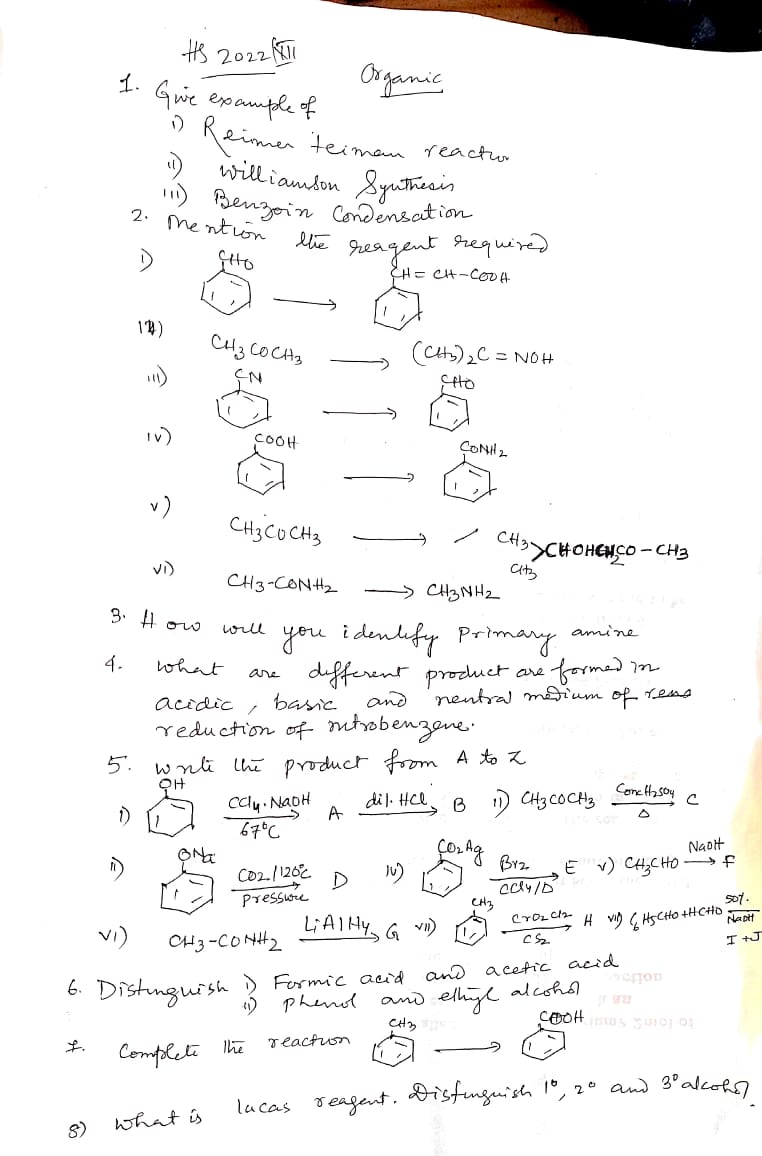
1. Give examples of: i) Reimer-Tiemann reaction ii) Williamson Synthesis iii) Benzoin Condensation 2. Mention the reagent required. 3. How will you identify primary amine? 4. What... 1. Give examples of: i) Reimer-Tiemann reaction ii) Williamson Synthesis iii) Benzoin Condensation 2. Mention the reagent required. 3. How will you identify primary amine? 4. What are different products formed in acidic, basic, and neutral medium from the reduction of nitrobenzene? 5. Write the product from A to Z. 6. Distinguish: i) Formic acid and acetic acid ii) Phenol and ethyl alcohol 7. Complete the reaction: (C6H5)CH2OH ↔ C6H5CHO 8. What is Lucas reagent? Distinguish 1°, 2°, and 3° alcohols.
Understand the Problem
The question is asking for examples of specific organic reactions, the reagents required for those reactions, methods to identify primary amines, and details about different reaction conditions. It also involves product formation, distinguishing between certain compounds, and completing chemical reactions.
Answer
1. i) Phenol to Salicylaldehyde ii) Ethanol + Sodium Ethoxide iii) Benzoin from Benzaldehyde 2. i) CHCl3 + KOH ii) Alkoxide ion iii) Cyanide ion 3. Hinsberg Test 4. Acidic: Aniline, Basic: Azoxybenzene, Neutral: Azobenzene 5. See image 6. i) NaHCO3 ii) Ferric Chloride 7. Oxidation of Benzyl Alcohol 8. Lucas reagent identifies alcohols.
i) Reimer-Tiemann Reaction: Phenol to Salicylaldehyde ii) Williamson Synthesis: Ethanol with Sodium Ethoxide iii) Benzoin Condensation: Benzoin from Benzaldehyde 2. i) Chloroform and KOH ii) Alkoxide ion iii) Cyanide ion 3. Hinsberg Test: Primary amines form soluble sulfonamides. 4. Nitrobenzene reduction:
- Acidic: Aniline
- Basic: Azoxybenzene
- Neutral: Azobenzene
- Refer to the image.
i) React with sodium bicarbonate: Formic acid reacts to release CO2. ii) Ferric chloride test: Phenol gives a violet color. 7. Oxidation of Benzyl Alcohol to Benzaldehyde using a mild oxidizing agent. 8. Lucas reagent is a mixture of HCl and ZnCl2.
- 1° alcohol: No reaction at room temp.
- 2° alcohol: Reaction in 5-10 min.
- 3° alcohol: Immediate reaction.
Answer for screen readers
i) Reimer-Tiemann Reaction: Phenol to Salicylaldehyde ii) Williamson Synthesis: Ethanol with Sodium Ethoxide iii) Benzoin Condensation: Benzoin from Benzaldehyde 2. i) Chloroform and KOH ii) Alkoxide ion iii) Cyanide ion 3. Hinsberg Test: Primary amines form soluble sulfonamides. 4. Nitrobenzene reduction:
- Acidic: Aniline
- Basic: Azoxybenzene
- Neutral: Azobenzene
- Refer to the image.
i) React with sodium bicarbonate: Formic acid reacts to release CO2. ii) Ferric chloride test: Phenol gives a violet color. 7. Oxidation of Benzyl Alcohol to Benzaldehyde using a mild oxidizing agent. 8. Lucas reagent is a mixture of HCl and ZnCl2.
- 1° alcohol: No reaction at room temp.
- 2° alcohol: Reaction in 5-10 min.
- 3° alcohol: Immediate reaction.
More Information
The Reimer-Tiemann reaction is notable for its use in organic synthesis to introduce aldehyde groups, while Hinsberg's test is a classical method for distinguishing primary amines.
Tips
Common mistakes include confusing amine identification tests and reaction conditions for Lucas reagent.
Sources
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information