If f(x) = { m x^2 + n, x < 0; n x + m, 0 ≤ x ≤ 1; n x^3 + m, x > 1 }
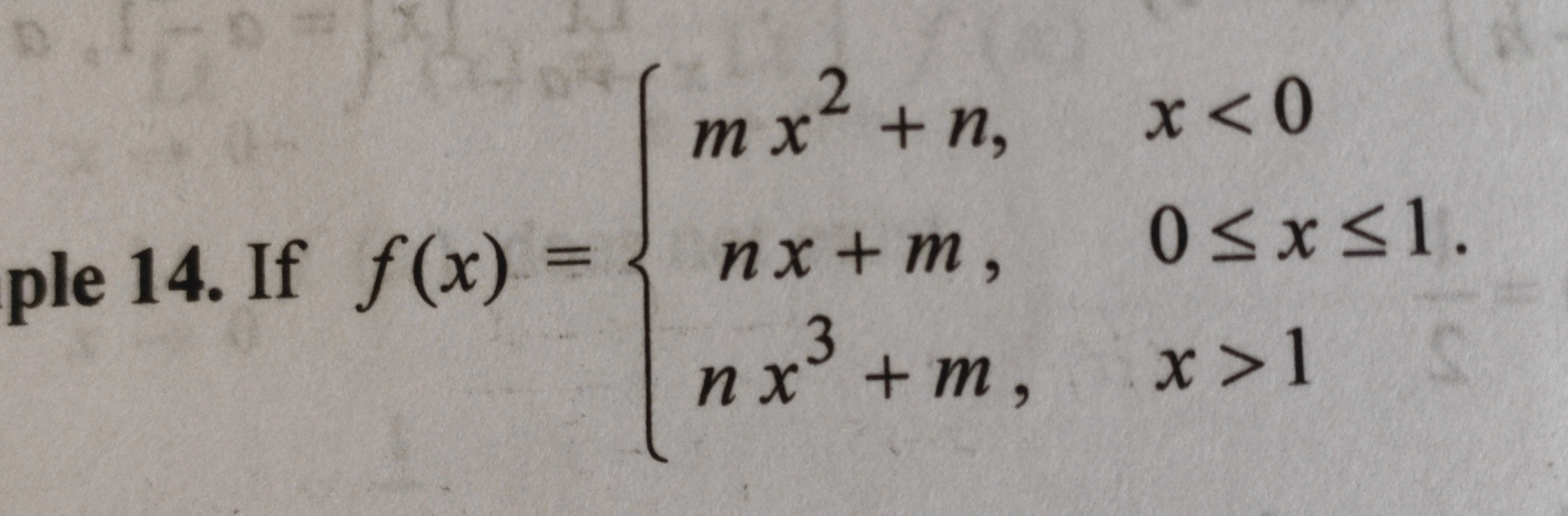
Understand the Problem
The question presents a piecewise function f(x) defined by different expressions depending on the value of x. The goal is likely to analyze or compute something related to this function, such as its continuity, limits, or integration across specified intervals.
Answer
The function is continuous for all \( x \) if \( n = m \).
Answer for screen readers
The function is continuous for all ( x ) if ( n = m ).
Steps to Solve
- Identify the pieces of the function The piecewise function is defined as:
- For $x < 0$: ( f(x) = m x^2 + n )
- For $0 \leq x \leq 1$: ( f(x) = n x + m )
- For $x > 1$: ( f(x) = n x^3 + m )
- Check continuity at the boundaries To ensure continuity at the transition points (0 and 1), we set the function values from adjacent pieces equal to each other:
-
At $x = 0$: [ \text{Limit as } x \to 0^-: f(0) = n \ \text{Limit as } x \to 0^+: f(0) = m ] Set ( n = m ).
-
At $x = 1$: [ \text{Limit as } x \to 1^-: f(1) = n(1) + m = n + m \ \text{Limit as } x \to 1^+: f(1) = n(1^3) + m = n + m ] Check for equality, which holds for all valid ( m ) and ( n ).
- Determine function behavior To analyze the overall behavior:
- For $x < 0$, the graph is a concave upwards parabola.
- For $0 \leq x \leq 1$, a straight line.
- For $x > 1$, a cubic function.
- Evaluate specific conditions, if given Any specific conditions or questions regarding maximum, minimum, or limits can apply. Determine if comparing or optimizing over certain intervals is necessary.
The function is continuous for all ( x ) if ( n = m ).
More Information
This piecewise function forms different types of graphs based on the value of ( x ), including a quadratic, linear, and cubic function. Understanding continuity helps in analyzing the function's behavior effectively.
Tips
- Ignoring the need for continuity conditions when analyzing piecewise functions.
- Not checking for equal limits at the boundaries can lead to missing crucial aspect of function behavior.