Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary role of chondrocytes in cartilage?
What is the primary role of chondrocytes in cartilage?
What characterizes hyaline cartilage among the types of cartilage mentioned?
What characterizes hyaline cartilage among the types of cartilage mentioned?
Which type of cartilage is specifically known for its strength under stress?
Which type of cartilage is specifically known for its strength under stress?
What happens to chondrocytes as they secrete extracellular matrix (ECM)?
What happens to chondrocytes as they secrete extracellular matrix (ECM)?
Signup and view all the answers
Which statement accurately reflects the relationship between chondroblasts and chondrocytes?
Which statement accurately reflects the relationship between chondroblasts and chondrocytes?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary function of cartilage in the body?
What is the primary function of cartilage in the body?
Signup and view all the answers
Which type of bone cell is primarily responsible for bone resorption?
Which type of bone cell is primarily responsible for bone resorption?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the epiphyseal plate's role in long bone development?
What is the epiphyseal plate's role in long bone development?
Signup and view all the answers
What is one of the key components that make up cartilage?
What is one of the key components that make up cartilage?
Signup and view all the answers
What process do osteoblasts primarily engage in at the ossification zone of the epiphyseal plate?
What process do osteoblasts primarily engage in at the ossification zone of the epiphyseal plate?
Signup and view all the answers
What happens to the cavity formed during ossification in the epiphyseal plate?
What happens to the cavity formed during ossification in the epiphyseal plate?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following best describes the condition of osteoporosis?
Which of the following best describes the condition of osteoporosis?
Signup and view all the answers
What is a potential consequence of decreased mechanical stimulation of osteocytes?
What is a potential consequence of decreased mechanical stimulation of osteocytes?
Signup and view all the answers
Where do osteoprogenitor stem cells primarily reside?
Where do osteoprogenitor stem cells primarily reside?
Signup and view all the answers
What characterizes the normal bone structure as compared to osteoporotic bone?
What characterizes the normal bone structure as compared to osteoporotic bone?
Signup and view all the answers
What happens to the interstitial lamellae during bone remodeling?
What happens to the interstitial lamellae during bone remodeling?
Signup and view all the answers
What aspect of osteoporotic bone contributes to its brittleness?
What aspect of osteoporotic bone contributes to its brittleness?
Signup and view all the answers
What type of ossification involves the direct differentiation of osteoblasts from mesenchyme?
What type of ossification involves the direct differentiation of osteoblasts from mesenchyme?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following bones undergoes intramembranous ossification?
Which of the following bones undergoes intramembranous ossification?
Signup and view all the answers
Which structure is formed as a result of continuous deposition of bony matrix?
Which structure is formed as a result of continuous deposition of bony matrix?
Signup and view all the answers
In endochondral ossification, what serves as the template for bone formation?
In endochondral ossification, what serves as the template for bone formation?
Signup and view all the answers
What replaces woven bone during the bone formation process?
What replaces woven bone during the bone formation process?
Signup and view all the answers
Which bones are primarily formed through endochondral ossification?
Which bones are primarily formed through endochondral ossification?
Signup and view all the answers
What structural component forms when blood vessels invade the trabeculae?
What structural component forms when blood vessels invade the trabeculae?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the first type of bone formed during ossification?
What is the first type of bone formed during ossification?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the first step in the process of bone repair following a fracture?
What is the first step in the process of bone repair following a fracture?
Signup and view all the answers
What type of collagen fibers are primarily released from the breakdown of nasal cartilage during bone repair?
What type of collagen fibers are primarily released from the breakdown of nasal cartilage during bone repair?
Signup and view all the answers
What replaces the soft procallus during the bone healing process?
What replaces the soft procallus during the bone healing process?
Signup and view all the answers
Which component of bone impedes the distribution of nutrients and oxygen to osteocytes?
Which component of bone impedes the distribution of nutrients and oxygen to osteocytes?
Signup and view all the answers
How long does it typically take for bone to heal completely after a fracture?
How long does it typically take for bone to heal completely after a fracture?
Signup and view all the answers
Which statement most accurately describes compact bone?
Which statement most accurately describes compact bone?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the role of osteoblasts in the bone healing process?
What is the role of osteoblasts in the bone healing process?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following describes the endosteum?
Which of the following describes the endosteum?
