Podcast
Questions and Answers
What are the three phases of the masticatory cycle?
What are the three phases of the masticatory cycle?
- Initial Phase, Secondary Phase, Terminal Phase
- Preparation Phase, Mixing Phase, Digestion Phase
- Opening Phase, Occlusal Phase, Closing Phase (correct)
- Opening Phase, Chewing Phase, Swallowing Phase
Which structure is NOT directly involved in the process of mastication?
Which structure is NOT directly involved in the process of mastication?
- Esophagus (correct)
- Muscles of mastication
- Teeth
- Saliva
What is the primary function of saliva in the digestive process?
What is the primary function of saliva in the digestive process?
- To aid in the formation of the bolus
- To initiate the breakdown of carbohydrates (correct)
- To provide nutrients
- To neutralize stomach acid
What is dysphagia?
What is dysphagia?
Which of the following is a consideration in the dental management of patients with dysphagia?
Which of the following is a consideration in the dental management of patients with dysphagia?
What is the primary function of the swallow centre located in the medulla?
What is the primary function of the swallow centre located in the medulla?
Which nerves are involved in transmitting afferent impulses to the swallow centre?
Which nerves are involved in transmitting afferent impulses to the swallow centre?
How long does it approximately take for the bolus to travel from the oral cavity to the stomach?
How long does it approximately take for the bolus to travel from the oral cavity to the stomach?
What triggers the reflex action of swallowing?
What triggers the reflex action of swallowing?
What type of swallow is considered to be voluntarily initiated?
What type of swallow is considered to be voluntarily initiated?
What role do the lips play during swallowing?
What role do the lips play during swallowing?
Which structure is primarily responsible for supporting the tongue?
Which structure is primarily responsible for supporting the tongue?
What is the primary function of the epiglottis during the swallowing process?
What is the primary function of the epiglottis during the swallowing process?
During the swallowing process, which structure relaxes to allow food to enter the oesophagus?
During the swallowing process, which structure relaxes to allow food to enter the oesophagus?
What initiates the swallowing process?
What initiates the swallowing process?
Which phase of swallowing involves the formation of a bolus of food?
Which phase of swallowing involves the formation of a bolus of food?
What anatomical feature prevents food from entering the nasopharynx during swallowing?
What anatomical feature prevents food from entering the nasopharynx during swallowing?
Which function is associated with the vocal cords during swallowing?
Which function is associated with the vocal cords during swallowing?
Which of the following is a consequence of dysphagia that relates to oral health?
Which of the following is a consequence of dysphagia that relates to oral health?
What positioning is recommended for a patient with dysphagia to ensure comfort during treatment?
What positioning is recommended for a patient with dysphagia to ensure comfort during treatment?
Which of the following considerations is essential when provision of treatment for a dysphagia patient?
Which of the following considerations is essential when provision of treatment for a dysphagia patient?
In assessing a patient with dysphagia, what is an important aspect to consider?
In assessing a patient with dysphagia, what is an important aspect to consider?
Which of the following increases the risk of dental caries for patients with dysphagia?
Which of the following increases the risk of dental caries for patients with dysphagia?
Which of the following is recommended to help prevent lengthy dental procedures for patients with swallowing difficulties?
Which of the following is recommended to help prevent lengthy dental procedures for patients with swallowing difficulties?
What type of toothbrush is suggested for patients with swallowing problems?
What type of toothbrush is suggested for patients with swallowing problems?
Which of the following is NOT a consideration for dietary adjustments in patients with dysphagia?
Which of the following is NOT a consideration for dietary adjustments in patients with dysphagia?
In managing dental procedures for patients with swallowing difficulties, which material is advisable to avoid?
In managing dental procedures for patients with swallowing difficulties, which material is advisable to avoid?
What is an important precaution to take when performing dental impressions for patients at risk of swallowing problems?
What is an important precaution to take when performing dental impressions for patients at risk of swallowing problems?
What should be considered when giving preventative advice to patients with dysphagia?
What should be considered when giving preventative advice to patients with dysphagia?
Which of the following is a better alternative if patients require antibiotics?
Which of the following is a better alternative if patients require antibiotics?
For patients with swallowing challenges, what type of dietary analysis is important?
For patients with swallowing challenges, what type of dietary analysis is important?
What initiates the swallow reflex?
What initiates the swallow reflex?
What occurs during the pharyngeal phase of swallowing?
