What are the key principles of covalent and ionic bonds, combustion reactions, and empirical formulas in chemistry?
Understand the Problem
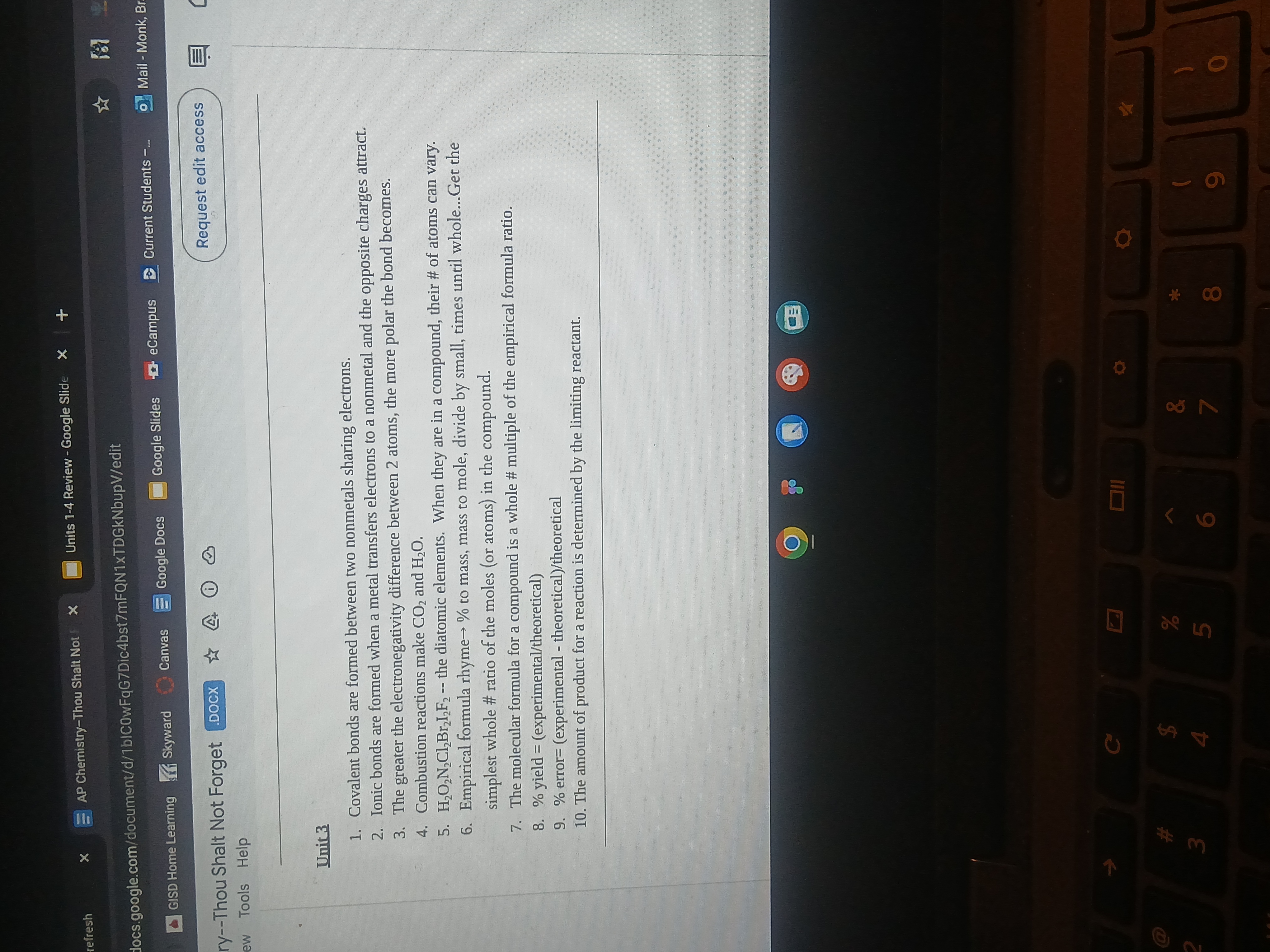
The question refers to principles regarding covalent and ionic bonds, combustion reactions, empirical formulas, and yield/error calculations in chemistry. It outlines fundamental concepts taught in chemistry courses.
Answer
Covalent bonds share electrons; ionic bonds transfer electrons. Combustion yields CO₂ and H₂O. Empirical formulas provide the simplest element ratios.
The final answer is: Covalent bonds involve sharing electrons between nonmetals, while ionic bonds involve transferring electrons from a metal to a nonmetal. Combustion reactions typically produce CO₂ and H₂O. Empirical formulas show the simplest integer ratio of elements in a compound.
Answer for screen readers
The final answer is: Covalent bonds involve sharing electrons between nonmetals, while ionic bonds involve transferring electrons from a metal to a nonmetal. Combustion reactions typically produce CO₂ and H₂O. Empirical formulas show the simplest integer ratio of elements in a compound.
More Information
Empirical formulas represent the simplest whole-number ratios, crucial for understanding compound composition. In combustion, carbon and hydrogen typically react with oxygen to form these end products.
Tips
Avoid confusing ionic and covalent bonds' electron interactions. In empirical formulas, ensure proper conversion of masses to moles before determining the ratios.
Sources
- Ionic and Covalent Bonds - Chemistry LibreTexts - chem.libretexts.org
- 7.2: Contrasting Ionic Compounds and Covalent Compounds - chem.libretexts.org
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information