Signup and view all the answers
What transformation occurs to chondroblasts as they become trapped within lacunae?
What transformation occurs to chondroblasts as they become trapped within lacunae?
Signup and view all the answers
What type of growth is characterized by the mitotic division of existing chondrocytes?
What type of growth is characterized by the mitotic division of existing chondrocytes?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following components is part of the inorganic portion of the bone matrix?
Which of the following components is part of the inorganic portion of the bone matrix?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the main function of proteoglycans in the organic portion of the matrix?
What is the main function of proteoglycans in the organic portion of the matrix?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following ions is NOT commonly found in the inorganic portion of the bone matrix?
Which of the following ions is NOT commonly found in the inorganic portion of the bone matrix?
Signup and view all the answers
What role do osteoclasts primarily serve in bone tissue?
What role do osteoclasts primarily serve in bone tissue?
Signup and view all the answers
Which growth pattern is more significant during postnatal development?
Which growth pattern is more significant during postnatal development?
Signup and view all the answers
What substance primarily contributes to the pink staining of the organic matrix when using eosin?
What substance primarily contributes to the pink staining of the organic matrix when using eosin?
Signup and view all the answers
What type of cartilage is primarily composed of Type II collagen?
What type of cartilage is primarily composed of Type II collagen?
Signup and view all the answers
What structure within bone allows for communication between osteocytes?
What structure within bone allows for communication between osteocytes?
Signup and view all the answers
How does the permeability of the ECM differ between bone and cartilage?
How does the permeability of the ECM differ between bone and cartilage?
Signup and view all the answers
In which part of the bone does secondary ossification occur around the time of birth?
In which part of the bone does secondary ossification occur around the time of birth?
Signup and view all the answers
What produces the synovial fluid within joints?
What produces the synovial fluid within joints?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the initial step in the process of chondrogenesis?
What is the initial step in the process of chondrogenesis?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the role of the perichondrium in cartilage formation?
What is the role of the perichondrium in cartilage formation?
Signup and view all the answers
During chondrogenesis, what differentiation occurs after mesenchymal cells undergo mitosis?
During chondrogenesis, what differentiation occurs after mesenchymal cells undergo mitosis?
Signup and view all the answers
Which condition is characterized by the deterioration of cartilage in joints?
Which condition is characterized by the deterioration of cartilage in joints?
Signup and view all the answers
What is a common consequence of damaged cartilage in osteoarthritis?
What is a common consequence of damaged cartilage in osteoarthritis?
Signup and view all the answers
In chondrogenesis, what is the primary function of chondroblasts after their formation?
In chondrogenesis, what is the primary function of chondroblasts after their formation?
Signup and view all the answers
Which population is commonly affected by osteoarthritis?
Which population is commonly affected by osteoarthritis?
Signup and view all the answers
What results from the separation of chondrocytes during chondrogenesis?
What results from the separation of chondrocytes during chondrogenesis?
Signup and view all the answers
What primarily characterizes the interterritorial matrix in cartilage?
What primarily characterizes the interterritorial matrix in cartilage?
Signup and view all the answers
Which cells are primarily responsible for synthesizing the extracellular matrix in cartilage?
Which cells are primarily responsible for synthesizing the extracellular matrix in cartilage?
Signup and view all the answers
What is a distinct characteristic of cartilage compared to other connective tissues?
What is a distinct characteristic of cartilage compared to other connective tissues?
Signup and view all the answers
What feature is associated with chondroblasts during cartilage formation?
What feature is associated with chondroblasts during cartilage formation?
Signup and view all the answers
Which type of cartilage is known for its durability and high proteoglycan content?
Which type of cartilage is known for its durability and high proteoglycan content?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary location of chondroblasts within the cartilage structure?
What is the primary location of chondroblasts within the cartilage structure?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following statements is true about glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) in cartilage?
Which of the following statements is true about glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) in cartilage?
Signup and view all the answers
What differentiates the interterritorial matrix from the territorial matrix?
What differentiates the interterritorial matrix from the territorial matrix?
Signup and view all the answers
What is housed within a lacuna in bone tissue?
What is housed within a lacuna in bone tissue?
Signup and view all the answers
Which lamellae are found immediately beneath the periosteum?
Which lamellae are found immediately beneath the periosteum?
