Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which phase involves the disappearance of the nucleolus and the nuclear membrane?
Which phase involves the disappearance of the nucleolus and the nuclear membrane?
Karyokinesis includes only three phases: Prophase, Anaphase, and Telophase.
Karyokinesis includes only three phases: Prophase, Anaphase, and Telophase.
False
What is the result of mitosis?
What is the result of mitosis?
Two daughter cells
During prophase, chromatin threads become shorter and thicker, forming __________.
During prophase, chromatin threads become shorter and thicker, forming __________.
Signup and view all the answers
Match the following events to their corresponding descriptions during prophase:
Match the following events to their corresponding descriptions during prophase:
Signup and view all the answers
During which phase of cell division do chromosomes align at the cell's equator?
During which phase of cell division do chromosomes align at the cell's equator?
Signup and view all the answers
The spindle fibers attach to the chromosomes during metaphase.
The spindle fibers attach to the chromosomes during metaphase.
Signup and view all the answers
What is the structure formed by the microtubules between the centrioles during metaphase?
What is the structure formed by the microtubules between the centrioles during metaphase?
Signup and view all the answers
In metaphase, chromosomes are arranged along the __________ of the spindle.
In metaphase, chromosomes are arranged along the __________ of the spindle.
Signup and view all the answers
Match the following terms with their descriptions:
Match the following terms with their descriptions:
Signup and view all the answers
During which stage of mitosis do chromosomes move toward the poles?
During which stage of mitosis do chromosomes move toward the poles?
Signup and view all the answers
Telophase involves the formation of two daughter nuclei.
Telophase involves the formation of two daughter nuclei.
Signup and view all the answers
What happens to the centromeres during Anaphase?
What happens to the centromeres during Anaphase?
Signup and view all the answers
During ___________, the cytoplasm divides to form two separate daughter cells.
During ___________, the cytoplasm divides to form two separate daughter cells.
Signup and view all the answers
Match the stages of mitosis with their descriptions:
Match the stages of mitosis with their descriptions:
Signup and view all the answers
What forms at the equator of a dividing plant cell during cytokinesis?
What forms at the equator of a dividing plant cell during cytokinesis?
Signup and view all the answers
In animal cells, cytokinesis begins with the formation of a cell plate.
In animal cells, cytokinesis begins with the formation of a cell plate.
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary role of the contractile ring in the formation of the furrow during cytokinesis in animal cells?
What is the primary role of the contractile ring in the formation of the furrow during cytokinesis in animal cells?
Signup and view all the answers
The _______ hypothesis suggests that chromosomes secrete a substance that causes the cell membrane to expand at the poles during cytokinesis.
The _______ hypothesis suggests that chromosomes secrete a substance that causes the cell membrane to expand at the poles during cytokinesis.
Signup and view all the answers
Match the following theories of furrow formation in animal cells with their descriptions:
Match the following theories of furrow formation in animal cells with their descriptions:
Signup and view all the answers
Which stage of mitosis is characterized by chromosomes reaching the equator?
Which stage of mitosis is characterized by chromosomes reaching the equator?
Signup and view all the answers
Cytokinesis occurs independently of mitosis.
Cytokinesis occurs independently of mitosis.
Signup and view all the answers
What is the role of spindle fibers during late anaphase?
What is the role of spindle fibers during late anaphase?
Signup and view all the answers
In telophase, chromosomes uncoil to form __________.
In telophase, chromosomes uncoil to form __________.
Signup and view all the answers
What does the contractile ring theory explain?
What does the contractile ring theory explain?
Signup and view all the answers
Match the stages of mitosis with their correct descriptions:
Match the stages of mitosis with their correct descriptions:
Signup and view all the answers
In plant cells, cytokinesis involves the formation of a furrow.
In plant cells, cytokinesis involves the formation of a furrow.
Signup and view all the answers
What happens to the nuclear envelope during telophase?
What happens to the nuclear envelope during telophase?
Signup and view all the answers
What occurs during the S-phase of the centrosome cycle?
What occurs during the S-phase of the centrosome cycle?
Signup and view all the answers
The astral relaxation theory states that the equatorial region has the highest surface tension during cell division.
The astral relaxation theory states that the equatorial region has the highest surface tension during cell division.
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary role of the mitotic apparatus in cell division?
