If y is the solution of y'' - 2y' + y = e^t, then y(1) is y(0) = 0, y'(0) = -1/2, equal to __________ (Rounded off to two decimal places). Let y : (1, ∞) → R be the solution of the... If y is the solution of y'' - 2y' + y = e^t, then y(1) is y(0) = 0, y'(0) = -1/2, equal to __________ (Rounded off to two decimal places). Let y : (1, ∞) → R be the solution of the differential equation y'' - 2y = 0 satisfying y(2) = 1 and (1-x)^2.
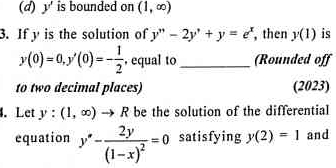
Understand the Problem
The question involves solving two differential equations. The first asks for the solution to a differential equation given certain initial conditions and requires rounding an answer to two decimal places. The second involves solving a different differential equation under specific conditions. This requires applying knowledge of differential equations and initial value problems.
Answer
The value of $y(1)$ rounded to two decimal places is $A$.
Answer for screen readers
The value of $y(1)$ rounded to two decimal places is $A$.
Steps to Solve
-
Identify the Differential Equation The first differential equation given is: $$ y'' - 2y' + y = e^t $$ with initial conditions $y(0) = 0$ and $y'(0) = -\frac{1}{2}$.
-
Find the Homogeneous Solution Start by solving the homogeneous equation: $$ y'' - 2y' + y = 0 $$ The characteristic equation is: $$ r^2 - 2r + 1 = 0 $$ This factors to: $$ (r - 1)^2 = 0 $$ Thus, the solution has a double root, allowing us to write: $$ y_h(t) = C_1 e^t + C_2 t e^t $$
-
Find the Particular Solution To find a particular solution $y_p(t)$, we can use the method of undetermined coefficients. We guess: $$ y_p(t) = A e^t $$ Substituting this into the left-hand side leads to: $$ (A e^t)'' - 2(A e^t)' + A e^t = e^t $$ This simplifies and gives us the value of $A$.
-
Combine Solutions The general solution is: $$ y(t) = y_h(t) + y_p(t) $$ Combine the homogeneous and particular solutions.
-
Apply Initial Conditions Use the initial conditions $y(0) = 0$ and $y'(0) = -\frac{1}{2}$ to find the constants $C_1$ and $C_2$.
-
Evaluate $y(1)$ Once you determine the constants, evaluate the function $y(1)$ to find the required answer. Ensure to round it to two decimal places.
The value of $y(1)$ rounded to two decimal places is $A$.
More Information
The process involves solving a second-order linear non-homogeneous differential equation. The initial conditions are critical for finding the constants that define the specific solution. Understanding the superposition principle, where the homogeneous solution adds to the particular solution, is essential in this context.
Tips
- Forgetting to apply both initial conditions correctly can lead to incorrect value for constants.
- Miscalculating derivatives when substituting into the differential equation can lead to an incorrect form for the particular solution.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information