Signup and view all the answers
What describes interstitial lamellae in bone tissue?
What describes interstitial lamellae in bone tissue?
Signup and view all the answers
What characteristic is specific to ground bone preparations?
What characteristic is specific to ground bone preparations?
Signup and view all the answers
What happens to the inorganic matrix during decalcification?
What happens to the inorganic matrix during decalcification?
Signup and view all the answers
What component of osteons is primarily responsible for nutrient and waste exchange?
What component of osteons is primarily responsible for nutrient and waste exchange?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary function of the central canal within an osteon?
What is the primary function of the central canal within an osteon?
Signup and view all the answers
How are the internal circumferential lamellae positioned relative to the bone marrow cavity?
How are the internal circumferential lamellae positioned relative to the bone marrow cavity?
Signup and view all the answers
What primarily forms the framework supporting soft tissues in the body?
What primarily forms the framework supporting soft tissues in the body?
Signup and view all the answers
Which component is predominantly found in cartilage and contributes to its properties?
Which component is predominantly found in cartilage and contributes to its properties?
Signup and view all the answers
What condition is characterized by decreased bone density and increased risk of fractures?
What condition is characterized by decreased bone density and increased risk of fractures?
Signup and view all the answers
Which growth process is essential for the lengthening of long bones during development?
Which growth process is essential for the lengthening of long bones during development?
Signup and view all the answers
Which layer of connective tissue surrounds cartilage and plays a role in its development?
Which layer of connective tissue surrounds cartilage and plays a role in its development?
Signup and view all the answers
What occurs during the ossification zone of the epiphyseal plate?
What occurs during the ossification zone of the epiphyseal plate?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the result of applying constant traction to the bone using braces?
What is the result of applying constant traction to the bone using braces?
Signup and view all the answers
What happens to the alveolar bone when pressure changes after brace removal?
What happens to the alveolar bone when pressure changes after brace removal?
Signup and view all the answers
Which type of cell is primarily involved in resorption during the bone remodeling process?
Which type of cell is primarily involved in resorption during the bone remodeling process?
Signup and view all the answers
What is formed as a result of osteoclast attachment at the site of resorption?
What is formed as a result of osteoclast attachment at the site of resorption?
Signup and view all the answers
How does the process of bone remodeling generally support health?
How does the process of bone remodeling generally support health?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the first step in the process of bone repair following a fracture?
What is the first step in the process of bone repair following a fracture?
Signup and view all the answers
What replaces the soft procallus during the bone healing process?
What replaces the soft procallus during the bone healing process?
Signup and view all the answers
What is directly responsible for the movement of teeth when braces are applied?
What is directly responsible for the movement of teeth when braces are applied?
Signup and view all the answers
During which stage of the remodeling process do osteoclasts form cavities in the bone?
During which stage of the remodeling process do osteoclasts form cavities in the bone?
Signup and view all the answers
Which component of bone impedes the distribution of nutrients and oxygen to osteocytes?
Which component of bone impedes the distribution of nutrients and oxygen to osteocytes?
Signup and view all the answers
How long does it typically take for bone to heal completely after a fracture?
How long does it typically take for bone to heal completely after a fracture?
Signup and view all the answers
Which statement most accurately describes compact bone?
Which statement most accurately describes compact bone?
Signup and view all the answers
What structure is formed as a result of continuous deposition of bony matrix?
What structure is formed as a result of continuous deposition of bony matrix?
Signup and view all the answers
What process transforms the procallus into a hard callus in bone healing?
What process transforms the procallus into a hard callus in bone healing?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following accurately describes the role of macrophages in bone repair?
Which of the following accurately describes the role of macrophages in bone repair?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the most widely distributed type of cartilage in the body?
What is the most widely distributed type of cartilage in the body?
Signup and view all the answers
Which feature differentiates articular cartilage from most other hyaline cartilage?
Which feature differentiates articular cartilage from most other hyaline cartilage?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the first step that occurs in the process of chondrogenesis?
What is the first step that occurs in the process of chondrogenesis?
Signup and view all the answers
What type of cartilage is characterized by its ability to resist compression due to its high water content?
What type of cartilage is characterized by its ability to resist compression due to its high water content?
Signup and view all the answers
In articular cartilage, what is the primary component that contributes to its semi-rigid consistency?
