Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary cause of rickets in children?
What is the primary cause of rickets in children?
- Vitamin D deficiency (correct)
- Injury or trauma
- Autoimmune response
- Genetic predisposition
What is a common characteristic of rheumatoid arthritis?
What is a common characteristic of rheumatoid arthritis?
- Is usually a result of external injury
- Affects only one joint
- Primarily affects men
- Involves an autoimmune mechanism (correct)
Which treatment is commonly used for managing rheumatoid arthritis?
Which treatment is commonly used for managing rheumatoid arthritis?
- Methotrexate (correct)
- Acupuncture
- Physical therapy exclusively
- Chiropractic adjustments
Which group is most commonly affected by osteoarthritis?
Which group is most commonly affected by osteoarthritis?
What pathological change occurs in rheumatoid arthritis's disease process?
What pathological change occurs in rheumatoid arthritis's disease process?
How does osteoarthritis typically manifest?
How does osteoarthritis typically manifest?
What aspect of osteoarthritis contributes to its classification?
What aspect of osteoarthritis contributes to its classification?
Which of the following is NOT a treatment goal for rheumatoid arthritis?
Which of the following is NOT a treatment goal for rheumatoid arthritis?
What is the process by which cells detach from a solid tumor and spread to distant sites?
What is the process by which cells detach from a solid tumor and spread to distant sites?
What term describes the loss of differentiation in cancerous cells?
What term describes the loss of differentiation in cancerous cells?
Which of the following is NOT a category of malignant neoplasms?
Which of the following is NOT a category of malignant neoplasms?
Which risk factor is linked to an increased risk of cancer due to genetic predisposition?
Which risk factor is linked to an increased risk of cancer due to genetic predisposition?
What are hematologic cancers primarily characterized by?
What are hematologic cancers primarily characterized by?
Which subcategory of hematologic cancer is characterized by the uncontrolled growth of white blood cells?
Which subcategory of hematologic cancer is characterized by the uncontrolled growth of white blood cells?
Which environmental agent is associated with increased cancer risk due to its carcinogenic effects?
Which environmental agent is associated with increased cancer risk due to its carcinogenic effects?
What is the relationship between smoking and alcohol consumption in terms of cancer risk?
What is the relationship between smoking and alcohol consumption in terms of cancer risk?
What are the common causes of anemia in cancer patients?
What are the common causes of anemia in cancer patients?
What are the primary goals of cancer treatment?
What are the primary goals of cancer treatment?
Which symptom is initially common in Ankylosing Spondylitis?
Which symptom is initially common in Ankylosing Spondylitis?
Which of the following treatment modalities is NOT commonly used for cancer?
Which of the following treatment modalities is NOT commonly used for cancer?
What is one of the diagnostic criteria for gout?
What is one of the diagnostic criteria for gout?
Which type of cancer develops in the glands that line organs?
Which type of cancer develops in the glands that line organs?
What type of medications is primarily used to treat Osteoarthritis?
What type of medications is primarily used to treat Osteoarthritis?
Which hormone is uniquely known for lowering blood glucose levels?
Which hormone is uniquely known for lowering blood glucose levels?
In which phase of gout is a person likely to be asymptomatic?
In which phase of gout is a person likely to be asymptomatic?
What type of cells within the islets of Langerhans secrete insulin?
What type of cells within the islets of Langerhans secrete insulin?
What typically worsens lower back pain in a person with Ankylosing Spondylitis?
What typically worsens lower back pain in a person with Ankylosing Spondylitis?
Which organ is primarily responsible for regulating blood glucose levels?
Which organ is primarily responsible for regulating blood glucose levels?
What is one of the actions of insulin besides promoting glucose uptake?
What is one of the actions of insulin besides promoting glucose uptake?
What is the known cause of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)?
What is the known cause of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)?
Which gender is typically less severely affected by Ankylosing Spondylitis?
Which gender is typically less severely affected by Ankylosing Spondylitis?
What type of therapy is recommended for Osteoarthritis management?
What type of therapy is recommended for Osteoarthritis management?
What is a characteristic feature of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus?
