Podcast Beta
Questions and Answers
What is a manifestation of conjunctivitis in a child?
What is a common symptom of infectious mononucleosis caused by EBV?
What are Koplik's spots associated with?
Which cells does EBV primarily infect?
Signup and view all the answers
Where are Koplik's spots typically found in the oral cavity?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following is a microscopic feature of Koplik's spots?
Signup and view all the answers
What laboratory finding is typically observed in patients with infectious mononucleosis?
Signup and view all the answers
In which condition does reactivation of EBV primarily lead to B-cell neoplasms?
Signup and view all the answers
What is a characteristic finding in the lungs of a measles patient?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following is NOT a common microscopic finding in measles?
Signup and view all the answers
What is a characteristic pathological finding in the lymph nodes during EBV infection?
Signup and view all the answers
What type of inflammation is indicated by neutrophilic exudate?
Signup and view all the answers
What mode of transmission is most commonly associated with EBV?
Signup and view all the answers
What is a feature of the measles rash?
Signup and view all the answers
Which observation indicates an immune response in lymphoid tissue during measles infection?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the most common cause of genital herpes?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary presentation of genital herpes lesions?
Signup and view all the answers
What type of inclusion bodies are characteristic of HSV infection?
Signup and view all the answers
What is a possible serious complication of HSV infection in neonates?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following symptoms is associated with disseminated HSV infection in neonates?
Signup and view all the answers
Where do Cowdry Type A inclusion bodies typically form in HSV-infected cells?
Signup and view all the answers
What systemic symptoms are seen in a disseminated HSV infection?
Signup and view all the answers
What is a common skin manifestation of HSV infection?
Signup and view all the answers
HSV infection can lead to necrotic lesions in which organs?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following is NOT characteristic of genital herpes lesions?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary viral agent responsible for mumps infection?
Signup and view all the answers
Which major gland is primarily affected by mumps parotitis?
Signup and view all the answers
What type of cells predominantly infiltrate the edematous interstitium of the parotid gland in mumps pathology?
Signup and view all the answers
What is a potential severe complication related to mumps affecting the testis?
Signup and view all the answers
What is a common clinical symptom of dengue fever?
Signup and view all the answers
Which type of hemorrhagic condition is associated with dengue fever?
Signup and view all the answers
How is dengue fever primarily transmitted?
Signup and view all the answers
What pathological finding is associated with mumps infection in the pancreas?
Signup and view all the answers
What clinical condition is linked with the presence of thrombocytopenia in dengue fever?
Signup and view all the answers
What type of viral disease is associated with perivenous demyelination in the central nervous system?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the dominant mode of transmission for CMV after the age of 15?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following is a characteristic finding in CMV-infected cells?
Signup and view all the answers
What type of inclusion bodies are associated with CMV infection?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following findings is typical in herpes zoster infection?
Signup and view all the answers
What is a potential mode of neonatal transmission of CMV?
Signup and view all the answers
What occurs alongside herpetic intranuclear inclusions in dorsal root ganglion cells infected by VZV?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the appearance of cells infected by CMV in lung alveoli under microscopic examination?
Signup and view all the answers
Which route is NOT associated with CMV transmission?
Signup and view all the answers
What type of inflammatory cells are predominantly associated with VZV ganglion cell infection?
Signup and view all the answers
In microscopic examination of herpes zoster, what features are observed in epithelial cells?
Signup and view all the answers
Study Notes
Measles
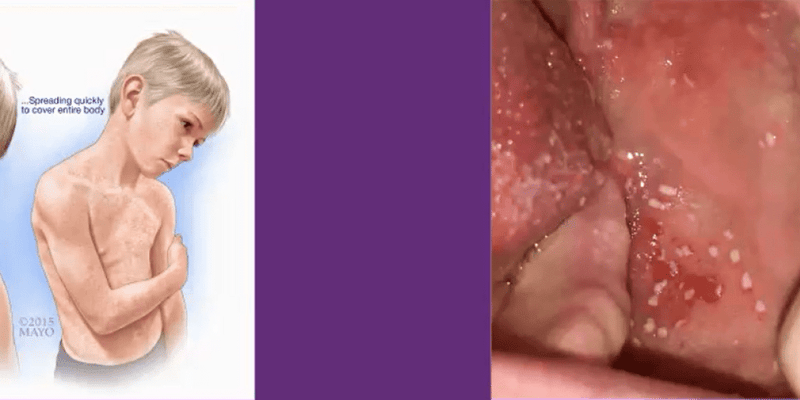
- Koplik's spots are ulcerated mucosal lesions in the oral cavity near the opening of the Stensen's duct
- Koplik's spots are pathognomonic for measles
- Microscopically, Koplik's spots consist of necrosis, neutrophilic exudate and neovascularization
- They are found in the oral cavity, particularly the lateral buccal mucosa and upper lip
- Measles rash and conjunctivitis are common symptoms
- Warthin-Finkeldey giant cells are multinucleated giant cells found in the lung
- Warthin-Finkeldey bodies are found in lymph nodes and the lungs
- Lung biopsy of a patient with measles pneumonia shows obliteration of the normal alveolar architecture
- Other microscopic findings include follicular hyperplasia and large germinal centers
Mumps
- Mumps is a contagious viral infection that causes swelling of the salivary glands, primarily the parotid glands.
