A Japanese bullet train decelerates at a constant rate in a straight line. The velocity of the train decreases from 50 m/s to 42 m/s in 30 seconds. (a) Calculate the change in velo... A Japanese bullet train decelerates at a constant rate in a straight line. The velocity of the train decreases from 50 m/s to 42 m/s in 30 seconds. (a) Calculate the change in velocity of the train. (b) Calculate the deceleration of the train, and explain how your answer shows the train is slowing down.
Understand the Problem
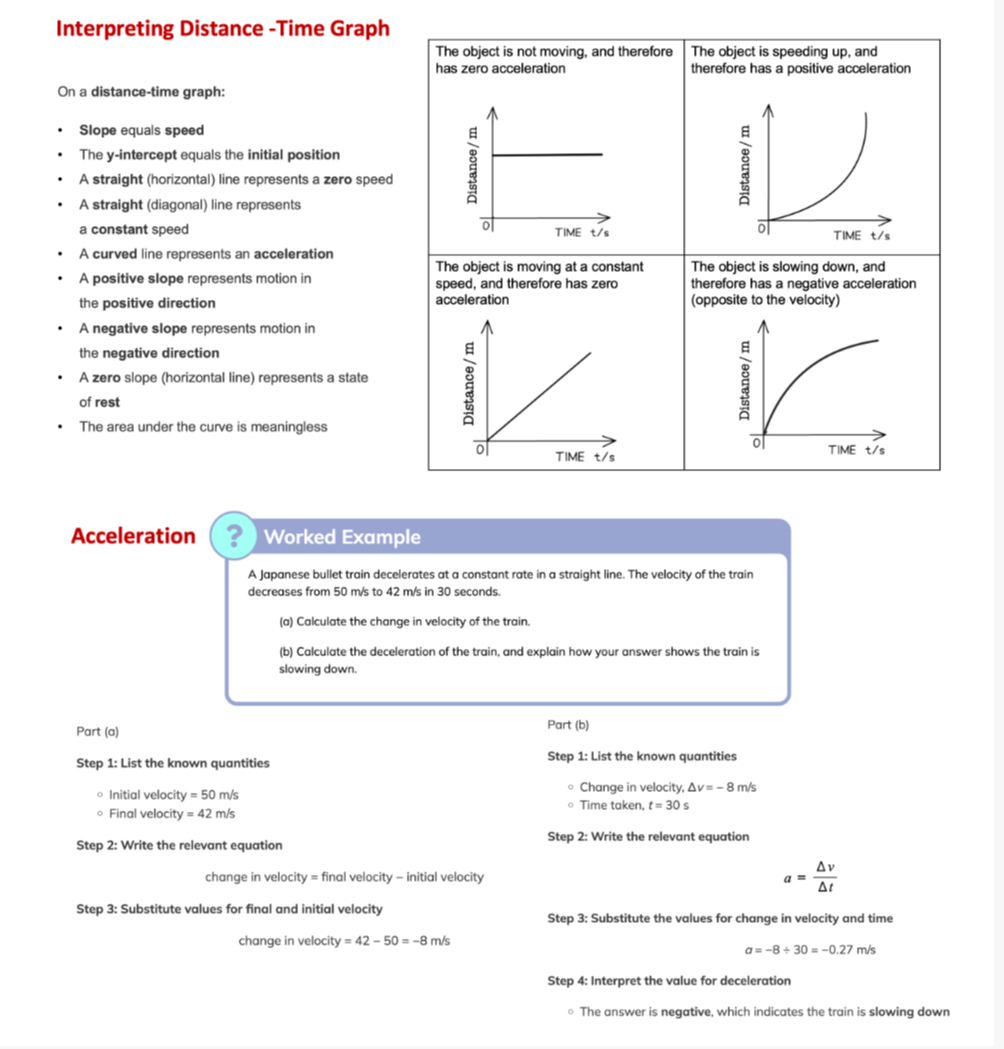
The question is asking to interpret a distance-time graph and understand the concepts of acceleration and deceleration using a given worked example of a bullet train. It emphasizes calculating the change in velocity and interpreting the results in the context of the train's motion.
Answer
-8 m/s change in velocity, -0.27 m/s² deceleration.
The change in velocity is -8 m/s and the deceleration is -0.27 m/s², indicating the train is slowing down.
Answer for screen readers
The change in velocity is -8 m/s and the deceleration is -0.27 m/s², indicating the train is slowing down.
More Information
Deceleration being negative confirms the reduction in speed, showing the train is slowing.
Tips
Ensure to keep track of signs when calculating change in velocity and deceleration.
Sources
- Acceleration (Edexcel IGCSE Physics: Double Science) - savemyexams.com
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information