Podcast
Questions and Answers
What are action potentials and how do they function in nerve cells?
What are action potentials and how do they function in nerve cells?
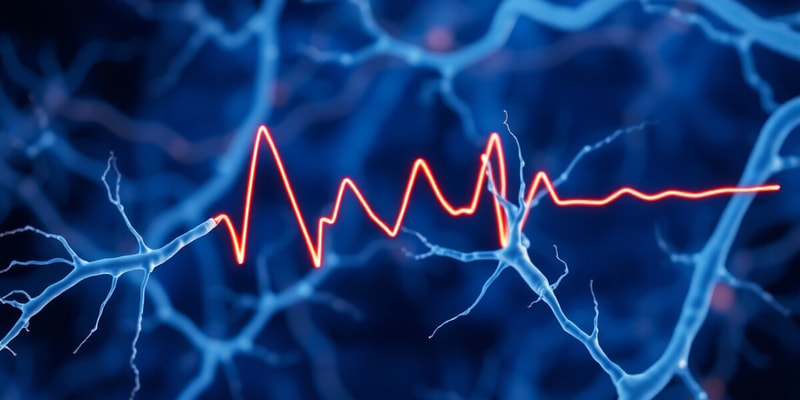
Action potentials are small identical electrical changes that propagate along a neuron, allowing communication within the nervous system.
Why do action potentials propagate in one direction?
Why do action potentials propagate in one direction?
Action potentials propagate in one direction due to the refractory period, which prevents immediate reactivation of previously activated segments of the axon.
What is the role of neuroglia and myelin sheath in nerve physiology?
What is the role of neuroglia and myelin sheath in nerve physiology?
Neuroglia provide support and protection for neurons, while the myelin sheath insulates axons and enhances the speed of action potential propagation.
How do specialized sensory cells contribute to synaptic transmission?
How do specialized sensory cells contribute to synaptic transmission?
Signup and view all the answers
Describe the mechanism of synaptic transmission.
Describe the mechanism of synaptic transmission.
Signup and view all the answers
What role do synapses play in neuronal circuits?
What role do synapses play in neuronal circuits?
Signup and view all the answers
Compare the mechanisms of local anesthetics and neurotoxins.
Compare the mechanisms of local anesthetics and neurotoxins.
Signup and view all the answers
How does diffusion contribute to synaptic transmission?
How does diffusion contribute to synaptic transmission?
Signup and view all the answers
Describe the process of neurotransmitter removal from the synapse and its significance in synaptic transmission.
Describe the process of neurotransmitter removal from the synapse and its significance in synaptic transmission.
Signup and view all the answers
Explain how drugs targeting the degradation of neurotransmitters can influence synaptic transmission in the context of depression.
Explain how drugs targeting the degradation of neurotransmitters can influence synaptic transmission in the context of depression.
Signup and view all the answers
What effect does blocking the reuptake of neurotransmitters have on synaptic transmission and what is a potential drug example?
What effect does blocking the reuptake of neurotransmitters have on synaptic transmission and what is a potential drug example?
Signup and view all the answers
Identify and explain the role of Ca2+ ions in synaptic transmission.
Identify and explain the role of Ca2+ ions in synaptic transmission.
Signup and view all the answers
Discuss the potential implications of failed neurotransmitter removal on mental health.
Discuss the potential implications of failed neurotransmitter removal on mental health.
Signup and view all the answers
What occurs when the graded potential at the axon hillock falls below -55 mV?
What occurs when the graded potential at the axon hillock falls below -55 mV?
Signup and view all the answers
What role does the myelin sheath play in the propagation of action potentials?
What role does the myelin sheath play in the propagation of action potentials?
Signup and view all the answers
Why do action potentials propagate in one direction along an axon?
Why do action potentials propagate in one direction along an axon?
Signup and view all the answers
How do local anesthetics affect action potentials?
How do local anesthetics affect action potentials?
Signup and view all the answers
What happens to nerve impulses when a sensory cell stimulus is removed?
What happens to nerve impulses when a sensory cell stimulus is removed?
Signup and view all the answers
Explain the significance of synapses in neuronal circuits.
Explain the significance of synapses in neuronal circuits.
Signup and view all the answers
What is the effect of neurotoxins on action potentials?
What is the effect of neurotoxins on action potentials?
Signup and view all the answers
Describe the mechanism of synaptic transmission.
Describe the mechanism of synaptic transmission.
Signup and view all the answers
How do more synapses affect neuronal circuits?
How do more synapses affect neuronal circuits?
Signup and view all the answers
What would be the physiological consequence of decreased sodium ion availability?
What would be the physiological consequence of decreased sodium ion availability?
Signup and view all the answers
What happens to the graded potential at the axon hillock when the stimulus remains sufficiently high?
What happens to the graded potential at the axon hillock when the stimulus remains sufficiently high?
Signup and view all the answers
At what membrane potential level does the generation of action potentials cease when the stimulus stops?
At what membrane potential level does the generation of action potentials cease when the stimulus stops?
Signup and view all the answers
Explain why action potentials can be generated rapidly in this scenario.
Explain why action potentials can be generated rapidly in this scenario.
Signup and view all the answers
How does the action potential differ when the stimulus is no longer present?
How does the action potential differ when the stimulus is no longer present?