- The virus enters the respiratory tract through inhalation of respiratory droplets
- It spreads to draining lymph nodes and replicates in T-lymphocytes
- Mumps can spread hematogenously to various organs
- Mumps parotitis is swelling and pain in the salivary glands
- Mumps encephalitis is characterized by perivenous demyelination and perivascular mononuclear cuffing.
- Mumps pancreatitis features acinar cell injury, release of digestive enzymes resulting in parenchymal necrosis, fat necrosis, and neutrophil-rich inflammation.
- Mumps orchitis presents with edema, mononuclear infiltration, and focal hemorrhages in the testes.
- Mumps orchitis may lead to infarction, necrosis, scarring, atrophy, and sterility.
- Mumps oophoritis is inflammation of the ovaries
- Mumps is characterized by a swollen neck region due to enlarged salivary glands
- Bilateral involvement in 70% of cases.
- The mumps virus infects ductal epithelial cells of the salivary gland
- Microscopic pathology involves edematous interstitium of the parotid gland, diffuse infiltration by lymphocytes, macrophages, and plasma cells, compressing the acini and ducts
- Neutrophils and necrotic debris may fill the lumen of the ducts, leading to focal damage to the lining epithelium
Dengue
- Dengue is a viral hemorrhagic fever caused by Flavivirus
- It is transmitted by mosquito bite (Aedes aegypti)
- Dengue infects mononuclear phagocytes and hepatocytes
- Clinical symptoms include headache, fever, myalgia, joint pain, conjunctival congestion, retro-orbital pain with generalized transient macular rash, and mild to severe hemorrhage
- Dengue hemorrhagic fever is a more severe form of dengue fever
- It is associated with hypoproteinemia, thrombocytopenia, prolonged bleeding time, and elevated prothrombin time
- Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever is a severe, life-threatening, multi-system syndrome involving vascular damage
- Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever causes widespread hemorrhage and shock.
- The diagnosis of dengue fever is based on clinical history, hemoconcentration, leukopenia with lymphocytosis, thrombocytopenia, and serological tests
- Gross pathology findings include conjunctival hemorrhage and pinpoint areas of bleeding
Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV)
- Genital herpes (Herpes Genitalia) is commonly caused by HSV-2
- HSV-2 causes vesicles on the genital mucus membranes and external genitalia, which rapidly convert to ulcerations.
- In neonates infected during passage through the birth canal, HSV can result in fulminating infection
- This is usually caused by HSV-2
- Neonatal HSV infection is characterized by generalized lymphadenopathy, splenomegaly, and necrotic foci throughout lungs, liver, adrenal glands, and CNS
- Cowdry type A inclusions (inclusion bodies) are large, pink to purple intranuclear inclusions in HSV-infected cells consisting of viral replication proteins and virions at various stages of assembly
- The inclusions push chromatin to the edge of the nucleus.
Herpes Zoster (Varicella Zoster Virus - VZV)
- Herpes zoster is a reactivation of varicella-zoster virus (VZV)
- VZV infects the dorsal root ganglion
- VZV infection of ganglion cells leads to ganglion cell necrosis, associated inflammation and herpetic intranuclear inclusions within the neurons and their supporting cells
- Herpes zoster (shingles) includes painful vesicular rashes distributed in a dermatomal pattern.
Cytomegalovirus (CMV)
- CMV infection can be acquired through neonatal transmission, genital route, saliva and respiratory secretions, feco-oral route, and iatrogenic transmission through blood transfusions or organ transplants.
- CMV-infected cells exhibit gigantism, presence of large intranuclear basophilic inclusion bodies surrounded by a clear halo (owl's eye).
Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV)
- EBV is a herpesvirus that causes infectious mononucleosis
- EBV is a factor in the development of several human cancers, including nasopharyngeal carcinoma, Burkitt lymphoma, B cell Non-Hodgkin lymphoma, and Hodgkin lymphoma
- EBV infects B cells and oropharyngeal epithelial cells
- EBV binds to Complement Receptor 2 (CR2), resulting in latent infection
- Transmission is through close human contact, frequently with saliva during kissing.
- In immunocompetent hosts, infection is often asymptomatic or results in infectious mononucleosis
- Infectious mononucleosis is characterized by fever, sore throat, generalized lymphadenopathy, splenomegaly, and the appearance of atypical lymphocytes (mononucleosis cells).
- Symptoms of infectious mononucleosis appear on the initiation of the host’s immune response
- Cellular immunity is mediated by CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes and NK cells.
- In patients with defective cellular immunity, EBV reactivation can lead to uncontrolled proliferation of B cells, resulting in EBV-associated B-cell neoplasms
- EBV causes cervical lymphadenopathy.
- Cervical lymphadenopathy in infectious mononucleosis commonly involves posterior cervical lymph nodes, axillary lymph nodes, and inguinal lymph nodes.
- Microscopic findings: Expansion of paracortical areas due to activation of the T cells.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Related Documents
Description
This quiz covers critical information about measles and mumps, including symptoms, histopathology, and pathognomonic signs like Koplik's spots and Warthin-Finkeldey giant cells. Test your knowledge on these contagious viral infections and their implications for public health.