Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the name of the characteristic skin rash that occurs in measles?
What is the name of the characteristic skin rash that occurs in measles?
- Maculopapular
- Morbilliform (correct)
- Petechial
- Urticarial
Which of the following is not a common complication of measles in healthy individuals?
Which of the following is not a common complication of measles in healthy individuals?
- Otitis media
- Bronchopneumonia
- Encephalitis
- Meningitis (correct)
What is the recommended method of transporting measles virus samples to the laboratory?
What is the recommended method of transporting measles virus samples to the laboratory?
- On ice (correct)
- At room temperature
- Frozen at -20°C
- Frozen at -70°C
What is the name of the white spots that may appear on the buccal mucosa of measles patients?
What is the name of the white spots that may appear on the buccal mucosa of measles patients?
What type of antibody is used to confirm a recent measles infection by enzyme immunoassay (EIA)?
What type of antibody is used to confirm a recent measles infection by enzyme immunoassay (EIA)?
What are the characteristic prodrome symptoms of measles?
What are the characteristic prodrome symptoms of measles?
Which individuals are more likely to experience severe measles?
Which individuals are more likely to experience severe measles?
How can healthcare facilities minimize the potential for healthcare-associated transmission of measles?
How can healthcare facilities minimize the potential for healthcare-associated transmission of measles?
How long does it take for IgM to be produced in response to measles infection after the onset of the rash?
How long does it take for IgM to be produced in response to measles infection after the onset of the rash?
How should measles virus samples be transported and stored?
How should measles virus samples be transported and stored?
There is a suspected case of measles in the ED of a facility, and the patient has been admitted. A nasopharyngeal swab was taken, placed in viral transport media, and sent to the lab where it was frozen at -20°C for 12 hours and then thawed and placed in culture. The culture results are negative for measles virus.
Why IP request to place the patient in an airborne infection isolation room?
There is a suspected case of measles in the ED of a facility, and the patient has been admitted. A nasopharyngeal swab was taken, placed in viral transport media, and sent to the lab where it was frozen at -20°C for 12 hours and then thawed and placed in culture. The culture results are negative for measles virus. Why IP request to place the patient in an airborne infection isolation room?
How can a specific diagnosis of measles be made?
How can a specific diagnosis of measles be made?
What is the name of the virus that causes measles?
What is the name of the virus that causes measles?
What is the most contagious phase of measles infection?
What is the most contagious phase of measles infection?
What are the whitish spots on the buccal mucosa that are distinctive for measles called?
What are the whitish spots on the buccal mucosa that are distinctive for measles called?
What is the best method to confirm a recent measles infection?
What is the best method to confirm a recent measles infection?
What is the recommended vaccination schedule for measles prevention in adults at high risk?
What is the recommended vaccination schedule for measles prevention in adults at high risk?
Measles is primarily transmitted through:
Measles is primarily transmitted through:
How long is the incubation period for measles?
How long is the incubation period for measles?
Which of the following is a key diagnostic sign and pathognomonic (distinctive) for measles?
Which of the following is a key diagnostic sign and pathognomonic (distinctive) for measles?
What is the characteristic pattern of the measles rash?
What is the characteristic pattern of the measles rash?
What are Koplik spots?
What are Koplik spots?
How can a recent measles infection be diagnosed?
How can a recent measles infection be diagnosed?
There is a specific antiviral therapy available for the treatment of measles.
There is a specific antiviral therapy available for the treatment of measles.
Measles patients most contagious
Measles patients most contagious
Because of the potential for rapid spread, one confirmed case of this disease is considered an urgent public health situation, and the IP should immediately report suspected and confirmed cases to the health department:
Because of the potential for rapid spread, one confirmed case of this disease is considered an urgent public health situation, and the IP should immediately report suspected and confirmed cases to the health department:
A measles exposure from a patient in a clinic was identified and an exposure workup was initiated. A staff exposure was defined as "nonimmune HCP with more than 5 minutes of same-room contact or face-to-face contact with the index patient." Forty eight HCP were identified as possible exposures. Of these, 44 had documented immunity to measles. Of the remaining HCP, three did not have the same room or face-to-face contact. How many HCP were at risk of developing measles because of this exposure?
A measles exposure from a patient in a clinic was identified and an exposure workup was initiated. A staff exposure was defined as "nonimmune HCP with more than 5 minutes of same-room contact or face-to-face contact with the index patient." Forty eight HCP were identified as possible exposures. Of these, 44 had documented immunity to measles. Of the remaining HCP, three did not have the same room or face-to-face contact. How many HCP were at risk of developing measles because of this exposure?
An adult patient is admitted through the Emergency Department with a 1-day history of rash, fever, and cough. The attending physician is concerned that the patient has measles, as the patient cannot recall whether he has had measles disease or vaccine in the past. The serum sample does not contain measles- specific IgG or IgM antibodies. What is the significance of this finding?
An adult patient is admitted through the Emergency Department with a 1-day history of rash, fever, and cough. The attending physician is concerned that the patient has measles, as the patient cannot recall whether he has had measles disease or vaccine in the past. The serum sample does not contain measles- specific IgG or IgM antibodies. What is the significance of this finding?
There is a suspected case of measles in the ED of a facility, and the patient has been admitted. A nasopharyngeal swab was taken, placed in viral transport media, and sent to the lab where it was frozen at -20°C for 12 hours and then thawed and placed in culture. The culture results are negative for measles virus. Which of the following should the IP request for this patient?