What is a characteristic feature of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus?
Which statement accurately describes Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus?
Which statement accurately describes Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus?
What condition is classified as Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM)?
What condition is classified as Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM)?
Which of the following is not a metabolic abnormality associated with Type 2 Diabetes?
Which of the following is not a metabolic abnormality associated with Type 2 Diabetes?
What is a key risk factor in the metabolic syndrome that is associated with diabetes?
What is a key risk factor in the metabolic syndrome that is associated with diabetes?
What is the primary hormonal issue in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus?
What is the primary hormonal issue in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus?
Which of these best describes Type 1B Diabetes?
Which of these best describes Type 1B Diabetes?
Which factor is not part of the five risk factors for metabolic syndrome?
Which factor is not part of the five risk factors for metabolic syndrome?
What is the primary process by which the number of cells increases in the body?
What is the primary process by which the number of cells increases in the body?
Which type of cell is least likely to divide and reproduce?
Which type of cell is least likely to divide and reproduce?
What characterizes benign tumors?
What characterizes benign tumors?
What is the main difference between malignant and benign neoplasms regarding growth?
What is the main difference between malignant and benign neoplasms regarding growth?
What is hyperplasia?
What is hyperplasia?
What defines undifferentiated stem cells?
What defines undifferentiated stem cells?
Which of the following statements about malignant tumors is true?
Which of the following statements about malignant tumors is true?
What term describes abnormal cellular changes leading up to cancer?
What term describes abnormal cellular changes leading up to cancer?
Flashcards
Rickets
Rickets
A condition where bones become soft and weak in children, primarily due to vitamin D deficiency.
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
An autoimmune and inflammatory disease primarily affecting joints, usually affecting multiple joints simultaneously. It affects women three times more often than men.
Osteoarthritis (OA)
Osteoarthritis (OA)
A progressive destruction of the cartilage in weight-bearing joints and finger joints, primarily affecting older adults and those with joint trauma
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Pathological Process
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Pathological Process
Signup and view all the flashcards
Osteomalacia
Osteomalacia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Rheumatoid Arthritis Diagnosis
Rheumatoid Arthritis Diagnosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment Goals
Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment Goals
Signup and view all the flashcards
Osteoarthritis Prevalence
Osteoarthritis Prevalence
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS)
Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Asymptomatic Hyperuricemia
Asymptomatic Hyperuricemia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gout
Gout
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chronic Tophaceous Gout
Chronic Tophaceous Gout
Signup and view all the flashcards
Intercritical Gout
Intercritical Gout
Signup and view all the flashcards
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Acute Gouty Arthritis
Acute Gouty Arthritis
Signup and view all the flashcards
NSAIDs
NSAIDs
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hyperplasia and Dysplasia
Hyperplasia and Dysplasia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Metaplasia
Metaplasia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Neoplasm
Neoplasm
Signup and view all the flashcards
Benign Tumors
Benign Tumors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Malignant Tumors
Malignant Tumors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cell Proliferation
Cell Proliferation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stem Cells
Stem Cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Progenitor Cells
Progenitor Cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the defining characteristic of cancer cells?
What is the defining characteristic of cancer cells?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is metastasis?
What is metastasis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is anaplasia?
What is anaplasia?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are hematologic cancers?
What are hematologic cancers?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are solid tumors?
What are solid tumors?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a risk factor for cancer?
What is a risk factor for cancer?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does alcohol affect the risk of cancer caused by smoking?
How does alcohol affect the risk of cancer caused by smoking?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does alcohol contribute to cancer development?
How does alcohol contribute to cancer development?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is anemia?
What is anemia?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the main causes of anemia in cancer patients?
What are the main causes of anemia in cancer patients?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the main goals of cancer treatment?
What are the main goals of cancer treatment?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is adenocarcinoma?
What is adenocarcinoma?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the two main types of tissue in the pancreas?
What are the two main types of tissue in the pancreas?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the role of insulin in blood sugar regulation?
What is the role of insulin in blood sugar regulation?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is diabetes mellitus?
What is diabetes mellitus?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the classifications of diabetes?
