53 Questions
What is the relationship between the body and spirit according to Descartes?
The body works like a machine with material properties, while the spirit is nonmaterial and does not follow the laws of nature
What is the pineal gland believed to be according to Descartes?
The seat of the soul
In Descartes' dualism, what is the interaction between theology and physics?
The belief that psychological and biological processes are separate phenomena
Which lobe of the cerebral cortex is primarily associated with processing visual information?
Occipital lobe
In stages of neural development, what does 'proliferation' refer to?
Rapid production of new cells
What is the term for the process of selective cell death and synapse elimination?
Apoptosis
Which term describes the period of overproduction followed by synapse pruning/elimination?
Synaptogenesis
In genetic terms, what does 'genotype' refer to?
What is in your DNA
What is the term for the ability of the brain to change?
Neuroplasticity
What is the process that covers neurons with myelin for faster transmission?
Myelination
What does puberty encompass?
Physical and psychological changes
What is the impact of the hormone cascade during puberty?
Hormone cascade leads to brain changes
Why does the age of onset of puberty vary?
Nutrition, stress, and weight gain can affect the age of onset of puberty
What continues to develop until late adolescence/early adulthood?
Emotional centers of the brain
What psychological traits are associated with late maturing boys?
More anxious, eager, attention seeking
What is the cephalocaudal pattern of motor development?
Development from head control to walking
In the context of motor development, what is the nature of the unfolding of a genetically programmed sequence of events?
Nature
Why does the stepping reflex 'disappear' a few weeks after birth, only to return a few months later?
As they get older, infants carry more weight on their legs
What did the experiment examining infants' stepping reflex reveal?
Heavier infants stepped less than lighter infants
In the context of motor development, what did the discussion about the rate of stepping being limited by muscle strength suggest?
Physical growth can significantly affect the phenotypes of infants
How might a parent's phenotype impact a child's phenotype?
By influencing the child's behavior and experiences, which in turn can affect gene expression in the child
What is the primary reason for examining changes in a boy's height at yearly intervals from birth to 18 years?
To observe continuous and gradual growth patterns
In the context of brain development, what is the significance of less synaptic pruning in a 10-year-old compared to a 17-year-old?
The 10-year-old will have denser neurons in the frontal lobe
What might be the consequence of significant synaptic pruning in an adolescent's brain?
Enhanced neural plasticity and adaptability
In what way can activity vs passivity influence language development?
Both activity and passivity lead to similar developmental outcomes in language acquisition
How can Jessica quickly deduce which brain belongs to the 10-year-old and which brain belongs to the 17-year-old?
By examining the density of neurons in the temporal lobe
Why might cohort comparison be more suitable than cross-sectional comparison for studying certain developmental aspects?
Cohort comparison provides insights into age-related changes over time, while cross-sectional comparison does not
What is the difference between continuous and discontinuous development?
Continuous development occurs smoothly and gradually, while discontinuous development occurs in distinct stages.
Which lobe of the cerebral cortex is primarily associated with language comprehension?
Temporal lobe
During which step of neurogenesis/synaptic pruning do neurons migrate to destinations based on chemical programming to find 'friends'?
Migrate and aggregate
What type of information is primarily processed in the occipital lobe of the cerebral cortex?
Visual information
In which part of the brain does synaptic density decrease as time goes on until adolescence?
Prefrontal cortex
What occurs during synaptogenesis in the context of neural development?
Neurons undergo branching out for faster transmission
In the context of motor development, what is the nature of the unfolding of a genetically programmed sequence of events?
Motor development occurs in distinct stages or steps.
What happens to synaptic density in the visual cortex as time goes on?
Synaptic density decreases over time.
What is the last step of neurogenesis and synaptic pruning?
Myelination
According to dynamic systems theory, what does 'internal orchestrator' refer to in the context of development?
Central controlling agent
What does dynamic systems theory propose as the driving force behind development?
Self-organizing components
In dynamic systems theory, what does the interconnected and interdependent nature of development suggest?
Influential interactions among components
How does dynamic systems theory explain individuals' development across contexts and timescales?
Increased variability
What type of interventions does dynamic systems theory suggest considering for development?
Dynamic and context-dependent interventions
According to dynamic systems theory, what example illustrates variability across context and timescales?
'Exposure to diverse linguistic environments' impact on language development
What are the two characteristics associated with John Locke's views on development?
Nature and nurture
What is the main concern of dynamic systems theory regarding development?
The interconnectedness and interdependence of developmental components
Which concept refers to the period when neurons migrate to their destinations based on chemical programming and form connections with other neurons?
Neural migration
What does the experiment involving exposing pregnant monkeys to unpredictable noises demonstrate?
Impact of teratogens during critical periods
In the context of development, which term describes the ability of the brain to change?
Neuroplasticity
What is the primary focus of the prenatal period in terms of sensory development?
Development of senses
Which process is characterized by overproduction of synapses followed by selective elimination or pruning?
Synaptogenesis
Which theory emphasizes self-efficacy and self-actualization as a process of finding meaning?
Humanistic
Which theory is associated with the idea that an individual human's developmental trajectory exemplifies the evolutionary history of the species?
Evolutionary
Which theory focuses on how humans acquire, store, and manipulate information about the world around them?
Cognitive
Which theory is characterized by the belief that an individual's developmental trajectory reflects the evolutionary history of the species?
Evolutionary
Study Notes
Relationship between Body and Spirit
- Descartes proposed dualism, viewing the body and spirit as distinct entities.
- The pineal gland, according to Descartes, is the point of interaction between the mind (spirit) and body.