What occurs during the pharyngeal phase of swallowing?
What closes to prevent food from entering the nasopharynx during swallowing?
What closes to prevent food from entering the nasopharynx during swallowing?
Which nerve is responsible for taste sensation from the posterior one-third of the tongue?
Which nerve is responsible for taste sensation from the posterior one-third of the tongue?
What action is performed by the larynx during the swallowing process?
What action is performed by the larynx during the swallowing process?
What is the term for swallowing difficulties?
What is the term for swallowing difficulties?
How is the bolus transported down the esophagus?
How is the bolus transported down the esophagus?
What triggers the opening of the hypopharyngeal sphincter?
What triggers the opening of the hypopharyngeal sphincter?
Which nerve provides motor function to the pharyngeal constrictors?
Which nerve provides motor function to the pharyngeal constrictors?
What is the primary role of the epiglottis during swallowing?
What is the primary role of the epiglottis during swallowing?
Flashcards
Mastication
Mastication
The process of chewing food, breaking it down into smaller pieces to aid in digestion.
Muscles of mastication
Muscles of mastication
The muscles responsible for chewing: masseter, temporalis, medial pterygoid, and lateral pterygoid. They work together to move the jaw up, down, and side to side.
Salivary amylase
Salivary amylase
The primary enzyme in saliva that begins the digestion of carbohydrates. It breaks down starch into simpler sugars.
Deglutition
Deglutition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dysphagia
Dysphagia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Automatic Swallow
Automatic Swallow
Signup and view all the flashcards
Voluntarily Initiated Swallow
Voluntarily Initiated Swallow
Signup and view all the flashcards
Swallow Center
Swallow Center
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tactile Receptors
Tactile Receptors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lip role in swallowing
Lip role in swallowing
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tongue role in swallowing
Tongue role in swallowing
Signup and view all the flashcards
Soft palate role in swallowing
Soft palate role in swallowing
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hyoid Bone
Hyoid Bone
Signup and view all the flashcards
Epiglottis
Epiglottis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vocal cord role in swallowing
Vocal cord role in swallowing
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cricopharyngeal Sphincter
Cricopharyngeal Sphincter
Signup and view all the flashcards
Swallowing Phases
Swallowing Phases
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pharyngeal Phase
Pharyngeal Phase
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oesophageal Phase
Oesophageal Phase
Signup and view all the flashcards
Swallowing Reflex
Swallowing Reflex
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glottis
Glottis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hypopharyngeal Sphincter
Hypopharyngeal Sphincter
Signup and view all the flashcards
Peristaltic Waves
Peristaltic Waves
Signup and view all the flashcards
Facial Nerve (VII)
Facial Nerve (VII)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glossopharyngeal Nerve (IX)
Glossopharyngeal Nerve (IX)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vagus Nerve (X)
Vagus Nerve (X)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Power-driven Scaling
Power-driven Scaling
Signup and view all the flashcards
3-in-1
3-in-1
Signup and view all the flashcards
Semi-supine Position
Semi-supine Position
Signup and view all the flashcards
Preventative Oral Care Advice for Dysphagia Patients
Preventative Oral Care Advice for Dysphagia Patients
Signup and view all the flashcards
Aspirating Toothbrush
Aspirating Toothbrush
Signup and view all the flashcards
Rubber Dam
Rubber Dam
Signup and view all the flashcards
Good Suction (Saliva Ejector and HVS)
Good Suction (Saliva Ejector and HVS)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Aspirating
Aspirating
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fast Setting Materials
Fast Setting Materials
Signup and view all the flashcards
Altered Diet/OH
Altered Diet/OH
Signup and view all the flashcards
Avoid Where Possible
Avoid Where Possible
Signup and view all the flashcards
Preventative Advice
Preventative Advice
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Mastication, Deglutition & Dysphagia
- Mastication is the process of chewing food
- Deglutition is the process of swallowing
- Dysphagia is difficulty swallowing
- GDC Learning Outcomes include describing relevant/appropriate dental, oral, craniofacial, and general anatomy and physiology, and explaining application to patient management
- Specific topics to relate to/include the muscles of mastication, tongue, saliva & salivation, the palate, xerostomia, and regional anatomy
Intended Learning Outcomes
- Understand the processes of mastication and deglutition, both in health and disease
- Identify structures involved in these processes
- Describe disorders affecting normal swallowing
- Outline considerations for dental management of patients with dysphagia
Mastication
- Mastication involves the mouth's structures (teeth, tongue, muscles of mastication, lips).