What are the classifications of diabetes?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM)
Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Metabolic Syndrome
Metabolic Syndrome
Signup and view all the flashcards
Insulin Resistance
Insulin Resistance
Signup and view all the flashcards
Increased Glucose Production by the Liver
Increased Glucose Production by the Liver
Signup and view all the flashcards
Increased Blood Pressure
Increased Blood Pressure
Signup and view all the flashcards
High Triglyceride Levels
High Triglyceride Levels
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Lecture 7: Metabolic & Rheumatic Disorders of Skeletal System, Neoplasia and Diabetes Mellitus
- Objectives:
- Study different disorders affecting musculoskeletal function.
- Define, examine the pathogenesis, and categorize neoplasia.
- Study diabetes and its complications.
1- Metabolic & Rheumatic Disorders of Skeletal System
- During childhood, skeletal structures grow in length and diameter, increasing bone mass.
- Skeletal disorders can arise from abnormal growth and developmental processes, potentially due to hereditary or congenital factors.
- Other contributing factors include metabolic disorders, hormonal influences, aging, and nutritional deficiencies.
Osteoporosis and Osteomalacia
- Osteoporosis: Characterized by the loss of mineralized bone mass, increasing porosity, and causing fragile bones prone to fractures.
- Osteomalacia: Results from inadequate bone mineralization (lack of vitamin D), leading to soft bones prone to fractures.
- Symptoms of osteomalacia include muscle pain and weakness, difficulty walking, muscle cramps, painful bones and joints.
- Symptoms of osteoporosis include painful bones & joints
- Diagnosis of both relies on X-ray studies, laboratory testing, bone scans, and bone biopsies.
Etiology of Osteoporosis
- Hormonal imbalance: Postmenopausal osteoporosis is a result of estrogen deficiency.
- Age: Risk increases with age.
- Gender: Women are more susceptible.
- Genetic predisposition:
- Activity level: Sedentary lifestyles are a contributing factor.
- Nutritional status: Nutritional deficiencies negatively affect bone health.
Etiology of Osteomalacia
- Vitamin D deficiency: Common causes include reduced Vitamin D absorption (due to biliary or intestinal diseases) and kidney failure.
- Calcium deficiency.
- Phosphate deficiency.
Rickets
- Rickets is the softening and weakening of bones in children.
- Rickets is caused by vitamin D deficiency.
- It is linked to kidney failures and malabsorptive syndromes, as in osteomalacia.
Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune, inflammatory disease, primarily targeting joints.
- Women are affected more frequently than men (approximately three times).
- The etiology and pathogenesis are speculated to involve genetic predisposition combined with a cell-mediated response to a microbial agent.
- The disease process involves synovial cell proliferation, plasma cell production, mast cell interaction, neovascularization, and edema, eventually leading to synovial hyperplasia and lymphoid nodules.
- The synovium spreads, resorbs cartilage, and spreads to the joint space, causing further damage.
Diagnosis and Treatment of RA
- Diagnosis involves history, physical examinations, and laboratory tests.
- Treatment aims at preventing and reducing pain, minimizing stiffness and swelling, maximizing mobility, and potentially halting the pathological process.
- Treatment involves drugs such as Methotrexate, Steroids, and NSAIDs.
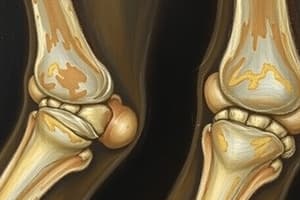
Osteoarthritis (OA)
- Osteoarthritis (OA) is a slowly progressive destruction of cartilage in weight-bearing joints (including fingers) in older adults and those who have suffered trauma earlier in life.
- OA's prevalence increases with age.
- OA is sometimes called degenerative joint disease.
- It's a leading cause of disability and pain in older adults
- Diagnosis involves detailed history, physical examinations, X-ray studies, and lab tests to rule out other diseases.
- Treatment involves medications (NSAIDs), intermittent hot and cold packs, physical/exercise therapy, and weight loss
Gout
- Gout is a group of disorders characterized by increased serum uric acid and urate crystal deposits in kidneys and joints.
