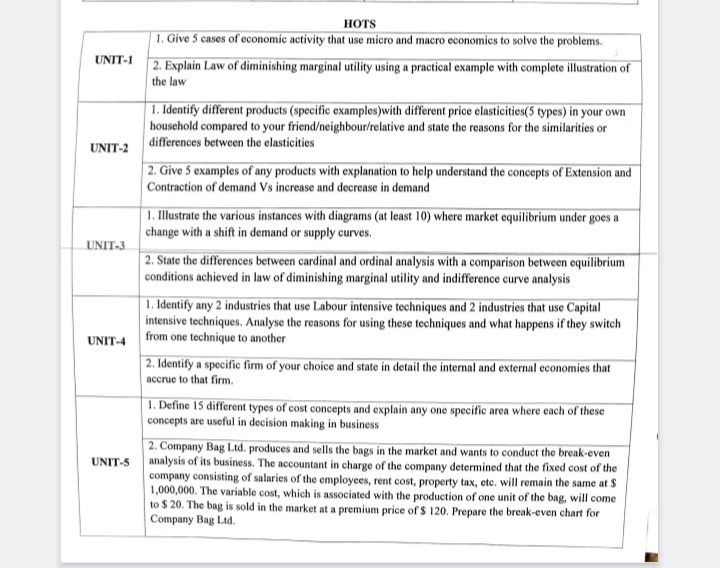
1. Give 5 cases of economic activity that use micro and macro economics to solve the problems. 2. Explain the Law of diminishing marginal utility using a practical example with com... 1. Give 5 cases of economic activity that use micro and macro economics to solve the problems. 2. Explain the Law of diminishing marginal utility using a practical example with complete illustration of the law. 3. Identify different products (specific examples) with different price elasticities (5 types) in your own household compared to your friend/neighbour/relative and state the reasons for the similarities or differences between the elasticities. 4. Give 5 examples of any products with explanation to help understand the concepts of Extension and Contraction of demand Vs increase and decrease in demand. 5. Illustrate the various instances with diagrams (at least 10) where market equilibrium under goes a change with a shift in demand or supply curves. 6. State the differences between cardinal and ordinal analysis with a comparison between equilibrium conditions achieved in law of diminishing marginal utility and indifference curve analysis. 7. Identify any 2 industries that use Labour intensive techniques and 2 industries that use Capital intensive techniques. Analyse the reasons for using these techniques and what happens if they switch from one technique to another. 8. Identify a specific firm of your choice and state in detail the internal and external economies that accrue to that firm. 9. Define 15 different types of cost concepts and explain any specific area where each of these concepts are useful in decision making in business. 10. Company Bag Ltd. produces and sells the bags in the market and wants to conduct the break-even analysis of its business. The accountant in charge of the company determined that the fixed cost of the company consisting of salaries of the employees, rent cost, property tax, etc. will remain the same at $ 1,000,000. The variable cost, which is associated with the production of one unit of the bag, will come to $ 20. The bag is sold in the market at a premium price of $ 120. Prepare the break-even chart for Company Bag Ltd.
Understand the Problem
The document contains a series of higher-order thinking skills (HOTS) questions relating to economics. The questions cover various topics including micro and macroeconomics, utility laws, elasticity, demand concepts, industry analysis, cost concepts, and break-even analysis.
Answer
Use the formula: Break-even point = Fixed Costs / (Selling Price - Variable Cost).
For the break-even analysis of Company Bag Ltd., use the formula: Break-even point (units) = Fixed Costs / (Selling Price per Unit - Variable Cost per Unit).
Answer for screen readers
For the break-even analysis of Company Bag Ltd., use the formula: Break-even point (units) = Fixed Costs / (Selling Price per Unit - Variable Cost per Unit).
More Information
The law of diminishing marginal utility implies that consumers get less satisfaction from consuming each additional unit of a good, leading to decreased willingness to pay the same price.
Tips
A common error is mixing up the concepts of 'change in demand' with 'change in quantity demanded.' Ensure clarity in terms.
Sources
- The Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility: How It Works, With Examples - investopedia.com
- Diminishing Marginal Utility | Definition, Principle & Examples - Lesson - study.com
- [DOC] Chapter 2 SOLUTIONS TO TEXT PROBLEMS - geneseo.edu
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information