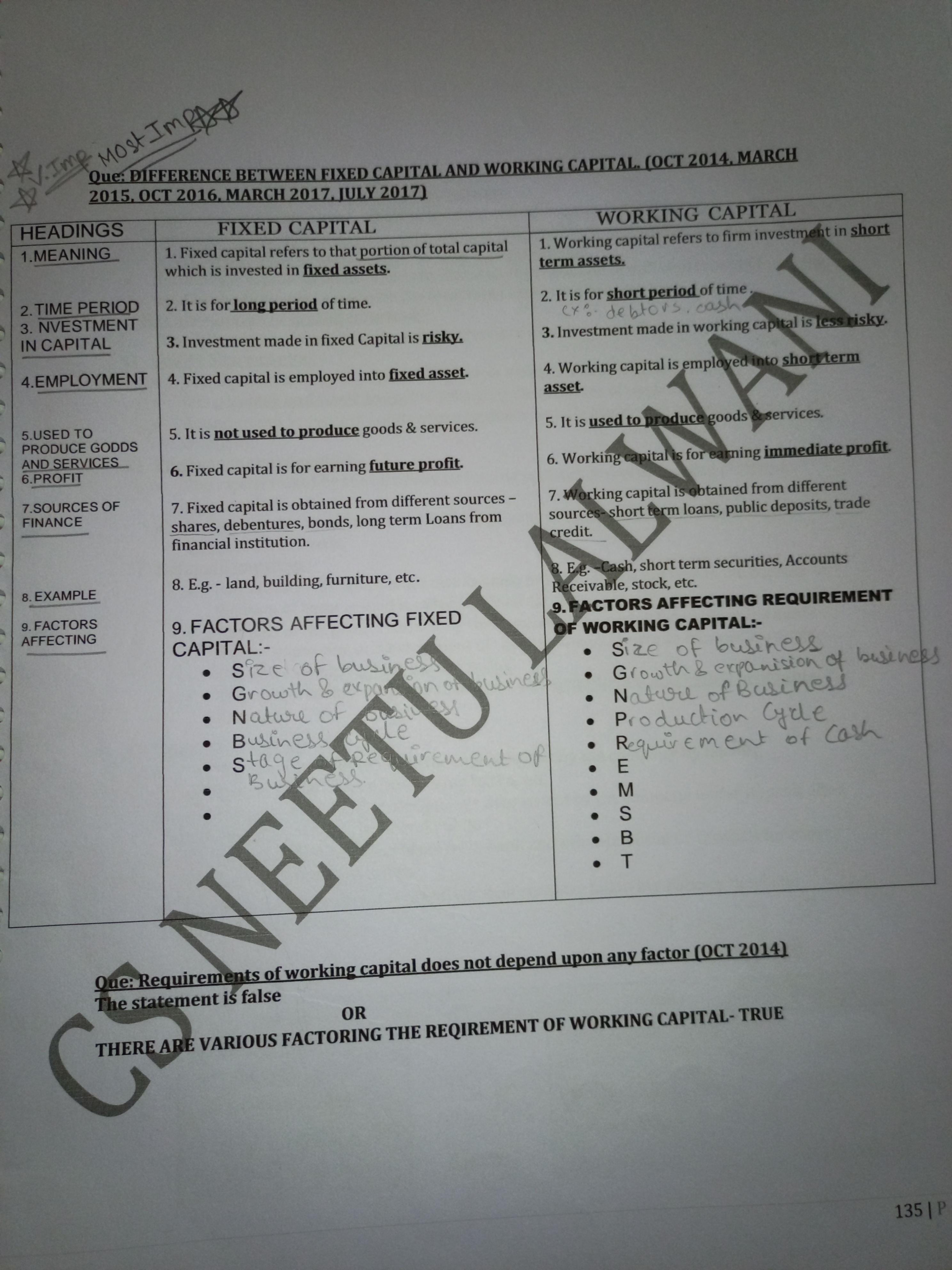
What is the difference between fixed capital and working capital?
Understand the Problem
The question is asking to distinguish between fixed capital and working capital, providing definitions and characteristics while comparing the two. It also addresses the factors affecting these types of capital and outlines a specific statement about working capital requirements that may be true or false.
Answer
Fixed capital is for long-term assets; working capital is for short-term operations.
Fixed capital is used for long-term needs, like buying equipment, while working capital is for short-term operational needs, like paying bills. Fixed capital involves investment in fixed assets and is riskier, whereas working capital supports daily operations and is less risky.
Answer for screen readers
Fixed capital is used for long-term needs, like buying equipment, while working capital is for short-term operational needs, like paying bills. Fixed capital involves investment in fixed assets and is riskier, whereas working capital supports daily operations and is less risky.
More Information
Fixed capital typically involves resources used to acquire long-term assets like buildings and machinery, while working capital covers current operational expenses. The nature of these capitals reflects the strategic planning and operational management needs of a business.
Tips
A common mistake is confusing the time horizons: fixed capital is long-term, while working capital is short-term.
Sources
- Fixed and Working Capital: What's the Difference? - National Funding - nationalfunding.com
- Top 5 Difference between Fixed Capital and Working Capital - BYJU'S - byjus.com
- Fixed vs Working Capital: Key Differences Explained - HDFC Bank - hdfcbank.com
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information