Interaction of Theology and Physics in Dualism
- Descartes believed that theology and physics could coexist, with each adhering to its own principles.
- He emphasized the role of rational thought in understanding the universe, aligning physics with philosophical inquiry.
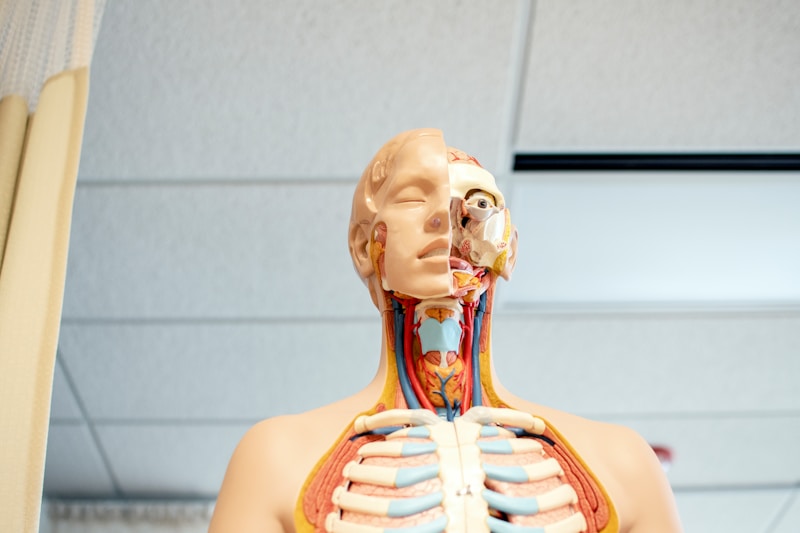
Cerebral Cortex and Visual Processing
- The occipital lobe is primarily associated with processing visual information.
- The temporal lobe is associated with language comprehension.
Neural Development Stages
- 'Proliferation' refers to the rapid generation of new neurons during neural development.
- Selective cell death and synapse elimination are termed 'apoptosis'.
Synaptic Overproduction and Pruning
- The period of overproduction followed by synapse pruning is known as 'synaptic pruning'.
- This process is crucial for refining neural connectivity and optimizing brain function.
Genetic Terms
- 'Genotype' refers to the genetic makeup of an individual, influencing various traits.
Brain Plasticity and Myelination
- Brain plasticity describes the brain's ability to change in response to experiences.
- Myelination is the process that coats neurons with myelin to facilitate faster transmission of signals.
Puberty and Hormonal Changes
- Puberty encompasses the physical and biological changes leading to sexual maturity.
- Hormone cascades during puberty trigger various developmental changes in the body.
Variability in Puberty Onset
- The age of onset of puberty varies due to genetic, environmental, and nutritional factors.
- Development continues until late adolescence and early adulthood.
Psychological Traits and Motor Development
- Late-maturing boys may exhibit traits such as increased sensitivity and social challenges.
- Cephalocaudal pattern refers to the development sequence from head to toe in motor skills.
Reflexes and Muscle Strength
- The stepping reflex disappears shortly after birth due to muscle strength limitations and returns as infants gain strength.
- Stepping reflex experiments outlined the role of physical readiness in motor skill emergence.
Phenotype Influences
- A parent's phenotype can affect a child's traits through genetic inheritance, impacting growth and development.
Height Changes in Boys
- Monitoring height changes yearly from birth to 18 years tracks growth patterns and potential health issues.
- Less synaptic pruning in younger children compared to older adolescents may indicate different developmental stages.
Consequences of Synaptic Pruning
- Significant synaptic pruning in adolescents can affect cognitive and emotional functions, potentially leading to mental health issues.
Language Development Influences
- Activity vs. passivity in childhood experiences significantly influences language development outcomes.
Age Comparison and Developmental Research
- Jessica can differentiate between the brains of a 10-year-old and 17-year-old by observing developmental markers.
- Cohort comparison is more suitable than cross-sectional comparison for understanding developmental trajectories.
Continuous vs. Discontinuous Development
- Continuous development suggests gradual changes, while discontinuous development proposes distinct stages.
Neurogenesis and Chemical Programming
- During neurogenesis, neurons migrate to their destinations based on chemical cues, forming connections with other neurons.
- Information processed primarily in the occipital lobe focuses on visual stimuli.
Synaptic Density Changes
- Synaptic density in the visual cortex decreases over time towards adolescence, indicating refinement of visual processing.
Dynamic Systems Theory
- The 'internal orchestrator' in dynamic systems theory refers to the innate regulatory processes driving development.
- Dynamic systems theory posits that a combination of interactions leads to developmental change.
Variability and Contextual Development
- Variability across contexts and timescales is illustrated within dynamic systems theory, emphasizing the need for adaptable interventions.
- John Locke emphasized the importance of environment and experience in shaping development.
Chemical Migration and Neuron Connection Development
- Neurons migrate based on chemical signals to establish connections with their "friends".
Prenatal Sensory Development and Change
- The prenatal period's primary focus is on sensory development and the establishment of foundational neural connections.
- Overproduction of synapses followed by selective pruning is termed synaptogenesis.
Theories of Development
- Theories such as self-efficacy focus on individual meaning-making processes within development.
- Evolutionary developmental psychology examines how human development reflects species evolution.
- The information processing theory focuses on how humans process, store, and manipulate knowledge.
Explore the concept of body and spirit connection in biological processes, as proposed by Descartes. Understand the idea of dualism and how it intertwines theology and physics. Delve into the role of the pineal gland and cerebral cortex in relation to the mind and body.
Make Your Own Quizzes and Flashcards
Convert your notes into interactive study material.