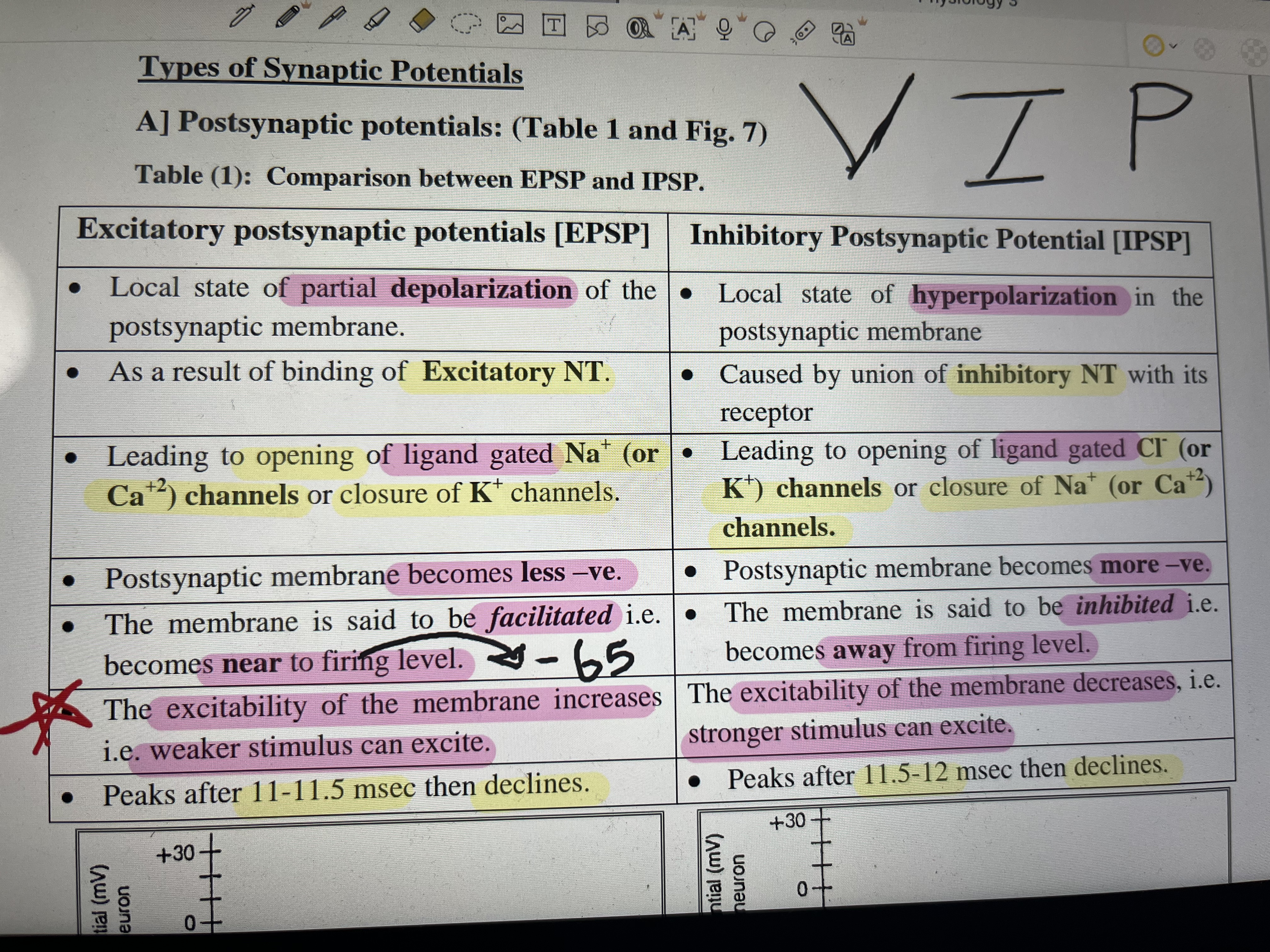
Types of synaptic potentials: Compare excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSP) and inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSP) in terms of their characteristics and effects.
Understand the Problem
The question addresses types of postsynaptic potentials, specifically focusing on their excitatory and inhibitory characteristics, mechanisms, and effects on the neuron's firing levels.
Answer
EPSPs cause depolarization and increase excitability; IPSPs cause hyperpolarization and decrease excitability.
EPSPs involve depolarization due to excitatory neurotransmitters causing Na+ or Ca2+ channel opening, and make the membrane less negative and more excitable. IPSPs involve hyperpolarization due to inhibitory neurotransmitters causing Cl- or K+ channel opening, making the membrane more negative and less excitable.
Answer for screen readers
EPSPs involve depolarization due to excitatory neurotransmitters causing Na+ or Ca2+ channel opening, and make the membrane less negative and more excitable. IPSPs involve hyperpolarization due to inhibitory neurotransmitters causing Cl- or K+ channel opening, making the membrane more negative and less excitable.
More Information
EPSPs make the membrane potential less negative (depolarization) and increase the likelihood of an action potential. IPSPs make the membrane potential more negative (hyperpolarization) and decrease the likelihood of an action potential.
Tips
Common mistakes include confusing the effects of neurotransmitters and ion channels involved in EPSPs and IPSPs.
Sources
- Excitatory and Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potentials - Neuroscience - ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potential - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics - sciencedirect.com
- Excitatory postsynaptic potential - Wikipedia - en.wikipedia.org
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information