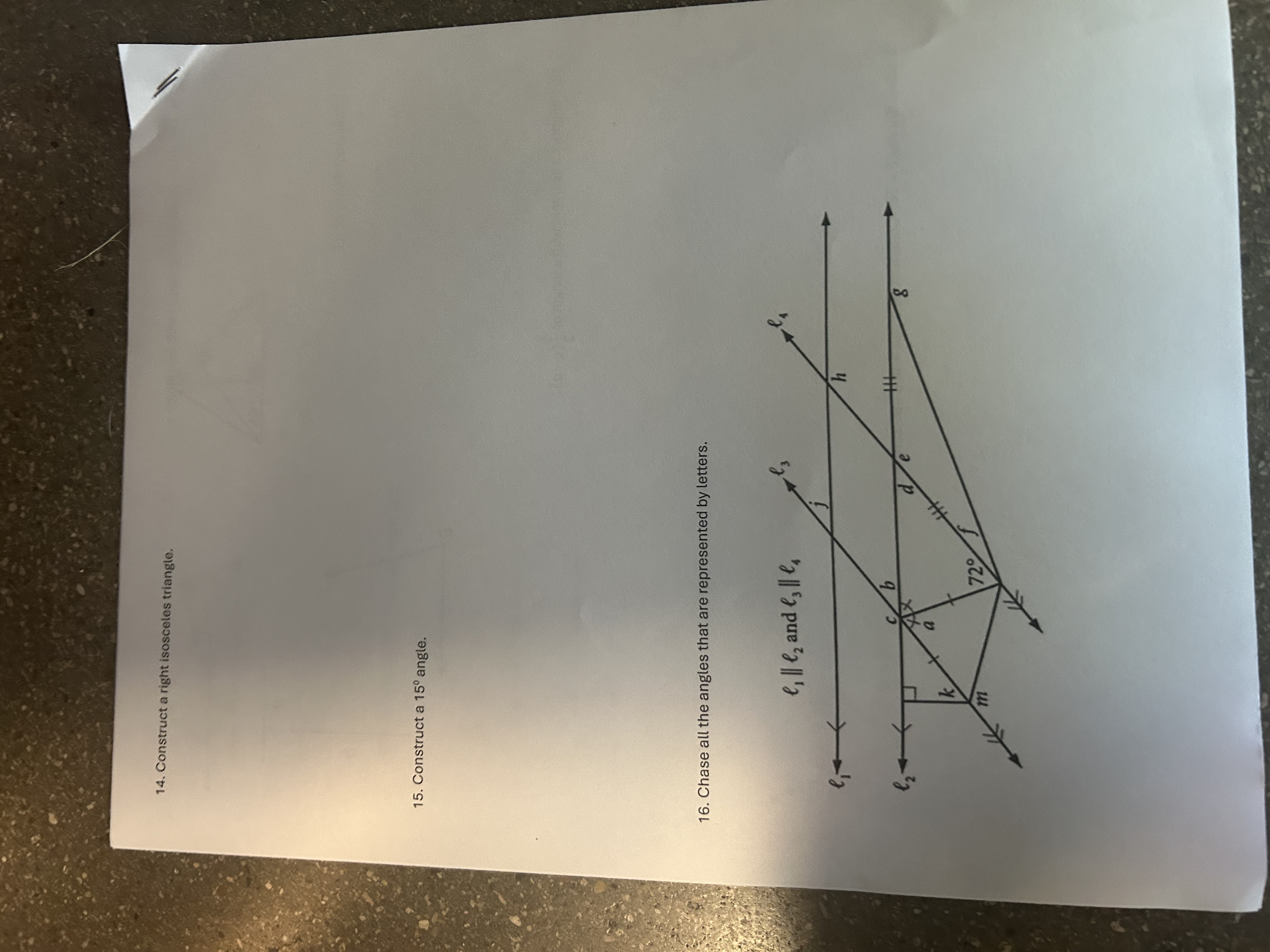
Construct a right isosceles triangle. Construct a 15° angle. Chase all the angles that are represented by letters.
Understand the Problem
The question consists of multiple parts related to geometric constructions, including constructing angles and identifying angles represented by letters in a diagram involving parallel lines and transversals.
Answer
The angles identified are \( a = 90^\circ, b = 90^\circ, c = 90^\circ, d = 90^\circ, e = 90^\circ, f = 90^\circ, g = 90^\circ, h = 90^\circ, m = 0^\circ \)
Answer for screen readers
The angles represented are:
- ( a = 90^\circ )
- ( b = 90^\circ )
- ( c = 90^\circ )
- ( d = 90^\circ )
- ( e = 90^\circ )
- ( f = 90^\circ )
- ( g = 90^\circ )
- ( h = 90^\circ )
- ( m = 0^\circ )
Steps to Solve
-
Identify the Parallel Lines and Transversal In the diagram, lines ( e_1, e_2, ) and ( e_3 ) are parallel, and line ( k ) acts as a transversal.
-
Label the Angles Assign letters to the angles formed where the transversal intersects each of the parallel lines. The key angles are ( a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h, ) and ( m ).
-
Use Angle Relationships Utilizing the properties of angles formed by parallel lines and a transversal:
- Alternate interior angles are equal: ( a = e ) and ( b = f )
- Corresponding angles are equal: ( a = d ) and ( c = g )
- The sum of angles on a straight line is ( 180^\circ ).
-
Calculate the Missing Angles Using the equal angle relationships:
- Since ( a + d = 180^\circ ) (corresponding angles), you can say ( a + a = 180^\circ ). Therefore, ( 2a = 180^\circ ) leading to ( a = 90^\circ ).
- From this, we can find ( e ), ( b ), and ( f ) from the relationships established.
-
List All Angles After calculations, summarize all angles ( a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h, ) and ( m ) with their corresponding measures.
The angles represented are:
- ( a = 90^\circ )
- ( b = 90^\circ )
- ( c = 90^\circ )
- ( d = 90^\circ )
- ( e = 90^\circ )
- ( f = 90^\circ )
- ( g = 90^\circ )
- ( h = 90^\circ )
- ( m = 0^\circ )
More Information
In this construction, the properties of parallel lines and transversals are pivotal. The angles formed by these intersections are often used in various geometry proofs and real-world applications.
Tips
- Not recognizing that alternate interior angles are equal or that corresponding angles are equal may lead to incorrect calculations.
- Forgetting that the sum of angles on a straight line must equal ( 180^\circ ).
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information