Signup and view all the answers
Describe the relationship between stimulus intensity and the generation of action potentials.
Describe the relationship between stimulus intensity and the generation of action potentials.
Signup and view all the answers
What role does diffusion play in the generation of action potentials in this context?
What role does diffusion play in the generation of action potentials in this context?
Signup and view all the answers
Why are action potentials described as 'really fast' in this scenario?
Why are action potentials described as 'really fast' in this scenario?
Signup and view all the answers
What occurs when the graded potential at the axon hillock is insufficient?
What occurs when the graded potential at the axon hillock is insufficient?
Signup and view all the answers
How does the axon hillock's threshold influence neuronal communication?
How does the axon hillock's threshold influence neuronal communication?
Signup and view all the answers
What implications does the cessation of stimulus have on neuronal signaling?
What implications does the cessation of stimulus have on neuronal signaling?
Signup and view all the answers
What causes the rapid influx of Na+ during an action potential?
What causes the rapid influx of Na+ during an action potential?
Signup and view all the answers
Explain the role of K+ channels at +30 mV during an action potential.
Explain the role of K+ channels at +30 mV during an action potential.
Signup and view all the answers
What are the three states of a voltage-regulated Na+ channel?
What are the three states of a voltage-regulated Na+ channel?
Signup and view all the answers
Why can a new action potential not be initiated during the refractory period?
Why can a new action potential not be initiated during the refractory period?
Signup and view all the answers
How does the Na+/K+ pump contribute to the resting membrane potential after an action potential?
How does the Na+/K+ pump contribute to the resting membrane potential after an action potential?
Signup and view all the answers
Describe the effect of an action potential at site A on adjacent sites.
Describe the effect of an action potential at site A on adjacent sites.
Signup and view all the answers
What prevents action potentials from traveling backwards during propagation?
What prevents action potentials from traveling backwards during propagation?
Signup and view all the answers
What happens to Na+ channels during a sustained high stimulus on a sensory cell?
What happens to Na+ channels during a sustained high stimulus on a sensory cell?
Signup and view all the answers
What electrical changes occur when K+ exits the neuron?
What electrical changes occur when K+ exits the neuron?
Signup and view all the answers
How does the summation of graded potentials affect action potential initiation?
How does the summation of graded potentials affect action potential initiation?
Signup and view all the answers
Study Notes
Action Potentials & Nerve Impulses
- Action potentials are small, identical electrical changes that occur in individual parts of a neuron.
- Action potentials propagate in one direction due to the refractory period of voltage-gated sodium channels.
- The refractory period is a brief period after an action potential where the sodium channels are inactive, preventing the backward propagation of the action potential.
- The sodium-potassium pump helps reset the resting membrane potential after an action potential.
Role of Neuroglia & Myelin Sheath
- Neuroglia are supporting cells in the nervous system.
- The myelin sheath is a fatty covering around axons that increases the speed of nerve impulse conduction.
- Myelin is produced by Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system and by oligodendrocytes in the central nervous system.
Synaptic Transmission
- Synapses are junctions between neurons where communication occurs.
- Synaptic transmission involves the release of neurotransmitters from the presynaptic neuron, their diffusion across the synaptic cleft, and their binding to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron.
- Neurotransmitters can be excitatory or inhibitory.
Local Anaesthetics & Neurotoxins
- Local anaesthetics block the voltage-gated sodium channels in nerve axons, preventing the propagation of action potentials.
- Neurotoxins can interfere with synaptic transmission by blocking the release or action of neurotransmitters.
Diffusion Times
- The distance over which diffusion can effectively transmit signals is limited by the time it takes for molecules to reach equilibrium.
- Diffusion times are rapid over short distances but become impractically long over longer distances.
- This limitation explains why nerve impulses rely on a mechanism like action potentials for long-distance transmission.
Action Potential Propagation
- Action potentials (APs) propagate in one direction
- Graded potential at the axon hillock must remain high enough to trigger repeatedly generated APs
- The sites for AP generation are very close together for fast propagation
- Repeated APs occur when there is a continuous stimulus
- When the stimulus stops, the graded potential at the axon hillock falls below -55 mV, and no new APs are generated.
Local Anaesthetics
- Local anaesthetics block voltage-gated Na+ channels
- This inhibits nerve impulses
Synaptic Transmission
- Synaptic transmission is the process by which neurons communicate with each other
- Neurons communicate using neurotransmitters
- Neurotransmitters are released from the presynaptic neuron and bind to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron
- This triggers a response in the postsynaptic neuron.
Synaptic Transmission and Anti-depressants
- Failure of synaptic transmission is thought to contribute to clinical depression
- Drugs that target synaptic transmission can be used to treat depression
- Examples of these drugs include:
- Nardil
- Marplan
- Drugs that block the enzyme that degrades neurotransmitters can improve transmission by keeping neurotransmitter concentrations high for longer.
- Drugs that block neurotransmitter reuptake can improve transmission by keeping neurotransmitter concentrations high for longer.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Related Documents
Description
This quiz covers fundamental concepts of action potentials, the role of neuroglia, and synaptic transmission in the nervous system. Test your knowledge on how electrical impulses propagate and how myelin sheath affects nerve conduction. It is essential for understanding neuronal communication.