What is the primary role of the mitotic apparatus in cell division?
Signup and view all the answers
During prophase, microtubules form around each centrosome creating an ________.
During prophase, microtubules form around each centrosome creating an ________.
Signup and view all the answers
Match the following components of the cell division process with their descriptions:
Match the following components of the cell division process with their descriptions:
Signup and view all the answers
What primarily makes up the composition of spindle fibers?
What primarily makes up the composition of spindle fibers?
Signup and view all the answers
The formation of spindle fibers occurs only in the cytoplasm and begins during metaphase.
The formation of spindle fibers occurs only in the cytoplasm and begins during metaphase.
Signup and view all the answers
What are the two ends of a microtubule called?
What are the two ends of a microtubule called?
Signup and view all the answers
Approximately ________% of cytoplasmic proteins contribute to the formation of spindle fibers.
Approximately ________% of cytoplasmic proteins contribute to the formation of spindle fibers.
Signup and view all the answers
Match the following components of the spindle with their descriptions:
Match the following components of the spindle with their descriptions:
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary cause of the movement of daughter chromosomes toward the poles during cell division?
What is the primary cause of the movement of daughter chromosomes toward the poles during cell division?
Signup and view all the answers
Spindle fibers are involved only in the elongation process during cell division.
Spindle fibers are involved only in the elongation process during cell division.
Signup and view all the answers
What type of movement do chromosomes exhibit during prometaphase?
What type of movement do chromosomes exhibit during prometaphase?
Signup and view all the answers
The contraction and elongation of spindle fibers depend on the addition and subtraction of __________.
The contraction and elongation of spindle fibers depend on the addition and subtraction of __________.
Signup and view all the answers
Match the following stages of cell division with their characteristics:
Match the following stages of cell division with their characteristics:
Signup and view all the answers
What role do spindle fibers play during cell division?
What role do spindle fibers play during cell division?
Signup and view all the answers
Continuous fibers do not connect with the chromosomes during cell division.
Continuous fibers do not connect with the chromosomes during cell division.
Signup and view all the answers
What happens during Anaphase-B in the context of chromosome movement?
What happens during Anaphase-B in the context of chromosome movement?
Signup and view all the answers
During prometaphase, chromosomes undergo __________ movement to align at the equator of the spindle.
During prometaphase, chromosomes undergo __________ movement to align at the equator of the spindle.
Signup and view all the answers
Match the types of spindle fibers with their descriptions:
Match the types of spindle fibers with their descriptions:
Signup and view all the answers
Study Notes
Mitosis Definition
- The process in which a parent cell divides into two daughter cells.
- Occurs in unicellular organisms and is indicated by a constriction appearing in the cell body.
Karyokinesis
- The division of the nucleus into two daughter nuclei.
- Four phases: Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, and Telophase.
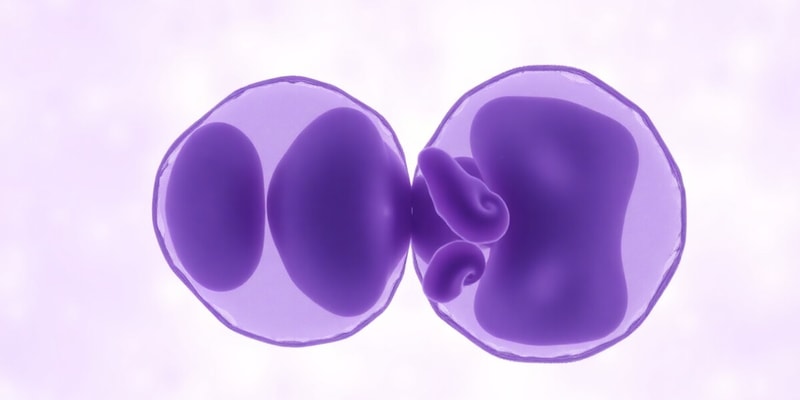
Prophase
- Characterized by changes in the nucleus and cytoplasm.
-
Nuclear Changes:
- Chromatin condenses into chromosomes, coiling and thickening.
- Chromosomes are already doubled after DNA replication during Interphase.
- Each chromosome appears split lengthwise, revealing two chromatids.
- The nucleolus and nuclear membrane disappear at the end of prophase.