...................
- A new sample should be collected and placed in a -20°C environment immediately
- A new sample should be collected and placed in culture immediately
- The patient should be placed in an airborne infection isolation room
- The patient should be placed in a standard room without isolation precautions
There is a suspected case of measles in the ED of a facility, and the patient has been admitted. A nasopharyngeal swab was taken, placed in viral transport media, and sent to the lab where it was frozen at -20°C for 12 hours and then thawed and placed in culture. The culture results are negative for measles virus. Which of the following should the IP request for this patient? ...................
- A new sample should be collected and placed in a -20°C environment immediately
- A new sample should be collected and placed in culture immediately
- The patient should be placed in an airborne infection isolation room
- The patient should be placed in a standard room without isolation precautions
Which of the following is not confirmatory of an active measles infection?
Which of the following is not confirmatory of an active measles infection?
The rash in measels appears after how many days from catarrhal prodromal phase
The rash in measels appears after how many days from catarrhal prodromal phase
• What is one of the acceptable presumptive evidence of immunity against measles?
• What is one of the acceptable presumptive evidence of immunity against measles?
How many doses of a measles-containing vaccine are required for school-age children and adults who are at high risk of measles exposure?
How many doses of a measles-containing vaccine are required for school-age children and adults who are at high risk of measles exposure?
Which of the following groups of adults are considered at high risk of measles exposure and need two doses of measles-containing vaccine?
Which of the following groups of adults are considered at high risk of measles exposure and need two doses of measles-containing vaccine?
What is the minimum age for receiving the first dose of a measles-containing vaccine for preschool-age children and adults who are not at high risk of measles exposure?
What is the minimum age for receiving the first dose of a measles-containing vaccine for preschool-age children and adults who are not at high risk of measles exposure?
What type of antibody indicates a past or recent infection with measles or vaccination against measles?
What type of antibody indicates a past or recent infection with measles or vaccination against measles?
Anyone who works in health care, even if he was born before 1957, must prove that he received Measles and Mumps vaccinations unless they have a history of physician-diagnosed or laboratory-confirmed immunity (IgG)
Anyone who works in health care, even if he was born before 1957, must prove that he received Measles and Mumps vaccinations unless they have a history of physician-diagnosed or laboratory-confirmed immunity (IgG)
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Measles Characteristics
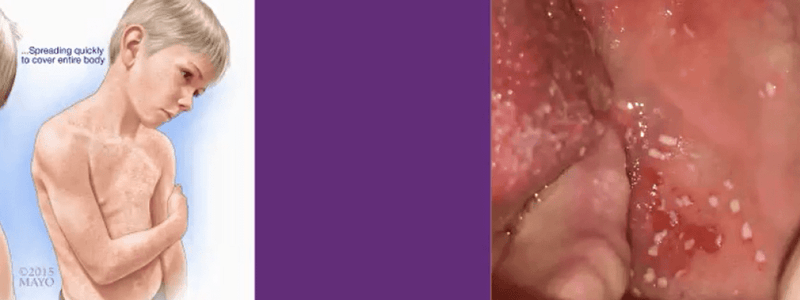
- The characteristic skin rash that occurs in measles is known as a maculopapular rash.
- Koplik spots are white spots that may appear on the buccal mucosa of measles patients.
Measles Complications
- Common complications of measles in healthy individuals do not include otitis media, diarrhea, and pneumonia.
- Severe measles is more likely to occur in individuals who are immunocompromised, pregnant, or have Vitamin A deficiency.
Measles Diagnosis
- A specific diagnosis of measles can be made by detecting measles IgM antibodies in serum or saliva.
- The best method to confirm a recent measles infection is by enzyme immunoassay (EIA).
- Detection of measles RNA in respiratory secretions or urine also confirms measles infection.
Measles Transmission
- Measles is primarily transmitted through direct contact with infectious droplets from the nose, mouth, or throat of an infected person.
- The incubation period for measles is 10-14 days.
- The most contagious phase of measles infection is 2-4 days before the onset of symptoms.
Measles Prevention
- The recommended vaccination schedule for measles prevention in adults at high risk is two doses of measles-containing vaccine.
- Adults at high risk of measles exposure include healthcare workers, students in post-secondary educational institutions, and individuals who travel internationally.
- The minimum age for receiving the first dose of a measles-containing vaccine for preschool-age children and adults who are not at high risk of measles exposure is 12 months.
Measles Management
- There is no specific antiviral therapy available for the treatment of measles.
- One confirmed case of measles is considered an urgent public health situation, and the infection preventionist (IP) should immediately report suspected and confirmed cases to the health department.
- Healthcare facilities can minimize the potential for healthcare-associated transmission of measles by implementing airborne infection isolation precautions.
Measles Laboratory Testing
- Measles virus samples should be transported and stored at -70°C or below.
- IgM antibodies are produced in response to measles infection within 1-3 days after the onset of the rash.
Measles Infection Control
- Individuals who are not immune to measles should be placed in an airborne infection isolation room.
- To minimize the potential for healthcare-associated transmission of measles, healthcare facilities should implement airborne infection isolation precautions.
Measles Immunity
- One of the acceptable presumptive evidence of immunity against measles is a documented history of measles vaccination or physician-diagnosed measles disease.
- Anyone who works in healthcare must prove that they received measles vaccinations or have a history of physician-diagnosed or laboratory-confirmed immunity (IgG) unless they were born before 1957.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.