Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following statements about thyroid hormones is INCORRECT?
Which of the following statements about thyroid hormones is INCORRECT?
Which of the following best describes the role of C cells in the thyroid gland?
Which of the following best describes the role of C cells in the thyroid gland?
Which of the following is NOT a direct effect of thyroid hormones on the body?
Which of the following is NOT a direct effect of thyroid hormones on the body?
What is the primary function of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) in the thyroid gland?
What is the primary function of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) in the thyroid gland?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following is the most accurate description of the relationship between the thyroid gland and calcium homeostasis?
Which of the following is the most accurate description of the relationship between the thyroid gland and calcium homeostasis?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following correctly describes the effect of the absence of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) on the thyroid gland?
Which of the following correctly describes the effect of the absence of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) on the thyroid gland?
Signup and view all the answers
Where are the receptors for thyroid hormones primarily located within target cells?
Where are the receptors for thyroid hormones primarily located within target cells?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following accurately describes the relationship between T4 and T3 in the synthesis and action of thyroid hormones?
Which of the following accurately describes the relationship between T4 and T3 in the synthesis and action of thyroid hormones?
Signup and view all the answers
Which physiological process is directly influenced by the "calorigenic effect" of thyroid hormones?
Which physiological process is directly influenced by the "calorigenic effect" of thyroid hormones?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary role of the thyroid follicles in the thyroid gland?
What is the primary role of the thyroid follicles in the thyroid gland?
Signup and view all the answers
Flashcards
Thyroid Gland
Thyroid Gland
Lies below the larynx, consists of two lobes joined by isthmus.
Thyroid Follicles
Thyroid Follicles
Hollow spheres lined by cuboidal epithelium, surrounded by capillaries.
Thyroglobulin
Thyroglobulin
Globular protein created by follicles, contains tyrosine for hormone synthesis.
Thyroxine (T4)
Thyroxine (T4)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Triiodothyronine (T3)
Triiodothyronine (T3)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thyroid-binding Globulins (TBGs)
Thyroid-binding Globulins (TBGs)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thyroid-stimulating Hormone (TSH)
Thyroid-stimulating Hormone (TSH)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Calorigenic Effect
Calorigenic Effect
Signup and view all the flashcards
C Cells
C Cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Effects of Thyroid Hormones
Effects of Thyroid Hormones
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
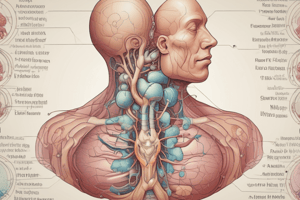
THYROID GLAND
- Located inferior to the thyroid cartilage of the larynx
- Composed of two lobes connected by an isthmus
- Thyroid Follicles: Hollow spheres lined by cuboidal epithelium, surrounded by capillaries
- Cells absorb iodide ions from the blood
- Follicle cavity contains colloid
- Contains C (clear) cells, or parafollicular cells
- Thyroglobulin: Globular protein synthesized by follicle cells, secreted into colloid, containing tyrosine (building block of thyroid hormones)
- Thyroid Hormones:
- Thyroxine (T4): Tetraiodothyronine, containing four iodine atoms
- Triiodothyronine (T3): Containing three iodine atoms
- Thyroid-binding Globulins (TBGs): Proteins binding about 75% of T4 and 70% of T3 in the bloodstream, with transthyretin and albumin binding the remainder
- A small percentage (0.3% T3 and 0.03% T4) remains unbound and diffuses into tissues
THYROID-STIMULATING HORMONE (TSH)
- Absence of TSH causes thyroid follicles to become inactive, with no synthesis or secretion of hormones
- TSH binds to plasma membrane receptors, activating enzymes for hormone production
- Thyroid hormones affect virtually every cell in the body, entering through transport systems, binding to receptors in the cytoplasm, on mitochondria surfaces, or in the nucleus
EFFECTS OF THYROID HORMONES
- Increase oxygen and energy consumption, impacting body temperature
- Increase heart rate and contraction force
- Improve sensitivity to sympathetic stimulation
- Maintain sensitivity of respiratory centers to oxygen/carbon dioxide
- Stimulate red blood cell formation and endocrine tissue activity
- Accelerate bone mineral turnover
- Essential for normal development of skeletal, muscular, and nervous systems in children
PARATHYROID GLANDS
- Located on the posterior surface of the thyroid gland
- Secrete parathyroid hormone (PTH) in response to low blood calcium levels
- Parathyroid Hormone (PTH): Antagonist for calcitonin, acting to increase blood calcium
- Stimulates osteoclasts, accelerating mineral turnover and calcium release
- Enhances calcium reabsorption by kidneys, reducing urinary losses
- Stimulates calcitriol formation and secretion by kidneys
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Related Documents
Description
Explore the anatomy and physiology of the thyroid gland, including its structure and the hormones it produces, such as thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). This quiz covers the key components of thyroid follicles and the role of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). Test your knowledge on the functions and importance of the thyroid in the endocrine system.