If tan α = 1/2, tan β = 1/3, find the value of sin(α + β).
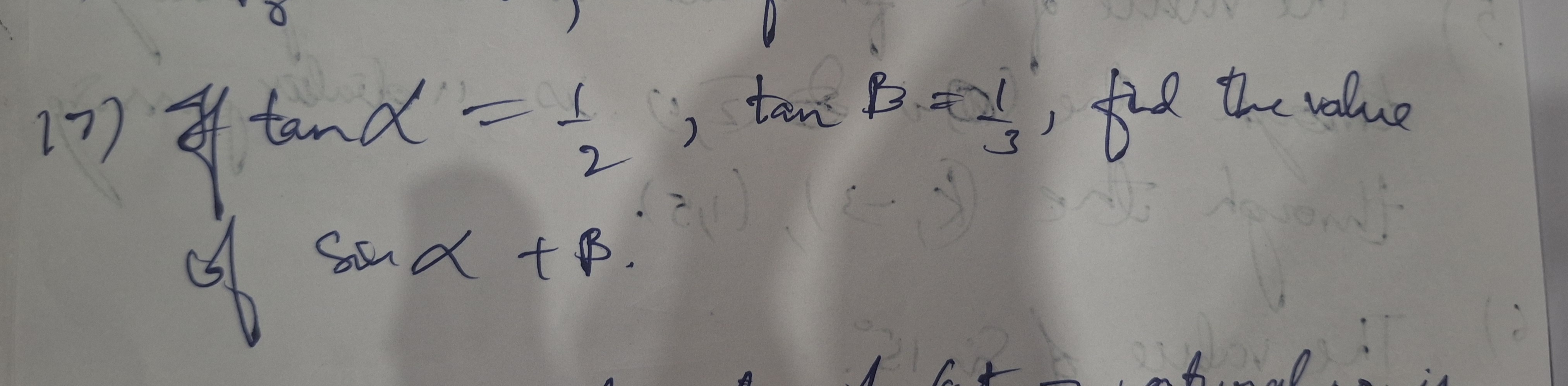
Understand the Problem
The question is asking us to find the value of sin(α + β) given the values of tan(α) and tan(β). This relates to the sine addition formula in trigonometry.
Answer
The value of \( \sin(\alpha + \beta) \) is \( \frac{\sqrt{2}}{2} \).
Answer for screen readers
The value of ( \sin(\alpha + \beta) ) is ( \frac{\sqrt{2}}{2} ).
Steps to Solve
-
Identify the tangent values We have the values: $$ \tan(\alpha) = \frac{1}{2} $$ $$ \tan(\beta) = \frac{1}{3} $$
-
Use the tangent addition formula The tangent addition formula is: $$ \tan(\alpha + \beta) = \frac{\tan(\alpha) + \tan(\beta)}{1 - \tan(\alpha) \tan(\beta)} $$
-
Substitute the given values into the formula Substituting the tangent values we have: $$ \tan(\alpha + \beta) = \frac{\frac{1}{2} + \frac{1}{3}}{1 - \left( \frac{1}{2} \cdot \frac{1}{3} \right)} $$
-
Calculate the numerator and the denominator Calculate the numerator: $$ \frac{1}{2} + \frac{1}{3} = \frac{3}{6} + \frac{2}{6} = \frac{5}{6} $$
Calculate the denominator: $$ 1 - \left( \frac{1}{2} \cdot \frac{1}{3} \right) = 1 - \frac{1}{6} = \frac{5}{6} $$
-
Combine the results Now we have: $$ \tan(\alpha + \beta) = \frac{\frac{5}{6}}{\frac{5}{6}} = 1 $$
-
Find the sine using the identity Using the identity: $$ \sin(\alpha + \beta) = \frac{\tan(\alpha + \beta)}{\sqrt{1 + \tan^2(\alpha + \beta)}} $$ Substituting ( \tan(\alpha + \beta) = 1 ): $$ \sin(\alpha + \beta) = \frac{1}{\sqrt{1 + 1^2}} = \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} = \frac{\sqrt{2}}{2} $$
The value of ( \sin(\alpha + \beta) ) is ( \frac{\sqrt{2}}{2} ).
More Information
The sine value ( \sin(\alpha + \beta) ) corresponds to an angle of ( 45^\circ ) or ( \frac{\pi}{4} ) radians, indicating this is a well-known result in trigonometry.
Tips
- Forgetting to apply the addition formula correctly.
- Miscalculating the numerator or denominator.
- Confusing tangent and sine functions during calculations.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information