यदि tan θ = 2ab/(a² - b²), तो cos θ का मान क्या होगा?
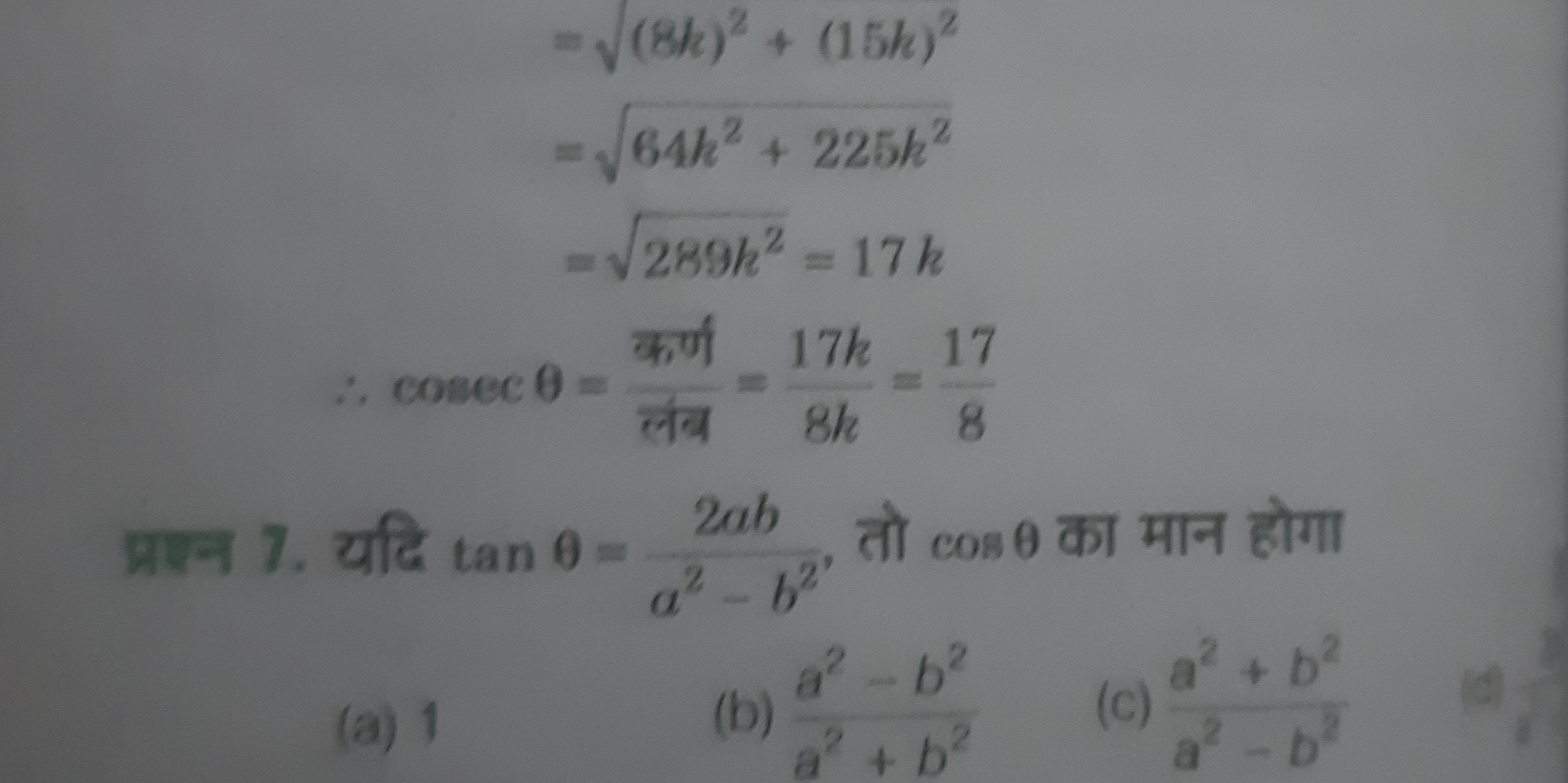
Understand the Problem
प्रश्न tan θ के बारे में जानकारी मांग रहा है और cos θ के मान की पहचान करने का अनुरोध कर रहा है। यह त्रिकोणमिति के सिद्धांतों पर आधारित है, जहां tan θ को a और b के संदर्भ में बताया गया है।
Answer
$$ \cos \theta = \frac{(a^2 - b^2)}{\sqrt{(a^2 - b^2)^2 + 4a^2b^2}} $$
Answer for screen readers
$$ \cos \theta = \frac{(a^2 - b^2)}{\sqrt{(a^2 - b^2)^2 + 4a^2b^2}} $$
Steps to Solve
- Understanding the Given Information
We are given that ( \tan \theta = \frac{2ab}{a^2 - b^2} ). To find ( \cos \theta ), we need to use the relationship among the trigonometric functions.
- Using the Identity for ( \tan \theta )
From the identity ( \cos^2 \theta + \sin^2 \theta = 1 ) and knowing that ( \tan \theta = \frac{\sin \theta}{\cos \theta} ), we can express ( \sin \theta ) in terms of ( \tan \theta ) and ( \cos \theta ):
$$ \sin \theta = \tan \theta \cdot \cos \theta $$
- Finding ( \sin \theta )
Substituting the value of ( \tan \theta ),
$$ \sin \theta = \frac{2ab}{a^2 - b^2} \cdot \cos \theta $$
- Substituting into the Pythagorean Identity
Plugging ( \sin \theta ) into the identity:
$$ \cos^2 \theta + \left(\frac{2ab \cdot \cos \theta}{a^2 - b^2}\right)^2 = 1 $$
- Simplifying the Equation
Expanding the equation:
$$ \cos^2 \theta + \frac{4a^2b^2 \cos^2 \theta}{(a^2 - b^2)^2} = 1 $$
Factoring out ( \cos^2 \theta ):
$$ \cos^2 \theta \left( 1 + \frac{4a^2b^2}{(a^2 - b^2)^2} \right) = 1 $$
- Final Expression for ( \cos^2 \theta )
Now solving for ( \cos^2 \theta ):
$$ \cos^2 \theta = \frac{1}{1 + \frac{4a^2b^2}{(a^2 - b^2)^2}} $$
- Finding ( \cos \theta )
Taking the square root to find ( \cos \theta ):
$$ \cos \theta = \frac{(a^2 - b^2)}{\sqrt{(a^2 - b^2)^2 + 4a^2b^2}} $$
$$ \cos \theta = \frac{(a^2 - b^2)}{\sqrt{(a^2 - b^2)^2 + 4a^2b^2}} $$
More Information
This formula shows that ( \cos \theta ) depends on the values of ( a ) and ( b ). It's derived from the relationships among the trigonometric identities.
Tips
- Neglecting the Pythagorean identity: It's important to remember that ( \sin^2 \theta + \cos^2 \theta = 1 ) must always hold true.
- Incorrectly rearranging terms: Be careful while manipulating the equations algebraically to avoid errors.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information