What are the properties and applications of the HPMA copolymer, SMA, and γ-PGA in drug delivery?
Understand the Problem
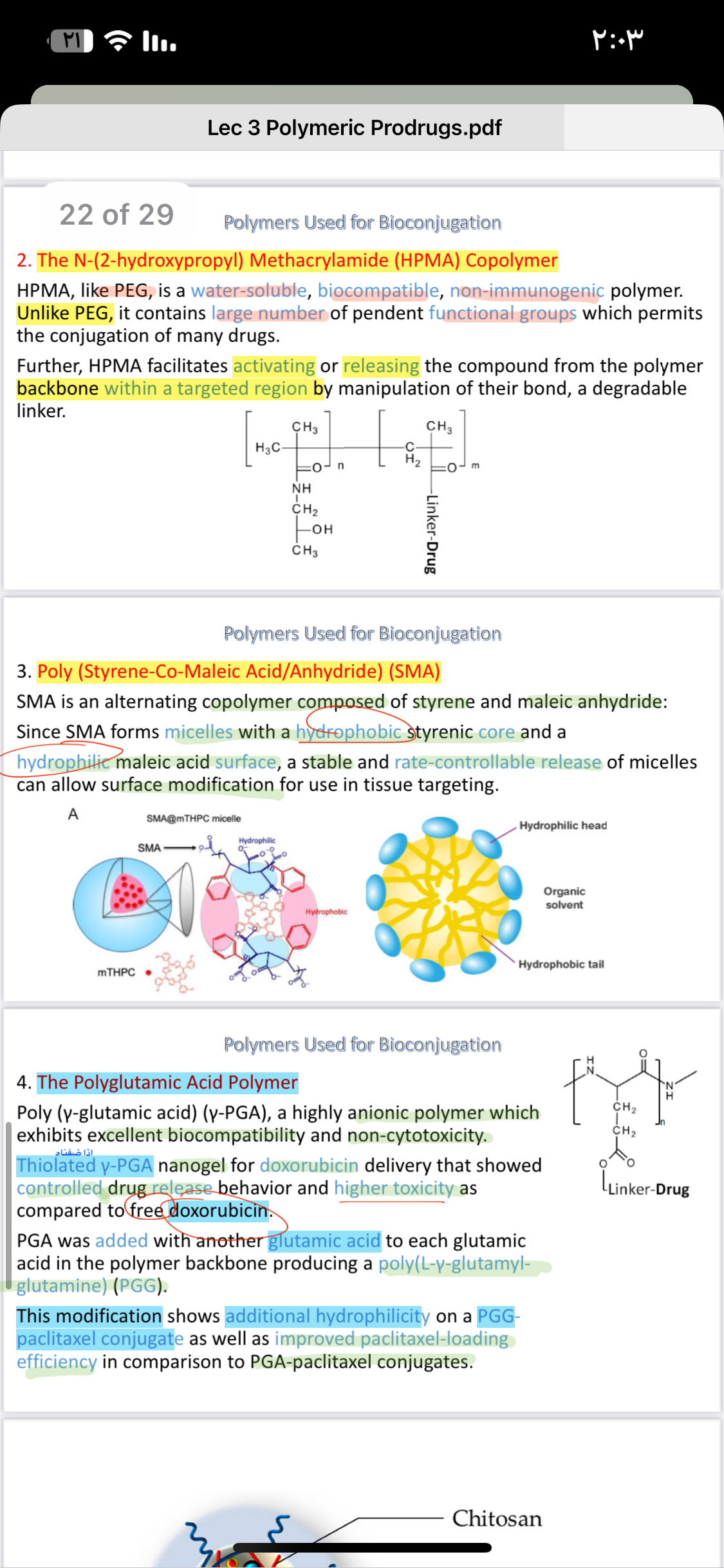
The question is seeking information about various polymers, specifically the N-(2-hydroxypropyl) methacrylamide (HPMA) copolymer, Poly (Styrene-Co-Maleic Acid/Anhydride) (SMA), and Poly (γ-glutamic acid) (γ-PGA), as used in bioconjugation and drug delivery systems.
Answer
HPMA copolymer aids in targeted drug release; SMA forms micelles for controlled release; γ-PGA is non-toxic, biodegradable, and enhances drug delivery.
HPMA copolymer is water-soluble, biocompatible, and helps in targeted drug release. SMA forms micelles for controlled release and tissue targeting. γ-PGA is non-toxic, biodegradable, enhances hydrophilicity, and improves drug delivery efficiency.
Answer for screen readers
HPMA copolymer is water-soluble, biocompatible, and helps in targeted drug release. SMA forms micelles for controlled release and tissue targeting. γ-PGA is non-toxic, biodegradable, enhances hydrophilicity, and improves drug delivery efficiency.
More Information
HPMA copolymer allows for effective targeting due to its pendent functional groups. SMA's micelle formation is beneficial for drug delivery systems needing rate-controllable release. γ-PGA offers biocompatibility and biodegradability, crucial for safe drug delivery applications.
Tips
A common mistake is confusing the functionality of these polymers; each has distinct properties and applications in drug delivery.
Sources
- HPMA Copolymer-Based Nanomedicines in Controlled Drug Delivery - pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- Bacterial-Derived Polymer Poly-γ-Glutamic Acid (γ-PGA) - NCBI - ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- Drug delivery applications of poly-γ-glutamic acid - fjps.springeropen.com
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information