What are the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Understand the Problem
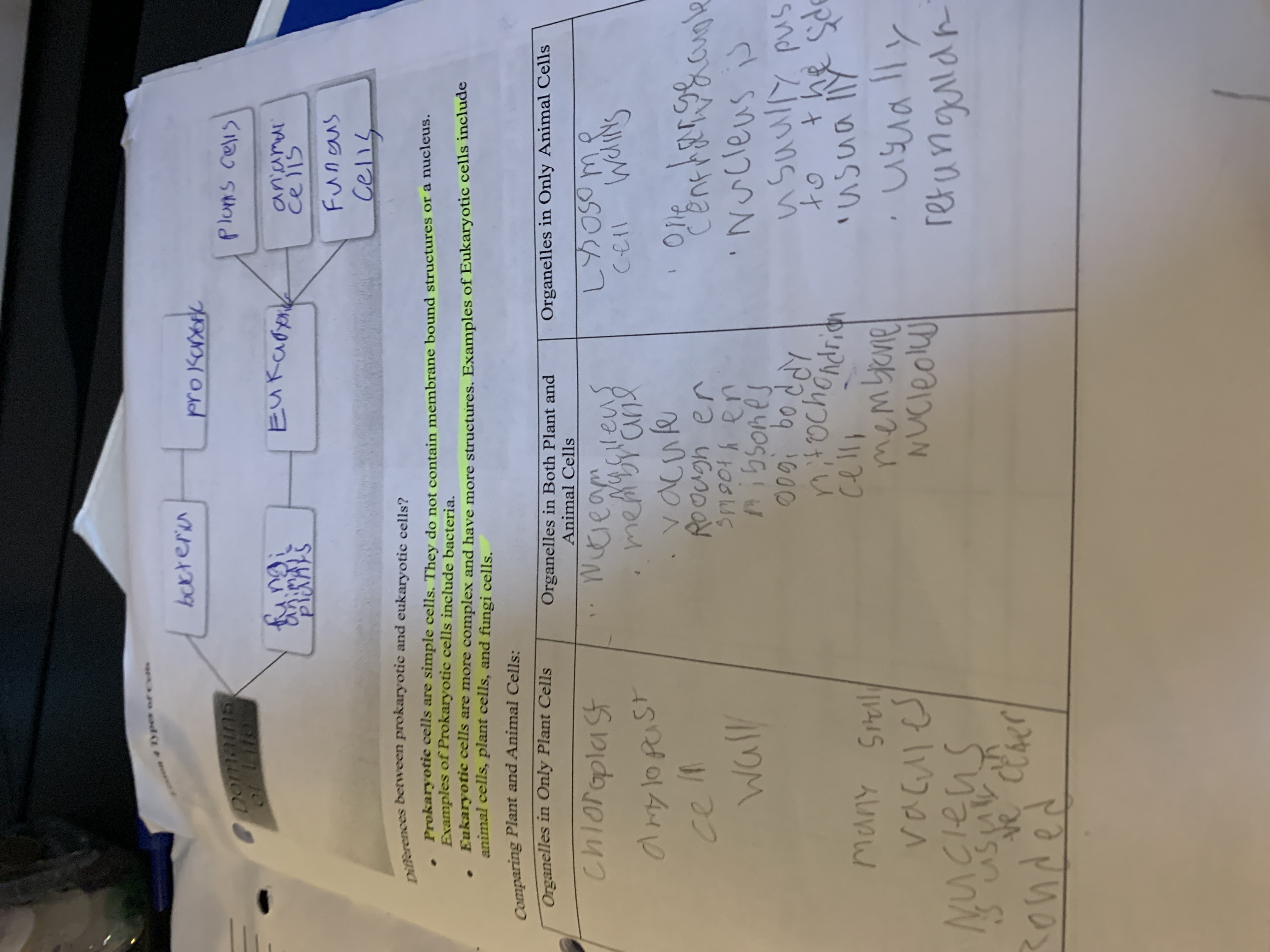
The question is asking to explain the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. It mentions key characteristics and examples of each type of cell.
Answer
Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus; eukaryotic cells have one.
Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, found in bacteria and archaea. Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, such as in animal, plant, and fungi cells.
Answer for screen readers
Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, found in bacteria and archaea. Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, such as in animal, plant, and fungi cells.
More Information
Prokaryotic cells are generally simpler and smaller, while eukaryotic cells are more complex and larger, equipped with specialized organelles for specific functions.
Tips
A common mistake is assuming all single-celled organisms are prokaryotic. In fact, some single-celled eukaryotic organisms exist.
Sources
- Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic Cells - technologynetworks.com
- Difference between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells - BYJU'S - byjus.com
- Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells (article) - Khan Academy - khanacademy.org
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information