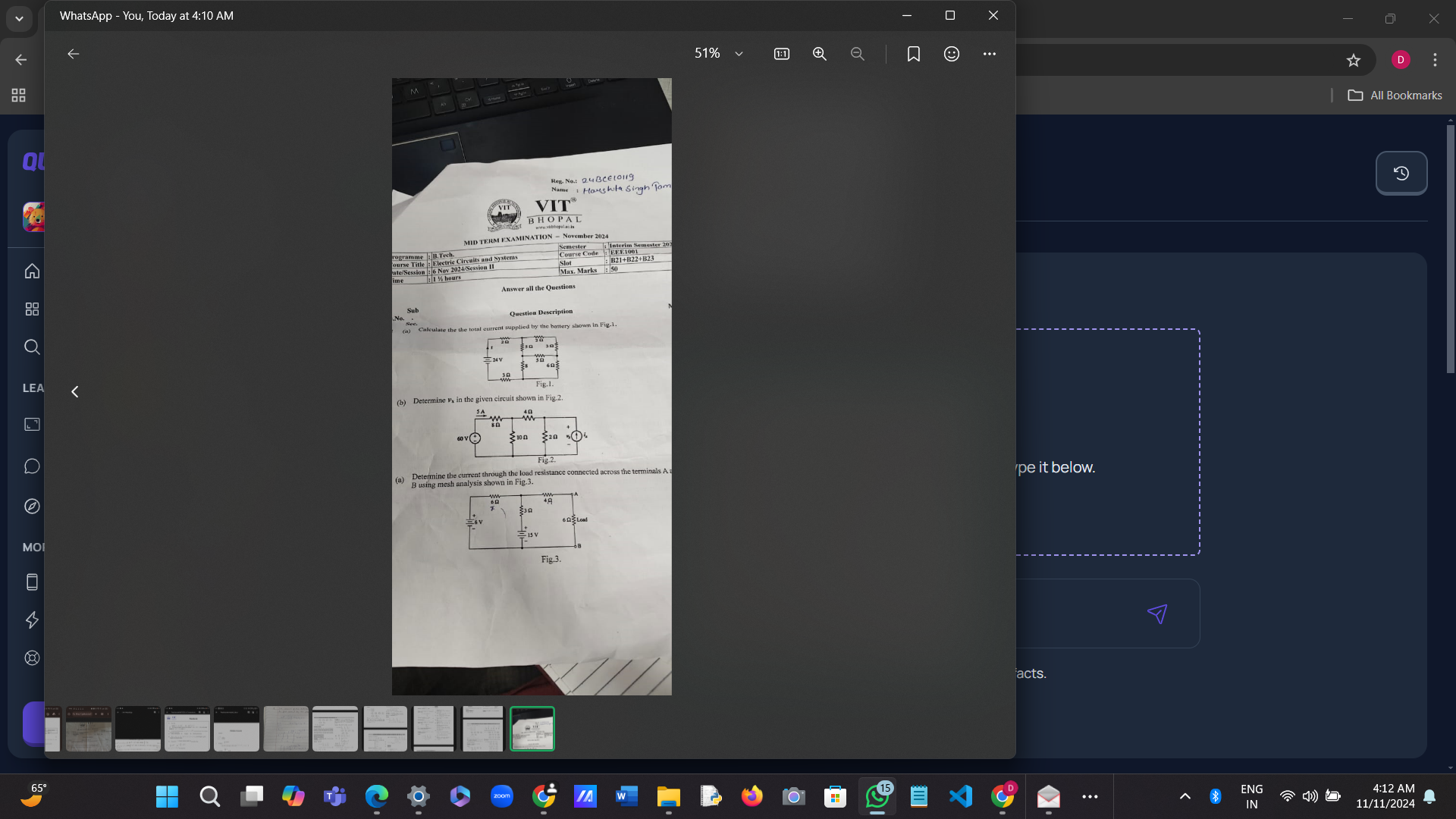
Calculate the total current supplied by the battery shown in Fig. 1. Determine the current in the given circuit shown in Fig. 2. Determine the current through the load resistance... Calculate the total current supplied by the battery shown in Fig. 1. Determine the current in the given circuit shown in Fig. 2. Determine the current through the load resistance connected across the terminals A-B using mesh analysis shown in Fig. 3.
Understand the Problem
The question involves analyzing electrical circuits to calculate total current supplied by a battery and determine current through a load resistance using mesh analysis. This requires application of circuit analysis techniques.
Answer
The total current supplied by the battery is calculated using \( I_{total} = \frac{V_{battery}}{R_{total}} \). The current through the load will be determined from mesh analysis.
Answer for screen readers
The total current supplied by the battery in Figure 1 is ( I_{total} = \frac{V_{battery}}{R_{total}} ). The current through the load resistance in Figure 3, calculated using mesh analysis, will depend on specific values provided in the problem.
Steps to Solve
-
Identify Components in Figure 1 Identify the components, including resistances and the voltage source in Figure 1. The circuit contains resistors and a battery that supplies current.
-
Determine Total Resistance Calculate the total resistance ($R_{total}$) seen by the battery. Since resistors can be in series or parallel, use the appropriate formulas:
- For resistors in series: $R_{total} = R_1 + R_2 + ... + R_n$
- For resistors in parallel: $$ \frac{1}{R_{total}} = \frac{1}{R_1} + \frac{1}{R_2} + ... + \frac{1}{R_n} $$
-
Apply Ohm's Law to Find Total Current Use Ohm's Law to find the total current supplied by the battery ($I_{total}$): $$ I_{total} = \frac{V_{battery}}{R_{total}} $$
-
Identify Components in Figure 2 Repeat the identification process for the circuit in Figure 2 using similar methods to calculate total resistance and current values.
-
Mesh Analysis for Figure 3 For the circuit in Figure 3, apply mesh analysis:
- Write KVL (Kirchhoff's Voltage Law) equations for each mesh, representing the sum of voltage drops across resistors and the voltage sources.
- Solve the Equations Solve the equations obtained from mesh analysis or KVL for the current through the load resistance connected across terminals A-B.
The total current supplied by the battery in Figure 1 is ( I_{total} = \frac{V_{battery}}{R_{total}} ). The current through the load resistance in Figure 3, calculated using mesh analysis, will depend on specific values provided in the problem.
More Information
For detailed calculations, the specific resistance values and battery voltage used will affect the result. These calculations are fundamental in electrical engineering for circuit design and analysis.
Tips
- Misidentifying Series/Parallel Configuration: Ensure to correctly identify if resistors are in series or parallel as it affects the total resistance significantly.
- Ignoring Voltage Sources: Always factor in the direction and magnitude of voltage sources when applying KVL in mesh analysis.
- Forgetting to Simplify Equations: Ensure each equation used in calculations is simplified properly to avoid mistakes in solving for current.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information