What are the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, and what are the structures of animal and plant cells?
Understand the Problem
The question appears to ask for information about the differences and similarities between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, as well as specific details about animal and plant cells. These are high-level biological concepts related to cell structure and classification.
Answer
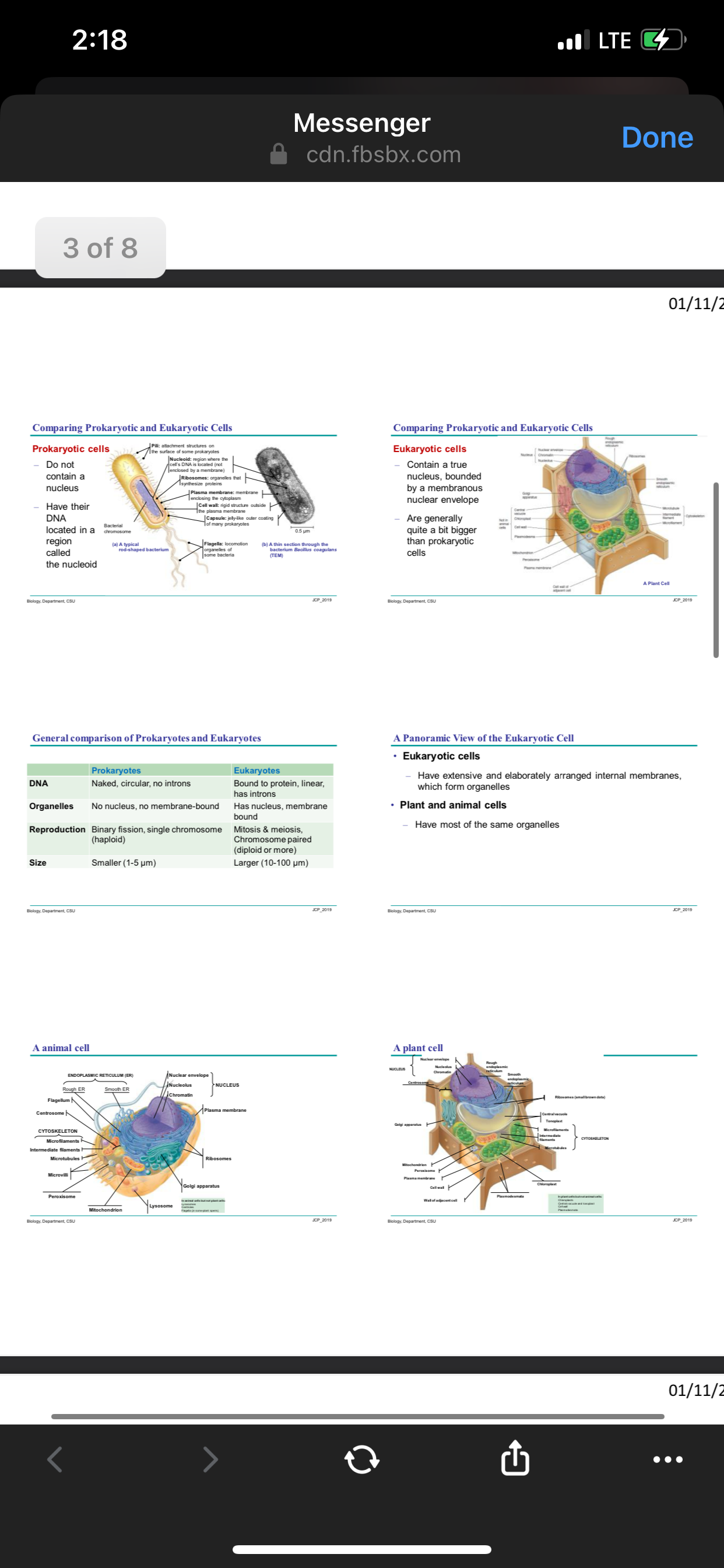
Prokaryotes lack a nucleus; eukaryotes have one. Animal cells have centrioles and lysosomes; plant cells have chloroplasts, a cell wall, and vacuole.
Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, whereas eukaryotic cells have them. Animal cells have structures like centrioles and lysosomes, while plant cells have chloroplasts, a cell wall, and a large central vacuole.
Answer for screen readers
Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, whereas eukaryotic cells have them. Animal cells have structures like centrioles and lysosomes, while plant cells have chloroplasts, a cell wall, and a large central vacuole.
More Information
Eukaryotic cells are typically larger and more complex than prokaryotic cells. Animal cells can change shape, while plant cells are mostly rigid due to the cell wall.
Tips
Confusing the presence of organelles in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells is common. Remember that eukaryotic cells have both a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.
Sources
- 5.2: Comparing Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells - Biology LibreTexts - bio.libretexts.org
- Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes: What Are the Key Differences? - technologynetworks.com
- Differences Between Plant and Animal Cells - ThoughtCo - thoughtco.com
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information