The co-ordinate of equilibrium position of the particle is x = ________ m
Understand the Problem
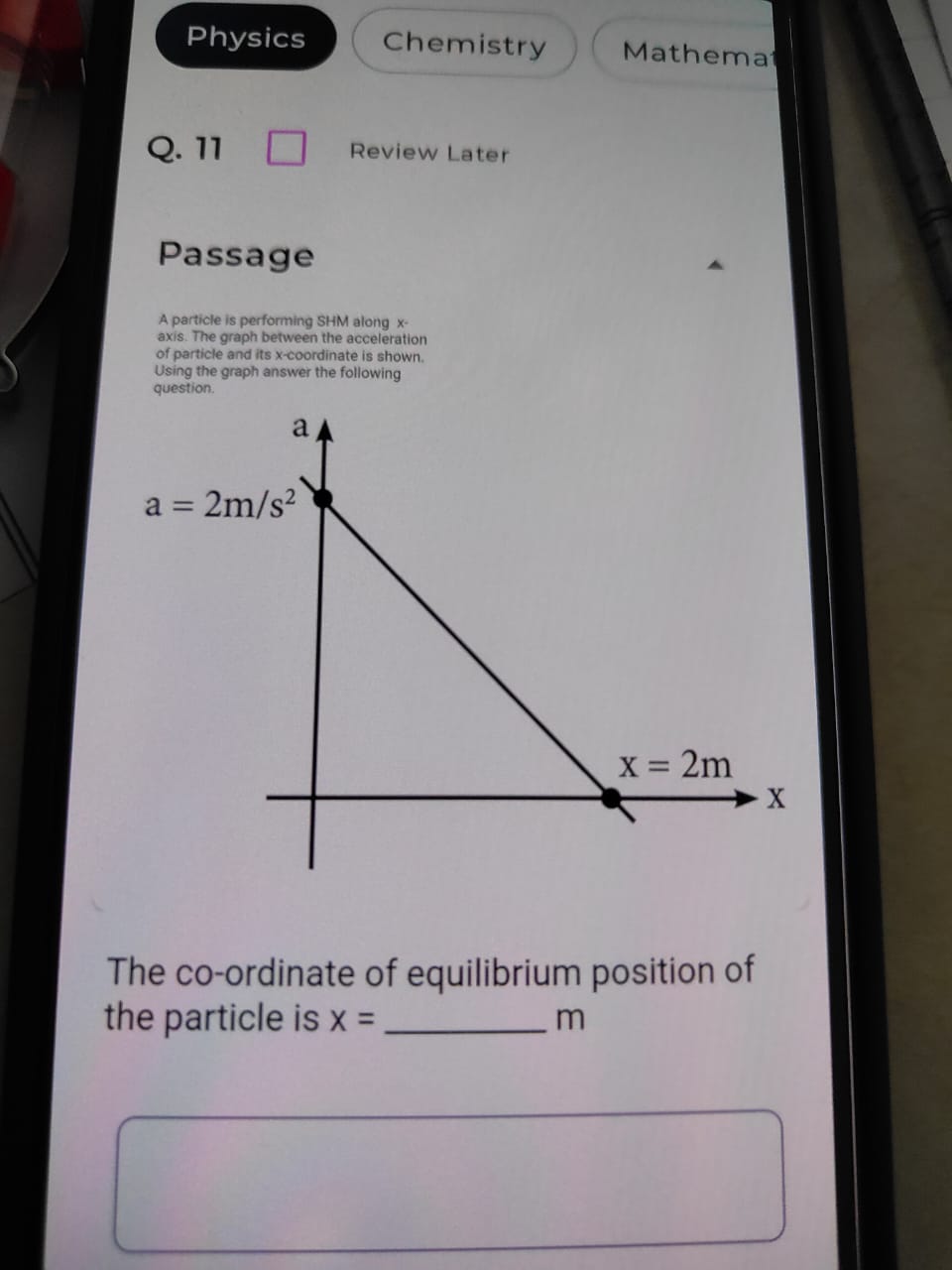
The question asks for the equilibrium position of a particle undergoing simple harmonic motion (SHM) along the x-axis, given a graph that relates acceleration and position.
Answer
$x = 0 \, \text{m}$
Answer for screen readers
The co-ordinate of equilibrium position of the particle is $x = 0 , \text{m}$.
Steps to Solve
- Understand the concept of equilibrium position in SHM
In simple harmonic motion (SHM), the equilibrium position is where the net force (and therefore acceleration) acting on the particle is zero. In the given graph, the acceleration $a$ is related to position $x$.
- Analyze the graph at the equilibrium position
From the graph, we see that acceleration $a$ is plotted against position $x$. The equilibrium position occurs where the graph crosses the x-axis, indicating that $a = 0$.
- Identify the coordinate from the graph
Looking at the graph, we see that the acceleration is given as $a = 2, \text{m/s}^2$ at a position $x = 2, \text{m}$. However, for equilibrium, we need where $a = 0$. The graph shows that acceleration becomes zero at the origin ($x = 0, \text{m}$).
The co-ordinate of equilibrium position of the particle is $x = 0 , \text{m}$.
More Information
In simple harmonic motion, the equilibrium position is crucial as it represents the point of maximum stability where forces balance. The particle oscillates around this point.
Tips
- Misinterpreting the graph: Students might overlook the point where acceleration equals zero. Always check where the graph crosses the x-axis.
- Forgetting the meaning of acceleration: It’s important to relate the acceleration directly to force in SHM.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information