Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which structure is involved in preventing food from entering the nasopharynx during swallowing?
Which structure is involved in preventing food from entering the nasopharynx during swallowing?
- Epiglottis
- Vocal cords
- Soft palate (correct)
- Hyoid bone
What is the primary disorder characterized by difficulty in swallowing?
What is the primary disorder characterized by difficulty in swallowing?
- Aspiration
- Dysphagia (correct)
- Anorexia
- Dysphasia
Which of the following is NOT a cause of dysphagia?
Which of the following is NOT a cause of dysphagia?
- Osteoporosis (correct)
- Cleft palate
- Parkinson's disease
- Stroke
In considering dental management for patients with dysphagia, which of the following is a common consideration?
In considering dental management for patients with dysphagia, which of the following is a common consideration?
What role does the epiglottis play during swallowing?
What role does the epiglottis play during swallowing?
Which of the following conditions does NOT contribute to difficulties in swallowing?
Which of the following conditions does NOT contribute to difficulties in swallowing?
What is the consequence of aspiration related to dysphagia?
What is the consequence of aspiration related to dysphagia?
Which dental management strategy is recommended for patients with dry mouth due to dysphagia?
Which dental management strategy is recommended for patients with dry mouth due to dysphagia?
Which phase of mastication involves closing the mouth around the food?
Which phase of mastication involves closing the mouth around the food?
What initiates the reflex of deglutition?
What initiates the reflex of deglutition?
Which nerve is NOT involved in transmitting the sensory impulses during swallowing?
Which nerve is NOT involved in transmitting the sensory impulses during swallowing?
During which phase of deglutition does the bolus travel down the esophagus?
During which phase of deglutition does the bolus travel down the esophagus?
Which of the following is a characteristic of the automatic swallow?
Which of the following is a characteristic of the automatic swallow?
What role do taste buds play in the process of mastication and deglutition?
What role do taste buds play in the process of mastication and deglutition?
Which statement about the muscular involvement in deglutition is true?
Which statement about the muscular involvement in deglutition is true?
What is the function of the hypopharyngeal sphincter during the swallowing process?
What is the function of the hypopharyngeal sphincter during the swallowing process?
Flashcards
Mastication
Mastication
The act of chewing food, breaking it down into smaller pieces.
Opening Phase of Mastication
Opening Phase of Mastication
The opening of the mouth and movement of the jaw to bring food into the mouth.
Closing Phase of Mastication
Closing Phase of Mastication
The closing of the jaw, bringing upper and lower teeth together to crush food.
Occlusal Phase of Mastication
Occlusal Phase of Mastication
Signup and view all the flashcards
Deglutition
Deglutition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oral Phase of Deglutition
Oral Phase of Deglutition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pharyngeal Phase of Deglutition
Pharyngeal Phase of Deglutition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Esophageal Phase of Deglutition
Esophageal Phase of Deglutition
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does the soft palate do during swallowing?
What does the soft palate do during swallowing?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is dysphagia?
What is dysphagia?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What causes dysphagia due to muscle weakness?
What causes dysphagia due to muscle weakness?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What causes dysphagia due to a structural abnormality?
What causes dysphagia due to a structural abnormality?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is reduced oral clearance?
What is reduced oral clearance?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Why does dysphagia cause an increase in plaque?
Why does dysphagia cause an increase in plaque?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Why is dry mouth a concern for people with dysphagia?
Why is dry mouth a concern for people with dysphagia?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does dysphagia increase caries risk?
How does dysphagia increase caries risk?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Mastication and Deglutition
-
Mastication (Chewing): The process of breaking down food.
- Opening phase: Initial movement of the jaw.
- Closing phase: Jaw closes around food.
- Occlusal phase: Grinding and pulverizing food.
-
Deglutition (Swallowing): The process of moving food from the mouth to the stomach.
- Reflex initiation: Sensory stimulation (taste, touch) in the mouth triggers a reflex.
- Neural pathway: Impulses travel through cranial nerves (trigeminal and glossopharyngeal) to the swallow center.
- Muscle contraction: Pharyngeal, laryngeal, and esophageal muscles contract in a coordinated sequence.
- Phases:
- Oral phase: Tongue manipulating food, moving bolus.
- Pharyngeal phase: Bolus moves through the pharynx.
- Esophageal phase: Bolus moves into the esophagus and stomach.
- Types of swallows:
- Automatic: No food present (dry swallow).
- Voluntary: Food or drink present.
- Sequence of events in voluntary swallow
- Lips close, and bolus is created.
- Bolus stays in front of the mouth, away from the nasopharynx.
- Nasal breathing: Larynx is open, and hypopharyngeal sphincter is closed.
- Soft palate is lowered to stop food from entering the nasopharynx.
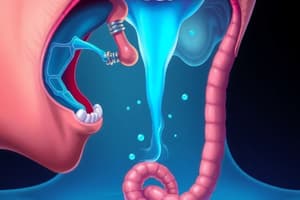
Structures Involved
- Mouth: Lips ensure oral closure; tongue forms the bolus.
- Soft palate: Raises to block the nasopharynx.
- Hyoid bone: Supports tongue & muscles.
- Epiglottis: Lowers to protect the airway.
- Vocal cords: Close to protect the airway.
- Cricoid cartilage: Relaxes, allowing food entry to the esophagus.
Dysphagia (Swallowing Difficulty)
-
Causes:
- Muscle/nerve damage: Stroke, cerebral palsy, Parkinson's disease.
- Structural abnormalities: Cleft palate, bony growths.
- Cancer (head & neck): cancer and treatment.
- Infections/irritations.
- Dementia/cognitive decline.
- Medications/alcohol.
-
Consequences:
- Aspiration: Food entering the lungs.
- Malnutrition/dehydration: Reduced food and liquid intake.
Dental Management Considerations for Dysphagia
- Reduced oral clearance: Food remaining in the mouth.
- Increased plaque/dental caries: Greater risk of oral disease.
- Dry mouth: Xerostomia.
- Patient assessment: Impact on daily life.
- Patient positioning: To aid swallowing.
- Preventative advice: Non-foaming toothpaste, mouthwash.
- Treatment considerations: Careful use of water & fast-setting materials.
- Salivary function: Assessing ability to swallow saliva.
- Regular breaks: Needed during treatments to reduce fatigue.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Description
Test your knowledge on the processes of mastication and deglutition. This quiz covers the phases of chewing and swallowing, including the necessary muscular actions and neural pathways involved. Perfect for students in physiology or health sciences.