What are the following parts of a heat engine: a heat reservoir at temperature T1 and a heat sink at temperature T2?
Understand the Problem
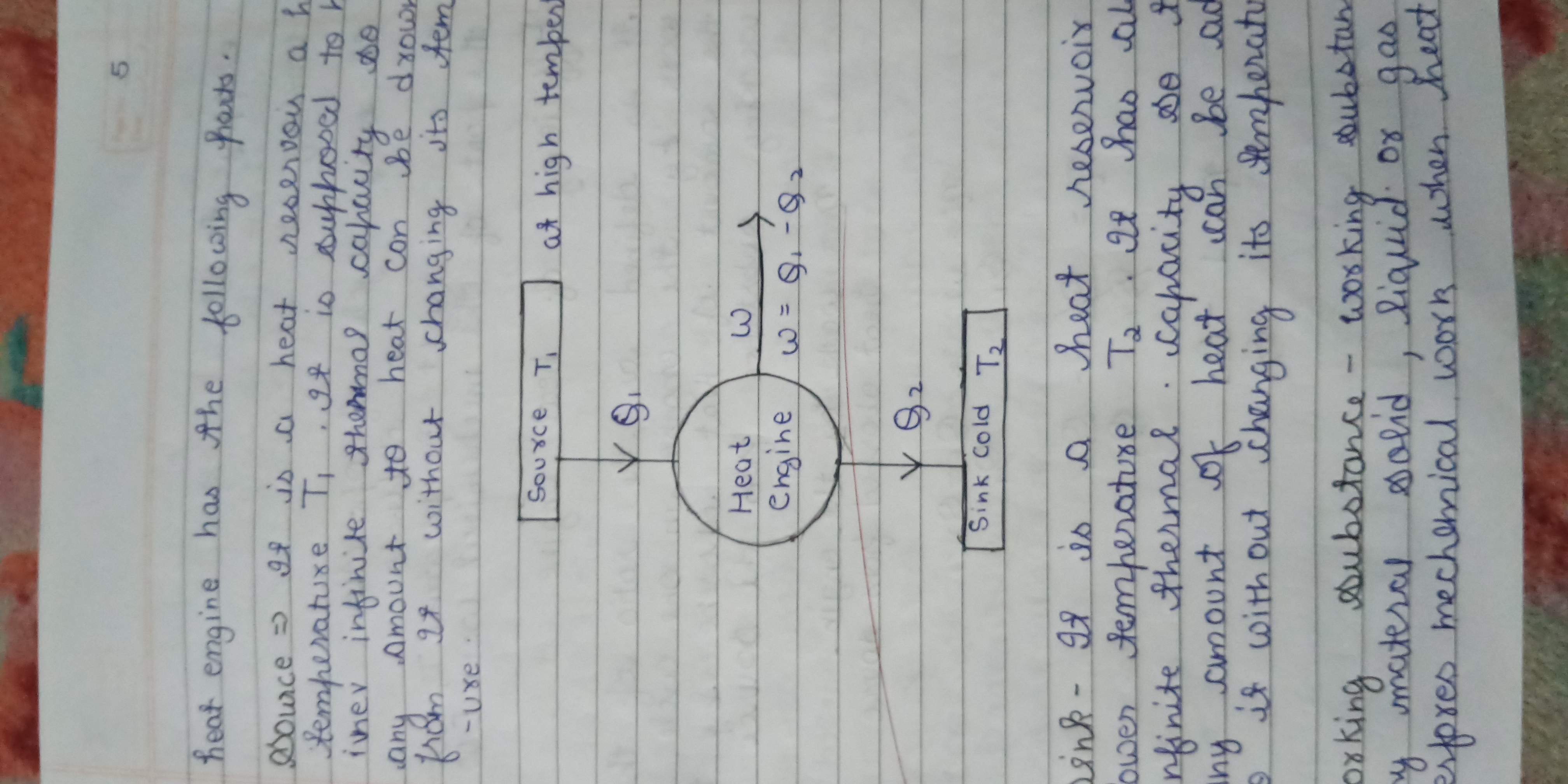
The question discusses the functioning of a heat engine, explaining the role of a heat source and sink along with their temperatures. It seems to touch upon concepts of thermodynamics, specifically the flow of heat and work done by the engine.
Answer
A heat engine has a heat reservoir at T1 and a heat sink at T2.
The heat engine consists of two main parts: a heat source or reservoir at a higher temperature (T1) and a heat sink at a lower temperature (T2). The heat source provides heat energy to the engine, and the heat sink absorbs excess heat, allowing the engine to perform work.
Answer for screen readers
The heat engine consists of two main parts: a heat source or reservoir at a higher temperature (T1) and a heat sink at a lower temperature (T2). The heat source provides heat energy to the engine, and the heat sink absorbs excess heat, allowing the engine to perform work.
More Information
A heat engine converts thermal energy to mechanical work using these reservoirs to maintain a temperature difference.
Tips
Common mistake: Confusing the roles of the heat source and sink. The source provides energy, while the sink absorbs residual heat.
Sources
- Solved Question 2: A Heat engine is a thermodynamic system - Chegg - chegg.com
- Carnot Cycle - Chemistry LibreTexts - chem.libretexts.org
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information