In articular cartilage, what is the primary component that contributes to its semi-rigid consistency?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following best describes the structure of articular cartilage?
Which of the following best describes the structure of articular cartilage?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following conditions results in nasal cartilage perforation and collapse?
Which of the following conditions results in nasal cartilage perforation and collapse?
Signup and view all the answers
What type of growth primarily occurs in cartilage during development?
What type of growth primarily occurs in cartilage during development?
Signup and view all the answers
What type of growth is primarily characterized by the differentiation of new chondroblasts from progenitor cells?
What type of growth is primarily characterized by the differentiation of new chondroblasts from progenitor cells?
Signup and view all the answers
What makes up approximately 50% of the dry weight of bone matrix?
What makes up approximately 50% of the dry weight of bone matrix?
Signup and view all the answers
Which component serves an important role in binding collagen and calcium in the bone matrix?
Which component serves an important role in binding collagen and calcium in the bone matrix?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following is primarily seen in articular cartilage and involved in the growth of the epiphyseal plates?
Which of the following is primarily seen in articular cartilage and involved in the growth of the epiphyseal plates?
Signup and view all the answers
Chondroblasts become trapped within lacunae and differentiate into which type of cell?
Chondroblasts become trapped within lacunae and differentiate into which type of cell?
Signup and view all the answers
Which organic components are important for the structure of the bone matrix?
Which organic components are important for the structure of the bone matrix?
Signup and view all the answers
Which ions are commonly found in the inorganic portion of the bone matrix?
Which ions are commonly found in the inorganic portion of the bone matrix?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the principal role of osteoclasts in the bone tissue?
What is the principal role of osteoclasts in the bone tissue?
Signup and view all the answers
Study Notes
Cartilage
- A type of connective tissue
- Composed of cells and an extracellular matrix (ECM)
- Three main types of cartilage: hyaline, elastic, and fibrocartilage
- Hyaline cartilage is the most common type and provides non-rigid support
- Elastic cartilage provides support with high flexibility
- Fibrocartilage provides strength under stress
- Cartilage is responsible for providing the framework supporting soft tissues
- It guides development and growth of long bones
- Found in the ear, nose, and walls of the respiratory tract
- Chondrocytes are round, mature cells surrounded by ECM, and lie within lacunae
- Chondrocytes may occur singly or in clusters, known as isogenous groups or aggregates
- Cells in an isogenous group are daughter cells from a mitotic event
- As chondrocytes continue secreting ECM, they get pushed away from one another
- The primary role of chondrocytes: to maintain ECM (also secretes)
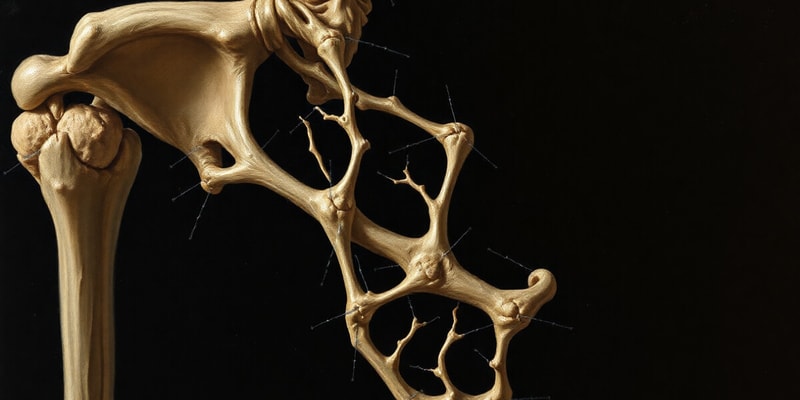
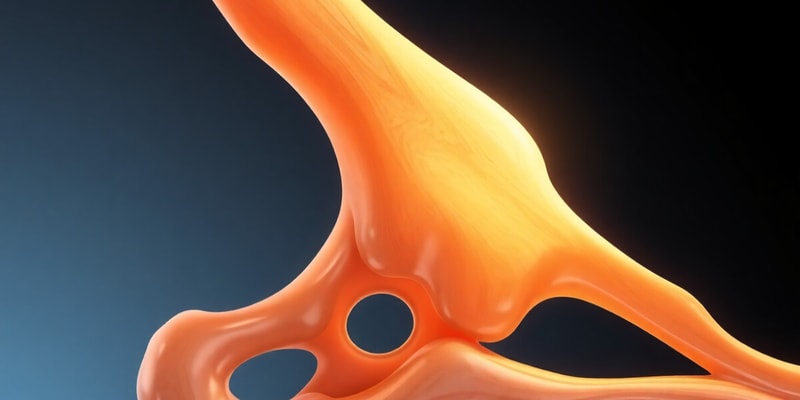
Bone
- A type of connective tissue that provides support, protection, and movement to the body
- Contains organic and inorganic components
- Composed of different types of cells including osteoblasts, osteocytes, and osteoclasts
- Bone surfaces are covered by periosteum and endosteum
- Periosteum: fibrous outer layer of bone
- Endosteum: thin membrane that lines the medullary cavity
- Osteoblasts are responsible for bone formation and are located on the bone surface
- Osteocytes are mature bone cells that are located within the bone matrix
- Osteoclasts are responsible for bone resorption and degradation
- Bone classification: long, short, flat, irregular, and sesamoid