-
Cytoplasmic Events:
- Centrioles divide and move to opposite poles.
- Astral rays radiate outwards from each daughter centriole.
Metaphase
- Characterized by the formation of the spindle and the alignment of chromosomes on the equator.
- The spindle is formed by microtubules that assemble between the centrioles at opposite poles, known as ampliaster.
- The chromosomes align at the equator, with their centromeres attached to spindle fibers.
Anaphase
- Defined by the separation of sister chromatids into daughter chromosomes and their movement toward opposite poles.
- Centromeres divide, allowing chromatids to separate.
- Spindle fibers contract, pulling the chromosomes towards the poles.
Telophase
- Completion of chromosome movement to the poles, formation of new nuclei, and uncoiling of chromosomes into chromatin.
- Chromosomes reach the poles and form two groups.
- Nuclear envelope and nucleolus reappear.
- Chromosomes uncoil back into chromatin.
Cytokinesis
- The division of the cytoplasm into two daughter cells.
- Occurs after nuclear division (telophase).
- The process differs in plant and animal cells.
Cytokinesis in Plant Cells
- Characterized by the formation of a cell plate and phragmoplast at the equator of the dividing cell.
Cytokinesis in Animal Cells
- Starts with a shallow groove or furrow in the cytoplasm at the equator.
- Grooves deepens and divides the cell.
- Several theories explain furrow formation.
Contractile Ring Theory
- Proposed by Marsland and Landau in 1954.
- Argues that a ring of contractile proteins forms around the equator, constricting the cytoplasm.
Spindle Elongation Theory
- Proposed by Dan in 1947 and 1958.
- Suggests that spindle microtubules elongate and push the cell poles apart, creating tension on the cell membrane.
Expanding Surface Theory
- Proposed by Mitchison in 1922 and supported by Dan and Dan in 1947.
- States that chromosomes secrete a substance that causes the cell membrane to expand at the poles, which leads to contraction at the equator, forming a furrow.
Centrosome Cycle
- The centrosome plays a critical role in mitosis and cell cycle.
- Contains a pair of centrioles at right angles to each other during G1 phase.
- Replicates during S phase, forming daughter centrioles.
- Centrioles elongate during G2 phase.
- At the beginning of mitosis, centrosomes move to opposite poles, initiating spindle formation.
- Microtubules form around each centrosome, creating an aster during prophase.
Mitotic Apparatus
- A complex, organized structure crucial for cell division.
- Composed of spindle fibers, which are microtubules created from the breakdown of the nuclear membrane.
Astral Relaxation Theory
- Proposed by Wolpert in 1960.
- Explains furrow formation by the varying tension on the cell surface during division, with lower tension at the poles and higher tension at the equator.
Spindle Fibers
- Parallel bundles of microtubules, approximately 250-270 Å in diameter.
- Their composition is mainly proteins (around 90%) and RNA (around 5%).
Formation of Spindle Fibers
- Originate cytoplasmically.
- Begin forming in late prophase, completing by the end of prophase.
Mitotic Apparatus or Mitotic Spindle
- Extends between two centrioles, with astral rays radiating outwards.
- Formed by microtubules that lengthen between the two poles.
- Centriole separation and migration to opposite poles completes spindle formation.
Chromosome Movement
- During prophase, chromosomes move randomly.
- During prometaphase, chromosomes move toward the equator in an oscillatory motion.
Chromosome Movement Model
- Depicts the movement of chromosomes during cell division.
- Spindle fibers aid in moving chromosomes to the poles.
- Spindle fibers types: continuous, chromosomal, and interzonal fibers.
Spindle Fibers' Roles
- Continuous fibers: extend from one pole to the other.
- Chromosomal fibers (kinetochore microtubules): extend from the pole to the centromere of a chromosome.
- Interzonal fibers: appear in anaphase and telophase, extending between the centromeres of separating chromatids.
- Spindle fibers play a crucial role in moving chromosomes to the poles.
-
Anaphase-B:
- Microtubules from opposite poles slide past each other, pushing them apart.
- A pulling force acts on the poles to move them apart.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Description
Explore the stages of mitosis, the process by which a parent cell divides into two daughter cells. This quiz covers key phases including prophase, metaphase, karyokinesis, and the overall definition of mitosis. Test your understanding of these essential biological concepts.