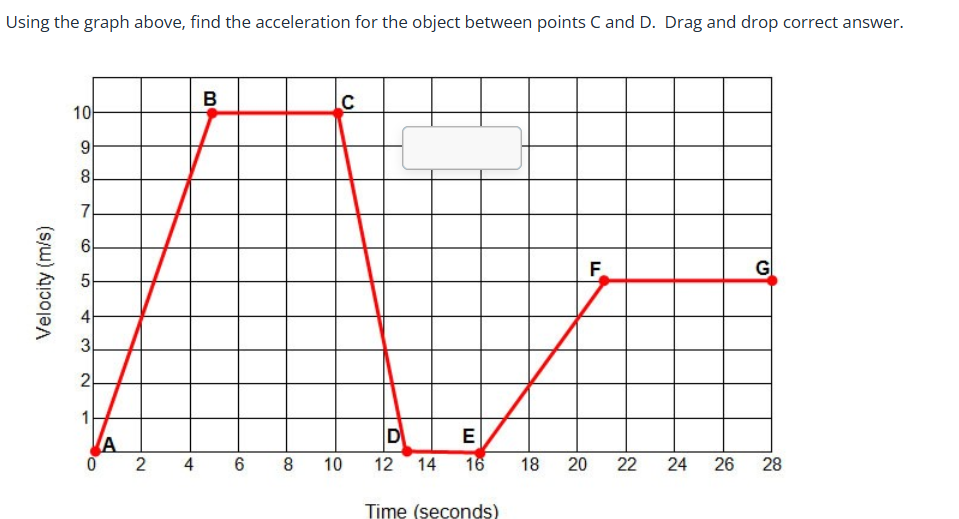
Using the graph above, find the acceleration for the object between points C and D.
Understand the Problem
The question is asking to calculate the acceleration of an object based on the velocity graph between points C and D. To find acceleration, we need to determine the change in velocity over time for that segment of the graph.
Answer
The acceleration is $-5 \, \text{m/s}^2$.
Answer for screen readers
The acceleration for the object between points C and D is $-5 , \text{m/s}^2$.
Steps to Solve
-
Identify the Velocity at Points C and D At point C (time = 14 seconds), the velocity is 10 m/s. At point D (time = 16 seconds), the velocity drops to 0 m/s.
-
Determine the Change in Velocity The change in velocity ($\Delta v$) from point C to point D can be calculated as: $$ \Delta v = v_D - v_C = 0 , \text{m/s} - 10 , \text{m/s} = -10 , \text{m/s} $$
-
Calculate the Change in Time The change in time ($\Delta t$) from point C to point D is: $$ \Delta t = t_D - t_C = 16 , \text{s} - 14 , \text{s} = 2 , \text{s} $$
-
Find the Acceleration Now, calculate the acceleration ($a$) using the formula: $$ a = \frac{\Delta v}{\Delta t} = \frac{-10 , \text{m/s}}{2 , \text{s}} = -5 , \text{m/s}^2 $$
The acceleration for the object between points C and D is $-5 , \text{m/s}^2$.
More Information
The negative acceleration indicates that the object is decelerating, meaning it's slowing down between points C and D. In this case, the object goes from a velocity of 10 m/s to a complete stop.
Tips
- Forgetting to take the final velocity minus the initial velocity, which could lead to a sign error in acceleration.
- Misreading the graph to determine the velocities at C and D.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information