- Bone growth, remodeling, and repair are continuous processes involved in maintaining bone structure
Bone Growth, Remodeling, and Repair
- There are two main types of ossification: intramembranous and endochondral ossification
- Intramembranous ossification involves the direct differentiation of mesenchymal cells into osteoblasts
- Examples of bones formed by intramembranous ossification: flat bones of the skull, Fontanelles, mandible and maxilla, and clavicle
- Endochondral ossification involves the use of pre-existing hyaline cartilage as a template for bone formation
- Examples of bones formed by endochondral ossification: bones of the limbs
- The epiphyseal plate is responsible for longitudinal bone growth
- Osteoporosis: a common condition in the elderly resulting in poor bone turnover where bone resorption exceeds formation
- Bone repair involves the formation of a fracture hematoma, procallus, hard callus, and woven bone, followed by the formation of compact bone.
- Bone healing takes approximately 6-8 weeks to complete
Clinical Applications
- Osteoporosis: A condition characterized by decreased bone density and increased bone fragility. It often occurs in the elderly and can lead to fractures.
- Cartilaginous Repair: Cartilage has a limited ability to heal due to its avascular nature. Injuries to cartilage can lead to osteoarthritis.
- Growth Plate Injury: Injuries to the epiphyseal plate can affect bone growth, especially in children and adolescents.
Cartilage
- Tough, durable form of supporting connective tissue
- Characterized by cells embedded in an extracellular matrix (ECM) with high concentrations of Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) and proteoglycans
- Interacts with collagen and elastic fibers
- Avascular, meaning it does not have blood vessels
- Interterritorial Matrix: Lighter staining due to lower proteoglycan content
- Territorial Matrix: Stains more intensely with hematoxylin due to higher proteoglycan content
- Perichondrium: Outer layer of dense connective tissue that surrounds most cartilage, important for growth and repair
Cells
- Chondroblasts: Immature cartilage forming cells, found in the inner chondrogenic layer, responsible for secreting ECM
- Chondrocytes: Mature cartilage cells, reside in lacunae within the ECM, maintain the cartilage matrix
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Found within the inner chondrogenic layer, can differentiate into chondroblasts and contribute to cartilage formation
Chondrogenesis
- Process of cartilage formation from mesenchyme
- Chondrogenesis involves:
- Rounding Up of Mesenchymal Cells: Mesenchymal cells aggregate and condense
- Mitosis and Differentiation: Mesenchymal cells divide and differentiate into chondroblasts
- Matrix Secretion: Chondroblasts secrete matrix components
- Lacunae Formation: Chondroblasts become trapped within lacunae
Cartilage Growth
- Interstitial Growth: Occurs within the cartilage itself, chondrocytes divide and secrete new matrix, seen in articular cartilage and epiphyseal plates
- Appositional Growth: Occurs at the surface of the cartilage, new chondroblasts differentiate from perichondrium, contributes to growth in thickness
Types of Cartilage
-
Hyaline Cartilage:
- Most common type
- Found in articular surfaces, nose, trachea, larynx, ribcage
- Matrix is rich in type II collagen fibers, clear and glassy appearance
-
Elastic Cartilage:
- Found in the ear, epiglottis
- Matrix contains elastic fibers, gives it flexibility
-
Fibrocartilage:
- Found in intervertebral discs, pubic symphysis
- Matrix is dense and contains thick collagen fibers, provides strength and support
Clinical Correlations
-
Arthritis: Degenerative disease characterized by joint pain, stiffness, and swelling
- Osteoarthritis: Wear and tear arthritis, damage to articular cartilage
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: Autoimmune disease, inflammation and destruction of joint tissues
Bone
- Specialized connective tissue characterized by its rigidity and hardness
