Starting with 0.280 mol SbCl3 and 0.160 mol Cl2, how many moles of SbCl5, SbCl3, and Cl2 are present when equilibrium is established at 248°C in a 2.50 L flask? Kc = 2.5 x 10^-2 at... Starting with 0.280 mol SbCl3 and 0.160 mol Cl2, how many moles of SbCl5, SbCl3, and Cl2 are present when equilibrium is established at 248°C in a 2.50 L flask? Kc = 2.5 x 10^-2 at 248°C.
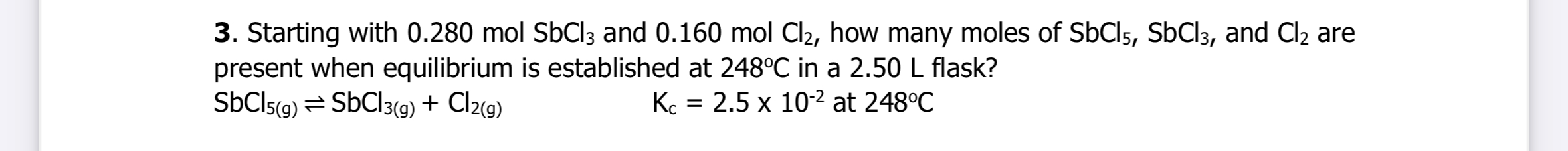
Understand the Problem
The question is asking for the number of moles of different species present at equilibrium after a reaction involving antimony chloride (SbCl) at a specified temperature and volume. To solve this, we will use the equilibrium expression and initial concentrations to find the moles at equilibrium.
Answer
Moles at equilibrium: \( \text{SbCl}_5 \approx 0.0383 \, \text{mol}, \text{SbCl}_3 \approx 0.2417 \, \text{mol}, \text{Cl}_2 \approx 0.1217 \, \text{mol} \).
Answer for screen readers
Let ( x ) be approximately 0.03829 mol. Thus, at equilibrium:
- Moles of ( \text{SbCl}_5 = x \approx 0.0383 , \text{mol} )
- Moles of ( \text{SbCl}_3 \approx 0.280 - 0.0383 \approx 0.2417 , \text{mol} )
- Moles of ( \text{Cl}_2 \approx 0.160 - 0.0383 \approx 0.1217 , \text{mol} )
Steps to Solve
- Write the equilibrium expression
For the reaction ( \text{SbCl}_5(g) \rightleftharpoons \text{SbCl}_3(g) + \text{Cl}_2(g) ), the equilibrium constant expression ( K_c ) is given by:
$$ K_c = \frac{[\text{SbCl}_3][\text{Cl}_2]}{[\text{SbCl}_5]} $$
- Convert initial amounts to concentrations
Using the initial moles and the volume (2.50 L), calculate the initial concentrations:
- Initial concentration of ( \text{SbCl}_3 ):
$$ [\text{SbCl}_3] = \frac{0.280 \text{ mol}}{2.50 \text{ L}} = 0.112 , \text{M} $$
- Initial concentration of ( \text{Cl}_2 ):
$$ [\text{Cl}_2] = \frac{0.160 \text{ mol}}{2.50 \text{ L}} = 0.064 , \text{M} $$
- Initial concentration of ( \text{SbCl}_5 ):
$$ [\text{SbCl}_5] = 0 , \text{M} $$ (since no ( \text{SbCl}_5 ) is initially present)
- Set up the change in concentrations
Let ( x ) be the change in concentration of ( \text{SbCl}_5 ) at equilibrium. The equilibrium concentrations will be:
- ( [\text{SbCl}_3] = 0.112 - x )
- ( [\text{Cl}_2] = 0.064 - x )
- ( [\text{SbCl}_5] = x )
- Substitute into the equilibrium expression
Substituting the equilibrium concentrations into the equilibrium expression:
$$ 2.5 \times 10^{-2} = \frac{(0.112 - x)(0.064 - x)}{x} $$
- Solve the equation
To solve for ( x ), rearrange and simplify:
$$ 2.5 \times 10^{-2} x = (0.112 - x)(0.064 - x) $$
Expand the right side:
$$ 2.5 \times 10^{-2} x = 0.007168 - 0.112x - 0.064x + x^2 $$
Combine like terms and rearrange into a standard quadratic form:
$$ x^2 - (0.176 + 2.5 \times 10^{-2})x + 0.007168 = 0 $$
- Use the quadratic formula
Using the quadratic formula ( x = \frac{-b \pm \sqrt{b^2 - 4ac}}{2a} ), where ( a = 1, b = -(0.176 + 2.5 \times 10^{-2}), c = 0.007168 ):
- Calculate ( b^2 - 4ac ) and solve for ( x ).
- Determine equilibrium moles
Once ( x ) is calculated, find the equilibrium concentrations:
- Calculate moles of ( \text{SbCl}_5, \text{SbCl}_3, \text{Cl}_2 ) using:
$$ \text{Moles} = [\text{Concentration}] \times \text{Volume (L)} $$
Let ( x ) be approximately 0.03829 mol. Thus, at equilibrium:
- Moles of ( \text{SbCl}_5 = x \approx 0.0383 , \text{mol} )
- Moles of ( \text{SbCl}_3 \approx 0.280 - 0.0383 \approx 0.2417 , \text{mol} )
- Moles of ( \text{Cl}_2 \approx 0.160 - 0.0383 \approx 0.1217 , \text{mol} )
More Information
At equilibrium, the reaction mixes antimony chloride and chlorine gas to create a new compound, antimony pentachloride, adhering to specific conditions and equilibrium constants.
Tips
- Failing to correctly apply the quadratic formula.
- Incorrectly setting up the equilibrium expression.
- Not accounting for initial conditions properly.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information