The value of \( \int_{-1}^{1} (x |x| + x^4) dx \) is
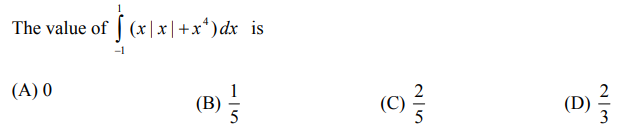
Understand the Problem
The question is asking for the evaluation of a definite integral involving the function (x |x| + x^4) over the interval from -1 to 1. This requires an understanding of integral calculus and how to handle absolute values within integrands.
Answer
The value of the integral is \( \frac{2}{3} \).
Answer for screen readers
The value of the integral is ( \frac{2}{3} ).
Steps to Solve
- Evaluate the integrand with respect to the interval
The function is defined as ( f(x) = x |x| + x^4 ). We need to analyze this based on the absolute value over the interval from (-1) to (1).
For ( x < 0 ) (i.e., (-1 \leq x < 0)):
- ( |x| = -x )
- Therefore, ( f(x) = x(-x) + x^4 = -x^2 + x^4 )
For ( x \geq 0 ) (i.e. (0 \leq x \leq 1)):
- ( |x| = x )
- Therefore, ( f(x) = x(x) + x^4 = x^2 + x^4 )
- Set up the definite integral
We split the integral at 0: $$ \int_{-1}^{1} (x |x| + x^4) , dx = \int_{-1}^{0} (-x^2 + x^4) , dx + \int_{0}^{1} (x^2 + x^4) , dx $$
- Evaluate the first integral
Calculating ( \int_{-1}^{0} (-x^2 + x^4) , dx ): [ \int (-x^2 + x^4) , dx = -\frac{x^3}{3} + \frac{x^5}{5} ] Now, evaluate from (-1) to (0): [ \left[ -\frac{0^3}{3} + \frac{0^5}{5} \right] - \left[ -\frac{(-1)^3}{3} + \frac{(-1)^5}{5} \right] = 0 - \left( \frac{1}{3} - \frac{1}{5} \right) ] Now finding a common denominator (15): [ -\left( \frac{5}{15} - \frac{3}{15} \right) = -\left( \frac{2}{15} \right) = \frac{2}{15} ]
- Evaluate the second integral
Calculating ( \int_{0}^{1} (x^2 + x^4) , dx ): [ \int (x^2 + x^4) , dx = \frac{x^3}{3} + \frac{x^5}{5} ] Now evaluate from (0) to (1): [ \left[ \frac{1^3}{3} + \frac{1^5}{5} \right] - \left[ \frac{0^3}{3} + \frac{0^5}{5} \right] = \frac{1}{3} + \frac{1}{5} ] Again finding a common denominator (15): [ \frac{5}{15} + \frac{3}{15} = \frac{8}{15} ]
- Combine the results
Now combine both integrals: $$ \int_{-1}^{1} (x |x| + x^4) , dx = \frac{2}{15} + \frac{8}{15} = \frac{10}{15} = \frac{2}{3} $$
The value of the integral is ( \frac{2}{3} ).
More Information
The integral evaluates to ( \frac{2}{3} ), which means the net area under the curve over the given interval is positive, contributing to the overall value.
Tips
- Forgetting about the absolute value: Ensure you account for changes in the function depending on the sign of ( x ).
- Incorrect limits on integration: Make sure to split the integral properly when the absolute value is involved.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information