- Uric acid is the end product of purine metabolism (from adenine and guanine).
- Primarily affects older men.
- Gout is diagnosed by the presence of a high uric acid level (>6.8 mg/dL) and the presence of uric acid crystals in affected joints.
- Gout has four phases: Asymptomatic hyperuricemia, Acute gout arthritis, Intercritical gout, and Chronic tophaceous gout.
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)
- SLE is a chronic inflammatory disease impacting many organ systems, including the musculoskeletal system.
- The etiology is unknown, but is thought to be linked to autoantibodies and immune complexes.
- Treatment involves nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), antimalarial drugs, corticosteroids, and immunosuppressants.
2- Neoplasia
- Neoplasia involves uncontrolled cell growth.
- Tumors can be benign or malignant.
- Benign tumors remain localized, lacking invasive capacity and with slow growth
- Malignant tumors are invasive, potentially fatal, and grow rapidly.
- Benign and malignant tumors each have surrounding rims of connective tissue capsules.
- Benign tumor capsules often facilitate surgery, assisting containment and separation.
- Neoplasms have different types from malignant solid tumors to hematologic cancers.
Cell Proliferation
- Cell proliferation is the process of increasing cell numbers through mitotic cell division.
- Normal tissue regulation involves maintaining a balance between dividing cells and cells undergoing apoptosis.
Physiology of Cell Proliferation
- There are three main groupings of cells in terms of their proliferation capabilities.
- Well-differentiated cells like neurons and cardiac muscle cells divide rarely.
- Progenitor cells repeatedly divide and reproduce, including blood, skin, and liver cells.
- Undifferentiated stem cells can rapidly divide and produce progenitor cells when needed.
3- Diabetes Mellitus and the Metabolic Syndrome
-
Insulin's Role: Insulin is the primary hormone regulating blood glucose:
- Promotes glucose uptake by cells and storage as glycogen
- Prevents glycogen and fat breakdown
- Inhibits gluconeogenesis and promotes protein synthesis
-
Diabetes Diagnosis:
- Fasting Plasma Glucose (FPG): Glucose level after 8 hours of fasting. Normal <100 mg/dL, Impaired Fasting Glucose 100-125 mg/dL, Diabetes ≥126 mg/dL
- Casual Blood Glucose Test: Glucose level at any time. ≥200 mg/dL is suggestive of diabetes, particularly when combined with symptoms like polyuria, polydipsia, polyphagia, and blurred vision.
- Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT): Glucose level after drinking a glucose solution.
- Glycosylated hemoglobin (A1C): Reflects average blood glucose levels over the past 2-3 months.
- Urine test: No longer a routine method for diabetes diagnosis due to the limitations of the test.
-
Classification of Diabetes:
- Type 1: Autoimmune destruction of beta cells in the pancreas, requiring insulin therapy.
- Type 1A: Immune-mediated type 1 diabetes.
- Type 1B: Idiopathic type 1 diabetes.
- Type 2: Insulin resistance and relative deficiency in pancreatic insulin secretion; often associated with obesity.
- Gestational diabetes: Diabetes diagnosed during pregnancy.
-
Stages of Diabetes: The stages of diabetes are based on different blood testing levels.
-
Acute Complications of Diabetes:
- Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA): Caused by extremely high blood glucose levels and a lack of insulin. Characterized by high glucose, abnormal ketone production, and metabolic acidosis.
- Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state (HHS): High blood glucose without significant ketone production, frequently seen in type 2 diabetes and is more life-threatening than DKA.
- Hypoglycemia: Extremely low blood sugar.
-
Dyslipidemia: Serum total cholesterol (TC) has a composite of LDL cholesterol.HDL cholesterol and VLDL cholesterol levels. TC/HDL ratio serves as a predictor for CVD risk.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Related Documents
Description
Test your knowledge on rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, and various cancers. This quiz covers causes, symptoms, and treatment goals related to these conditions, providing a comprehensive overview of important medical concepts. Ideal for students and professionals in the health sciences.