- The purpose of mastication is to break down food to make swallowing easier, enabling the digestive process to commence.
- The masticatory cycle includes opening, closing, and occlusal phases.
- Saliva is crucial for mixing food into bolus for easier swallowing and initiating digestion. An enzyme in saliva is necessary to begin the digestive process.
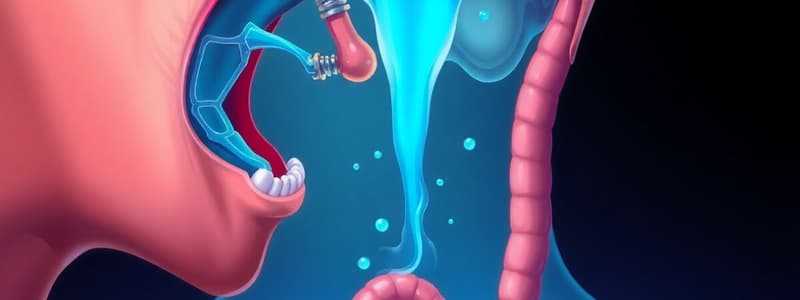
Deglutition (The Normal Swallow)
- Swallowing is a complex process needing coordinated actions from 25 skeletal muscles.
- It takes about 7 seconds for food to go from the oral cavity to the stomach
- The openings between the oropharynx, nasopharynx, and laryngopharynx/larynx are closed simultaneously
- Three phases of swallowing: oral, pharyngeal, and esophageal
- During swallowing the larynx moves, the epiglottis and soft palate close off the airway and nasopharynx, and the vocal cords close.
Swallowing Structures
- Lips, Tongue, Soft Palate, Hyoid Bone, Epiglottis, Vocal Cords, and Cricoid Cartilage are key structures.
Phases of Swallowing
- Oral phase: Food is prepared, chewed, and shaped into a bolus
- Pharyngeal phase: Begins with the bolus reaching the back of the tongue, the soft palate/epiglottis/larynx move to close the airway and nasopharynx
- Oesophageal phase: Bolus is moved to the stomach through peristalsis
Disorders of the Pharyngeal Stage
- Delay in the swallow reflex can lead to food or liquids entering the airway before the reflex has begun to protect it.
- Reduced pharyngeal peristalsis can cause residue to remain in the pharynx and potentially enter the airway after the swallow.
Disorders of the Oesophageal Stage
- Reduced peristalsis in the oesophagus can lead to reflux in the oesophagus and potential aspiration. Poor positioning of the patient after eating can also contribute to this.
Abnormal Swallow (Associated Problems)
- Infection can affect normal swallowing, particularly by aspiration, and is often associated with a chest infection
- Dehydration leads to insufficient fluid intake when swallowing difficulty exists. Consequences can encompass infection, confusion, and reduced saliva production.
- Malnutrition results from inadequate nutritional intake and is a significant consequence of dysphagia because eating and swallowing are impacted.
Gastric Reflux and Heartburn
- Stomach contents can be forced up into the esophagus, producing heartburn, and inflammation can also occur.
- The esophageal lining is vulnerable because it does not have the same protection as the stomach.
Dental Management of Dysphagia
- Dysphagia influences oral health by reducing oral clearance, potentially leading to increased plaque and calculus deposits, dry mouth, and caries risk.
- Assessment, positioning, preventative advice, and additional considerations for treatment/care are essential for patients with dysphagia.
Nerve Innervation
- Various cranial nerves are involved in both chewing and swallowing functions, including those for taste, sensory, and motor control.
Dysphagia (Swallowing Difficulties)
- Dysphagia is a condition of difficulty swallowing and is often due to a throat infection that causes pain
- Risk factors encompass stroke/cerebral palsy/Parkinson's disease, structural abnormalities (such as cleft palate), cancer/treatments, infections, dementia, and recreational/prescription medications.
- Possible signs/symptoms of dysphagia include: food or drink going down the wrong way, coughing, feeling that food is stuck in the throat, food or drink left in the mouth after swallowing, dribbling, taking a long time to swallow, needing effort to clear the throat after swallowing, croaky/wet sounding voice, and inability to chew food properly
Additional Resources
- Leaflets and videos providing information on swallowing difficulties, available online via the Stroke Association website
- YouTube videos that illustrate anatomical aspects of the pharynx
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.