2(x + 6) = 3(x + 1)
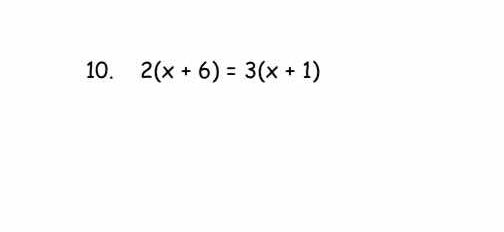
Understand the Problem
The question is asking to solve the equation 2(x + 6) = 3(x + 1) for the value of x. This requires applying algebraic techniques, including distribution and isolation of the variable.
Answer
The solution is \( x = 9 \).
Answer for screen readers
The final answer is ( x = 9 ).
Steps to Solve
- Distribute on both sides
Apply the distributive property to both sides of the equation:
$$ 2(x + 6) = 2x + 12 $$
$$ 3(x + 1) = 3x + 3 $$
This yields the new equation:
$$ 2x + 12 = 3x + 3 $$
- Rearrange the equation
To isolate $x$, move all terms involving $x$ to one side and constant terms to the other:
$$ 2x + 12 - 3x = 3 - 3 $$
This simplifies to:
$$ -1x + 12 = 3 $$
- Isolate the variable
Next, solve for $x$ by isolating it:
$$ -1x = 3 - 12 $$
This results in:
$$ -1x = -9 $$
- Solve for x
Divide both sides by -1 to find $x$:
$$ x = 9 $$
The final answer is ( x = 9 ).
More Information
This problem demonstrates the use of the distributive property and the process of solving a linear equation. Such equations are foundational in algebra, and mastering them is essential for more advanced mathematics.
Tips
- Forgetting to distribute: Students may neglect to apply the distributive property correctly.
- Sign errors: When isolating the variable, students often make mistakes with signs, either losing the negative or forgetting to flip the sign when moving terms.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information