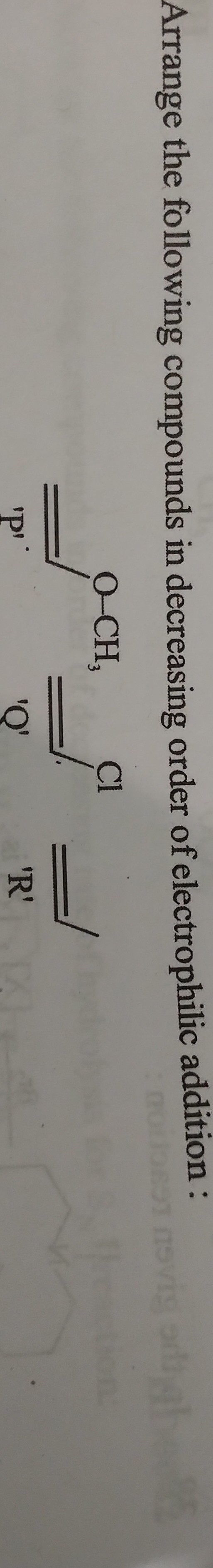
Arrange the following compounds in decreasing order of electrophilic addition.
Understand the Problem
The question is asking to arrange different compounds (labeled P, Q, and R) in order of their decreasing ability for electrophilic addition reactions. This involves understanding the structure of the compounds and how their electronic properties influence reactivity.
Answer
The order is $P > R > Q$.
Answer for screen readers
The order of compounds in decreasing ability for electrophilic addition is:
$$ P > R > Q $$
Steps to Solve
- Identify the Compounds' Properties
Analyze the given compounds P, Q, and R based on their functional groups and electronic effects.
- Understand Electrophilic Addition
Electrophilic addition reactions are more favorable in compounds with greater electron density, as they can stabilize the electrophile. The presence of electron-donating groups increases the reactivity, while electron-withdrawing groups decrease it.
-
Assess Electron-donating and Electron-withdrawing Groups
- Compound P has a methoxy group (-OCH₃), which is an electron-donating group.
- Compound Q has a chloro group (-Cl), which is slightly electron-withdrawing.
- Compound R has no additional groups; it's simply an alkyne.
-
Determine Relative Reactivity
Based on their structures:
- Compound P's electron-donating group enhances its electrophilic addition capability.
- Compound Q, with a slight electron-withdrawing group, is less reactive.
- Compound R, being a simple alkyne, is generally reactive but less so compared to an electron-rich double bond.
- Order of Reactivity
Arrange the compounds in order of decreasing ability for electrophilic addition:
- The most reactive compound will be first, followed by medium reactivity, and the least reactive last.
The order of compounds in decreasing ability for electrophilic addition is:
$$ P > R > Q $$
More Information
Compound P has an electron-donating methoxy group, increasing its reactivity for electrophilic addition. Compound R is a simple alkyne, which is reactive but less so compared to P. Compound Q has a chlorine group, making it the least reactive due to its electron-withdrawing nature.
Tips
- Confusing the effects of electron-donating and electron-withdrawing groups. To avoid this, remember that electron-donating groups (like -OCH₃) increase reactivity, while electron-withdrawing groups (like -Cl) decrease it.
- Neglecting the basic structure of the compounds when analyzing their reactivity.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information