What are single-gene defects and how are they inherited?
Understand the Problem
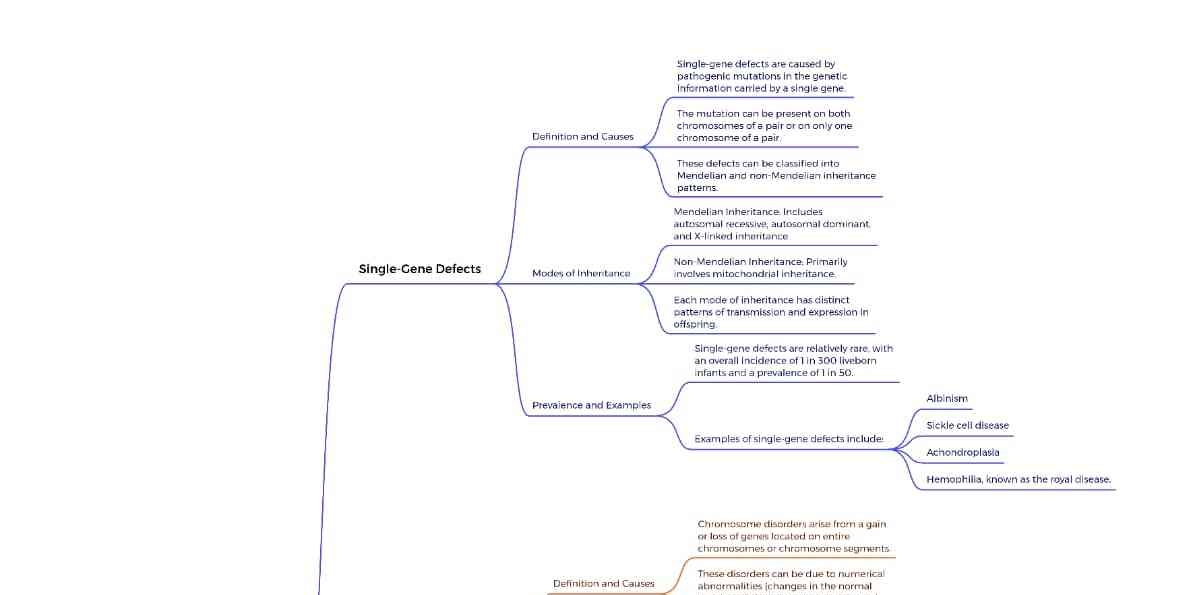
The image outlines the concept of single-gene defects, detailing definitions, modes of inheritance, prevalence, and examples of such genetic conditions.
Answer
Single-gene defects arise from mutations in a single gene with predictable inheritance patterns.
Single-gene defects are caused by mutations in a single gene. These defects are inherited through Mendelian patterns, such as autosomal or X-linked, and can manifest when the mutation is present on one or both chromosomes of a pair.
Answer for screen readers
Single-gene defects are caused by mutations in a single gene. These defects are inherited through Mendelian patterns, such as autosomal or X-linked, and can manifest when the mutation is present on one or both chromosomes of a pair.
More Information
Single-gene disorders often follow Mendelian inheritance patterns and can include conditions like cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anemia, and hemophilia.
Tips
A common mistake is assuming single-gene disorders are always severe; their effects vary widely and can be mild.
Sources
- Single-Gene Disorders - Understanding Genetics - NCBI Bookshelf - ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- Inheritance of Single-Gene Disorders - Fundamentals - Merck Manuals - merckmanuals.com
- What are Single Gene Disorders? - News-Medical - news-medical.net
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information