-
Matrix:
- Organic Portion: Type I collagen, proteoglycans, glycoproteins
- Inorganic Portion: Calcium hydroxyapatite, calcium phosphate, other ions
-
Cells:
- Osteoblasts: Responsible for bone formation
- Osteocytes: Mature bone cells, maintain bone matrix
- Osteoclasts: Responsible for bone resorption
Bone Histology
- Osteons: Basic structural unit of compact bone, composed of concentric lamellae surrounding a central canal
- Lamellae: Thin layers of bone tissue, contain collagen fibers arranged in a specific pattern
- Canaliculi: Narrow channels that connect lacunae, allowing for nutrient and waste exchange
- Lacunae: Spaces within the bone matrix where osteocytes reside
- Periosteum: Outer fibrous layer surrounding bone, important for growth and repair
- Endosteum: Inner lining of the marrow cavity, contains osteogenic cells
Histologic Preparations
- Ground Bone: Unpreserved bone, ground thin for light microscopy, shows lamellar structure, lacunae, and canaliculi
- Decalcified Bone: Bone treated to remove inorganic portion, allows for visualization of cells, collagen fibers, and organic matrix
Bone: Definition and Components
- Bone is a connective tissue with rigidity and hardness.
- Composed of matrix (inorganic and organic) and cells (osteoblasts, osteocytes, and osteoclasts).
- The organic portion of bone is rich in Type I collagen fibers, staining pink with eosin, and has minimal ground substance.
- The inorganic portion contains calcium hydroxyapatite (most abundant), calcium phosphate (significant amount), and other ions like HCO3-, Citrate, Mg 2+, K+, Na+.
Cartilage: Definition and Components
- A connective tissue with cells and an extracellular matrix (ECM).
- ECM is composed of specialized cells called chondrocytes located in cavities called lacunae.
- Chondroblasts are trapped within lacunae and differentiate into chondrocytes.
- Chondrocytes continuously multiply and secrete matrix, leading to new cartilage formation.
Cartilage Growth
- Interstitial growth: Occurs within pre-existing cartilage.
- Appositional growth: Occurs on the surface of pre-existing cartilage.
Bone Functions
- Provides structural support to the body.
- Protection of vital organs.
- Storage of calcium and phosphate minerals.
- Production of blood cells in the bone marrow.
- Facilitates movement through joints.
Bone Growth, Remodeling, and Repair
- Bone Growth: The growth plate (epiphyseal plate) is responsible for longitudinal bone growth.
- Bone Remodeling: Occurs throughout life, balancing bone formation (by osteoblasts) and bone resorption (by osteoclasts). This process is influenced by mechanical stress, ensuring the skeleton adapts to changing demands.
- Bone Repair: The process of healing broken bones, involving stages like hematoma formation, procallus formation, callus formation, and bone remodeling.
Clinical Applications
- Osteoporosis: A disease characterized by reduced bone density, leading to increased fracture risk.
Epiphyseal Plate
- Plays a vital role in longitudinal bone growth.
- Consists of hyaline cartilage with distinct zones: resting, proliferating, hypertrophic, and calcified cartilage zone.
- Cartilage is progressively replaced by bone, leading to bone elongation.
- The growth plate is responsible for the length of long bones, ceasing growth at maturity.
Review Questions
- What are the major components of bone and cartilage?
- What are the different types of cartilage and where are they found?
- How do bones grow and remodel?
- What are the stages of bone repair?
- What is osteoporosis and how does it affect the body?
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Related Documents
Description
Explore the essential characteristics of cartilage and bone, two vital types of connective tissue. This quiz covers various cartilage types, including hyaline, elastic, and fibrocartilage, and their functions in the body. Test your knowledge on the structure, role, and significance of these tissues in providing support and protection.