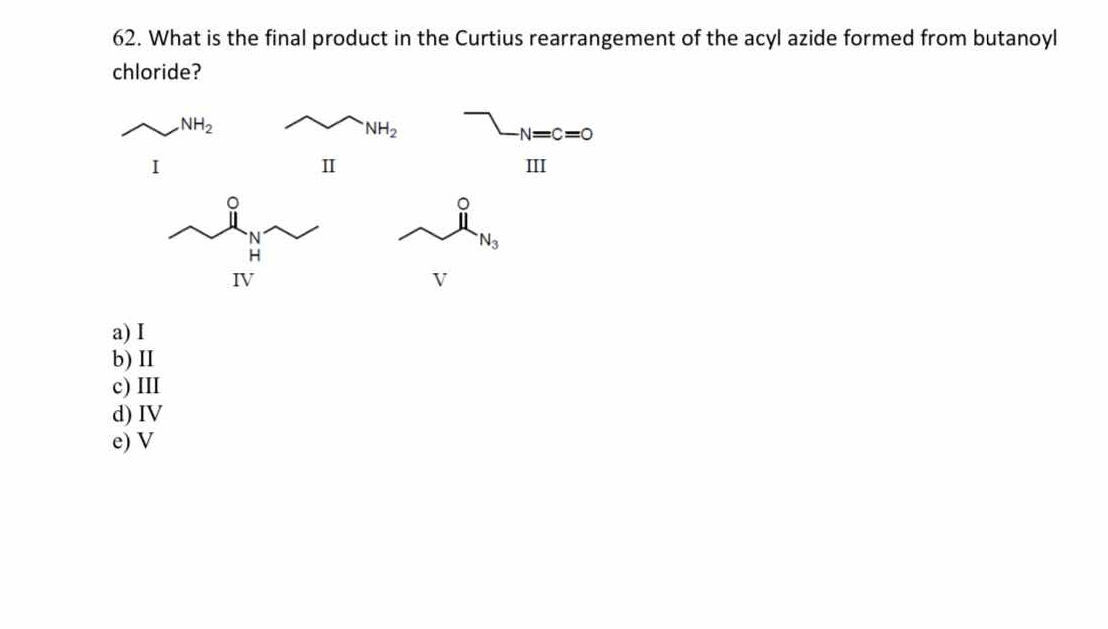
What is the final product in the Curtius rearrangement of the acyl azide formed from butanoyl chloride?
Understand the Problem
The question is asking for the final product of the Curtius rearrangement specifically from the acyl azide derived from butanoyl chloride. This involves understanding the mechanistic pathway of the Curtius rearrangement and evaluating the provided structural options (I to V) to identify the correct final product.
Answer
II (butylamine)
The final product in the Curtius rearrangement of the acyl azide formed from butanoyl chloride is butylamine (II).
Answer for screen readers
The final product in the Curtius rearrangement of the acyl azide formed from butanoyl chloride is butylamine (II).
More Information
During the Curtius rearrangement, an acyl azide is converted into an isocyanate, which can further react to form an amine. In this case, an acyl azide derived from butanoyl chloride ultimately forms butylamine.
Tips
A common mistake is to overlook that the isocyanate intermediate often reacts further to form amines.
Sources
- N=C=O III O H N3 IV V III II IV V I - Numerade - numerade.com
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information