Determine the size of the pipe in section (3) using the longest length method.
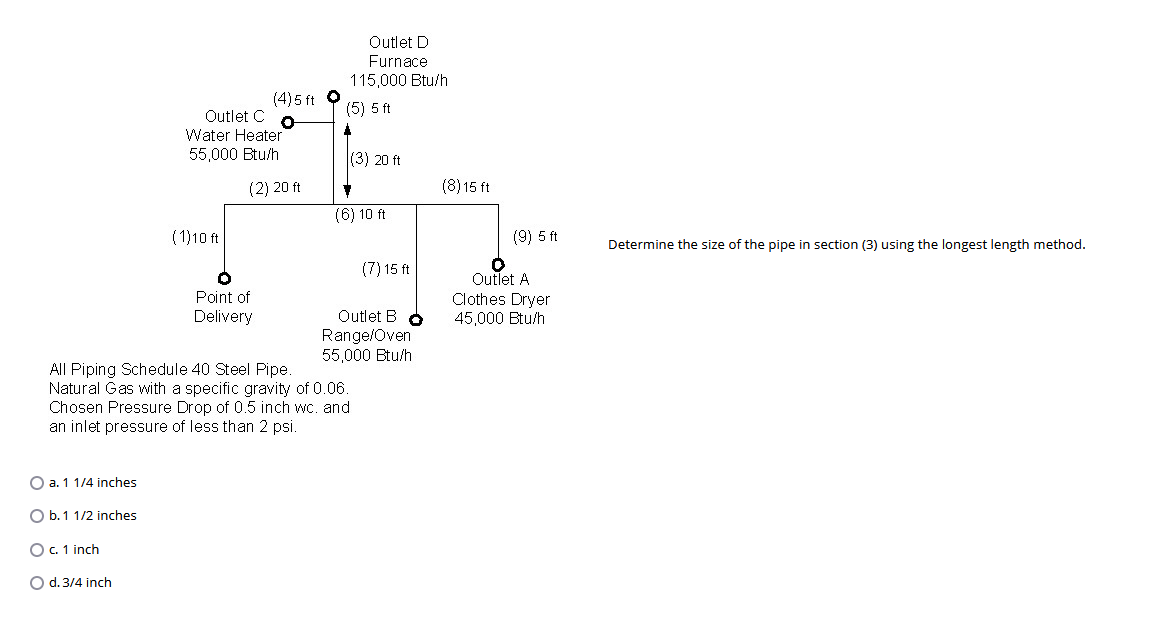
Understand the Problem
The question asks us to determine the size of a pipe in section (3) using the longest length method based on the given specifications and gas flow requirements. This involves calculating the appropriate pipe diameter considering the length of the pipe and the flow rate.
Answer
The size of the pipe is $1 \frac{1}{2}$ inches.
Answer for screen readers
The size of the pipe in section (3) is 1 1/2 inches.
Steps to Solve
-
Determine Total Flow Rate in Section (3)
Calculate the total flow rate at section (3) by summing the flow rates of all outlets connected in that section.
- Outlet D (Furnace): 115,000 Btu/h
- Outlet B (Range/Oven): 55,000 Btu/h
- Outlet A (Clothes Dryer): 45,000 Btu/h
$$ Q_{total} = 115,000 + 55,000 + 45,000 = 215,000 \text{ Btu/h} $$
-
Calculate Equivalent Length of Pipe
Use the longest length method to find the total equivalent length. The lengths are:
- Distance from the Point of Delivery to section (3): 20 ft
- Distance to Outlet D: 5 ft
- Distance to Outlet B: 15 ft (from top)
- Distance to Outlet A: 5 ft (from side)
Total length from the Point of Delivery to the furthest outlet (which is Outlet D):
$$ L_{total} = 20 + 5 + 15 = 40 \text{ ft} $$
-
Use Pressure Drop to Determine Required Pipe Size
For natural gas, apply the formula for calculating pressure drop for a given length. From the tables (or smoothed equations for natural gas), calculate the diameter based on:
$$ P_{drop} = \frac{0.5 \text{ in wc}}{L_{total}} $$
-
Refer to Pipe Sizing Charts
Using the equivalent length and flow rate, refer to standard pipe sizing charts for natural gas (Schedule 40) to find the diameter that can accommodate a flow rate of 215,000 Btu/h with the pressure drop specified.
The size of the pipe in section (3) is 1 1/2 inches.
More Information
In gas piping, the pressure drop is crucial for maintaining flow efficiency. Larger pipes reduce pressure loss, which is important for systems with high BTU requirements.
Tips
- Failing to sum all flow rates accurately.
- Ignoring the proper unit conversions if necessary (Btu/h to cf/h, etc.).
- Misreading the pipe sizing chart, leading to incorrect diameter selection.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information