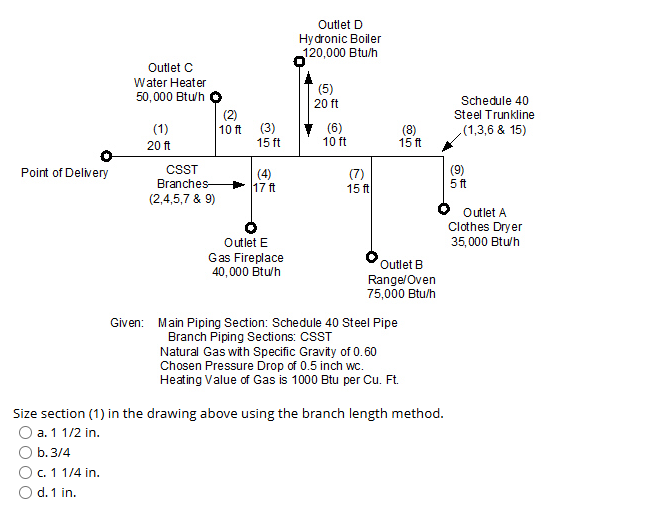
Size section (1) in the drawing above using the branch length method.
Understand the Problem
The question is asking to determine the size of a specific section of piping in a gas distribution system using the given branch length method, based on the provided diagram and information about the system's specifications.
Answer
The size of section (1) is $1 \frac{1}{2}$ in.
Answer for screen readers
The correct pipe size for section (1) is $1 \frac{1}{2}$ in.
Steps to Solve
- Identify Total Flow Rates Combine the flow rates of each outlet connected to the section (1) to find the total flow rate. The outlets have the following specifications:
- Outlet (D) = 120,000 Btu/h
- Outlet (C) = 50,000 Btu/h
- Outlet (B) = 75,000 Btu/h
- Outlet (E) = 40,000 Btu/h
- Outlet (A) = 35,000 Btu/h
Add these values to find the total:
$$
\text{Total flow} = 120,000 + 50,000 + 75,000 + 40,000 + 35,000 = 320,000 \text{ Btu/h}
$$
- Determine Equivalent Length Calculate the equivalent length of each branch based on the given diagram and lengths. Here are the lengths to consider:
- Segment (1) = 20 ft
- Segment (2) = 10 ft
- Segment (4) = 7 ft
- Segment (5) = 20 ft
- Segment (7) = 15 ft
- Segment (8) = 10 ft
- Segment (9) = 5 ft
The equivalent length in total can be computed as:
$$
\text{Total Length} = (20 + 10 + 7 + 20 + 15 + 10 + 5) \text{ ft} = 87 \text{ ft}
$$
-
Consult Gas Pipe Sizing Chart Using the total flow rate of 320,000 Btu/h and the calculated equivalent length of 87 ft, refer to a gas pipe sizing chart or table that corresponds with the pressure drop of 0.5 inches wc for CSST or Schedule 40 Steel Pipe.
-
Determine Pipe Diameter From the sizing chart, identify the appropriate diameter that can accommodate the total flow rate of 320,000 Btu/h with respect to the determined length and pressure drop. Based on typical charts, a typical diameter for the calculated flow is usually around 1.5 inches.
The correct pipe size for section (1) is $1 \frac{1}{2}$ in.
More Information
This answer is based on standard practices in determining gas line sizing. The flow rates, lengths, and pressure drops determine the appropriate pipe diameter to ensure safe and efficient gas flow.
Tips
- Miscalculating Total Flow: Ensure that all contributing outlets are accounted for in the flow calculations.
- Ignoring Lengths of Piping Sections: It is crucial not to overlook the distances for accurate sizing.
- Using Incorrect Tables or Charts: Always consult the correct sizing chart specific to the type of piping being used.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information