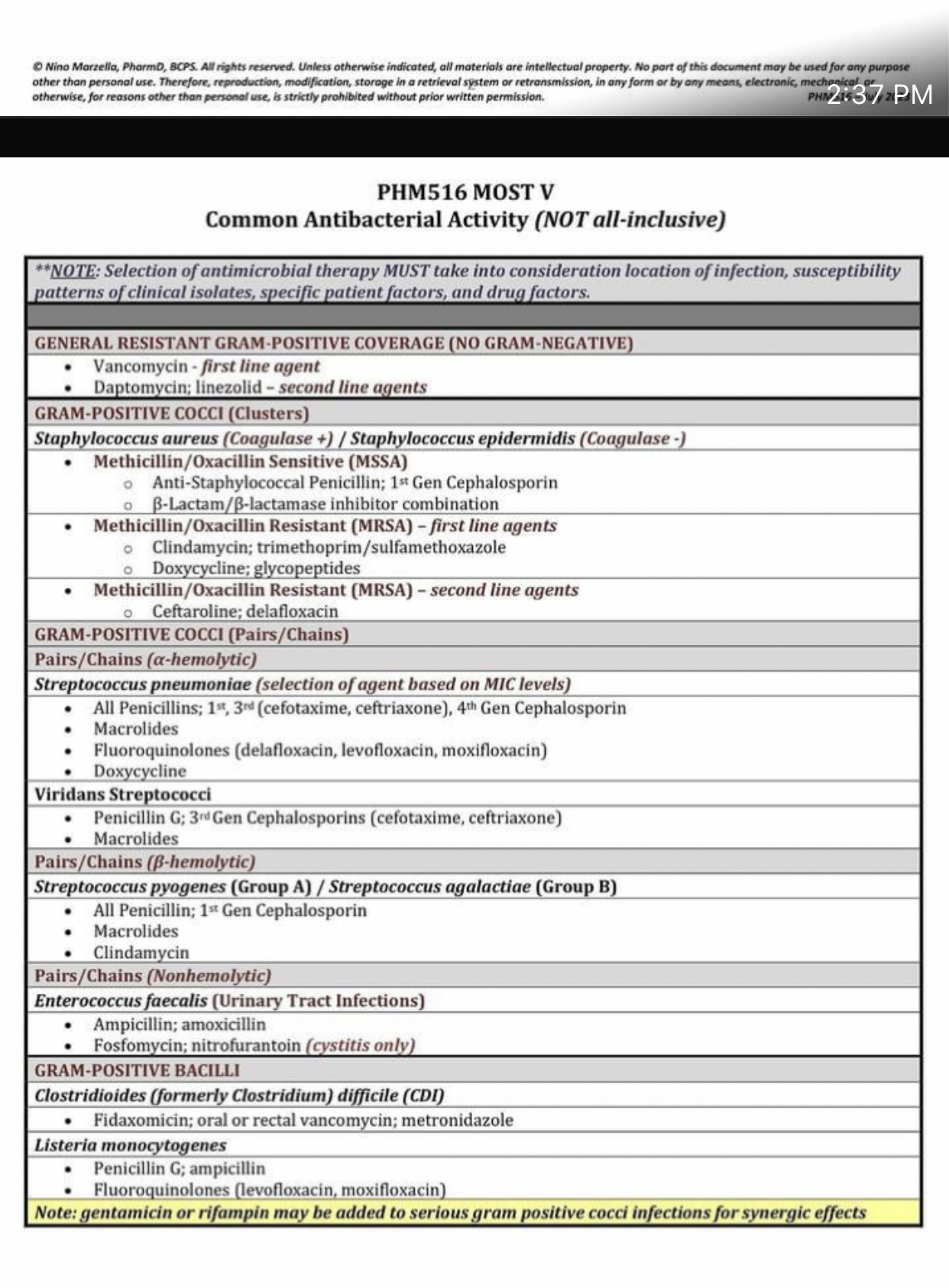
What is the common antibacterial activity for treating gram-positive infections?
Understand the Problem
The document lists various antibacterial agents and their effectiveness against different types of gram-positive bacteria. It emphasizes the importance of selecting the appropriate antimicrobial therapy based on factors like the location of infection and specific patient factors.
Answer
Vancomycin, daptomycin, linezolid, ceftaroline, clindamycin, macrolides
The common antibacterial agents for treating gram-positive infections include vancomycin, daptomycin, linezolid, ceftaroline, clindamycin, and macrolides.
Answer for screen readers
The common antibacterial agents for treating gram-positive infections include vancomycin, daptomycin, linezolid, ceftaroline, clindamycin, and macrolides.
More Information
These antibiotics are effective against various strains of gram-positive bacteria, with vancomycin being a primary treatment option. Specific antibiotics like ceftaroline are particularly effective against resistant strains such as MRSA.
Tips
Ensure to take into consideration the susceptibility patterns of bacterial isolates and specific patient factors when selecting an antibiotic.
Sources
- Resistance of Gram-Positive Bacteria to Current Antibacterial Agents - ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- New-Generation Antibiotics for Treatment of Gram-Positive Infections - ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- Antimicrobial therapies for Gram-positive infections - pharmaceutical-journal.com