What are the pathways of gluconeogenesis from glycerol, propionyl CoA, and glucogenic amino acids?
Understand the Problem
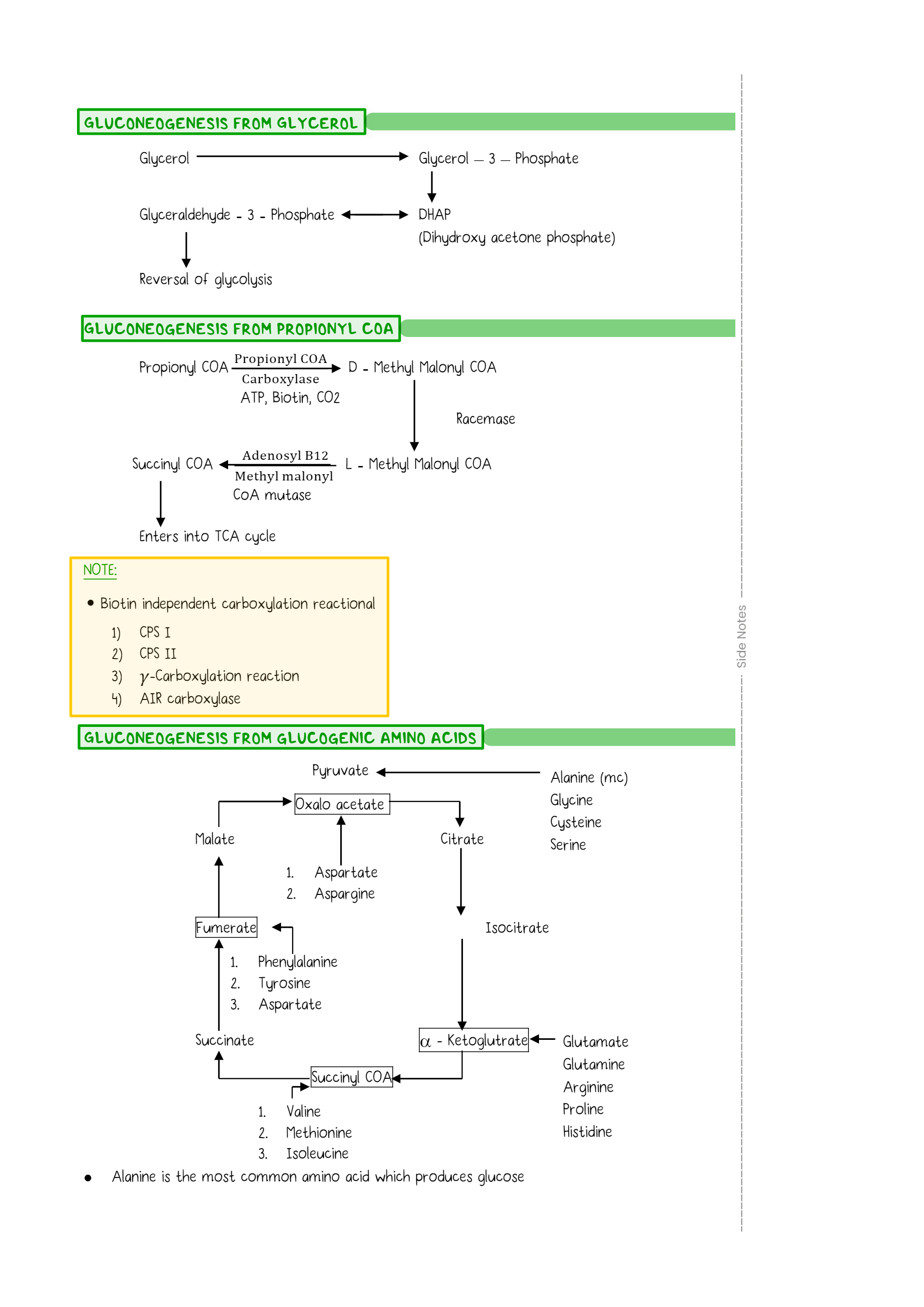
The question depicts a diagrammatic representation of gluconeogenesis from various substrates including glycerol, propionyl CoA, and glucogenic amino acids. It illustrates the metabolic pathways involved in the conversion of these substrates into glucose.
Answer
Glycerol → DHAP; Propionyl CoA → Succinyl CoA → TCA cycle; Amino acids → Pyruvate/Oxaloacetate.
The pathways are: glycerol to DHAP; propionyl CoA to succinyl CoA via D-methylmalonyl CoA; glucogenic amino acids to various intermediates like pyruvate and oxaloacetate, entering gluconeogenesis.
Answer for screen readers
The pathways are: glycerol to DHAP; propionyl CoA to succinyl CoA via D-methylmalonyl CoA; glucogenic amino acids to various intermediates like pyruvate and oxaloacetate, entering gluconeogenesis.
More Information
Gluconeogenesis is essential in fasting for maintaining blood glucose levels, utilizing non-carbohydrate substrates.
Tips
A common mistake is not recognizing the role of intermediates like oxaloacetate in connecting the TCA cycle and gluconeogenesis.
Sources
- Gluconeogenesis - Biochemistry - Medbullets Step 1 - step1.medbullets.com
- Gluconeogenesis - Wikipedia - en.wikipedia.org
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information