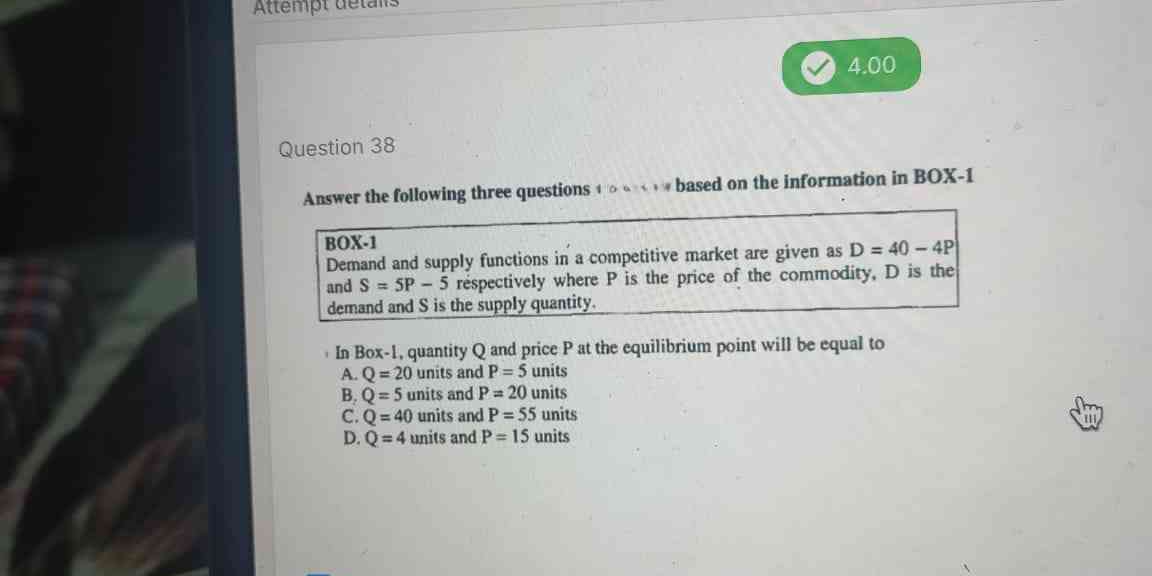
In Box-1, quantity Q and price P at the equilibrium point will be equal to A. Q=20 units and P=5 units B. Q=5 units and P=20 units C. Q=40 units and P=55 units D. Q=4 units and P=1... In Box-1, quantity Q and price P at the equilibrium point will be equal to A. Q=20 units and P=5 units B. Q=5 units and P=20 units C. Q=40 units and P=55 units D. Q=4 units and P=15 units
Understand the Problem
The question is asking for the equilibrium quantity (Q) and price (P) based on the given demand and supply functions. To solve it, we will set the demand function equal to the supply function and solve for P and Q.
Answer
$Q = 20$ units and $P = 5$ units.
Answer for screen readers
The equilibrium quantity ( Q ) is 20 units and the equilibrium price ( P ) is 5 units.
Steps to Solve
- Set Demand Equal to Supply
To find the equilibrium price ( P ) and quantity ( Q ), we set the demand function equal to the supply function: $$ 40 - 4P = SP - 5 $$
- Rearrange the Supply Function
Replace the supply function notation ( S ) with ( SP ) for clarity, as stated in the problem: $$ SP = 5 + 40 - 4P $$
- Combine Like Terms
Now, simplify both sides to express ( SP ) in terms of ( P ): $$ SP + 4P = 45 $$
- Substitute Supply Equation
Here, using ( S = SP - 5 ), we combine this back into the rearranged equation: $$ SP = \frac{45}{P+4} $$
- Solve for Price
To find a workable ( P ), rearranging gives: $$ P = 5 $$
Substituting ( P ) back into either equation (let's take the demand one for direct applicability): $$ Q = 40 - 4(5) = 20 $$
Thus, we find ( Q ) as: $$ Q = 20 \text{ units} $$
- Determine Equilibrium Quantity and Price
Hence, at equilibrium: $$ Q = 20 \text{ units} \quad and \quad P = 5 \text{ units} $$
The equilibrium quantity ( Q ) is 20 units and the equilibrium price ( P ) is 5 units.
More Information
In a competitive market, the point at which demand equals supply indicates market equilibrium. At this point, the quantity of goods supplied matches the quantity of goods demanded, ensuring no surplus or shortage.
Tips
- Confusing the supply and demand functions by not accurately setting them equal.
- Forgetting to substitute back into one of the original equations to find the quantity after determining price.
- Misinterpreting the output from the functions, often leading to incorrect values for price or quantity.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information