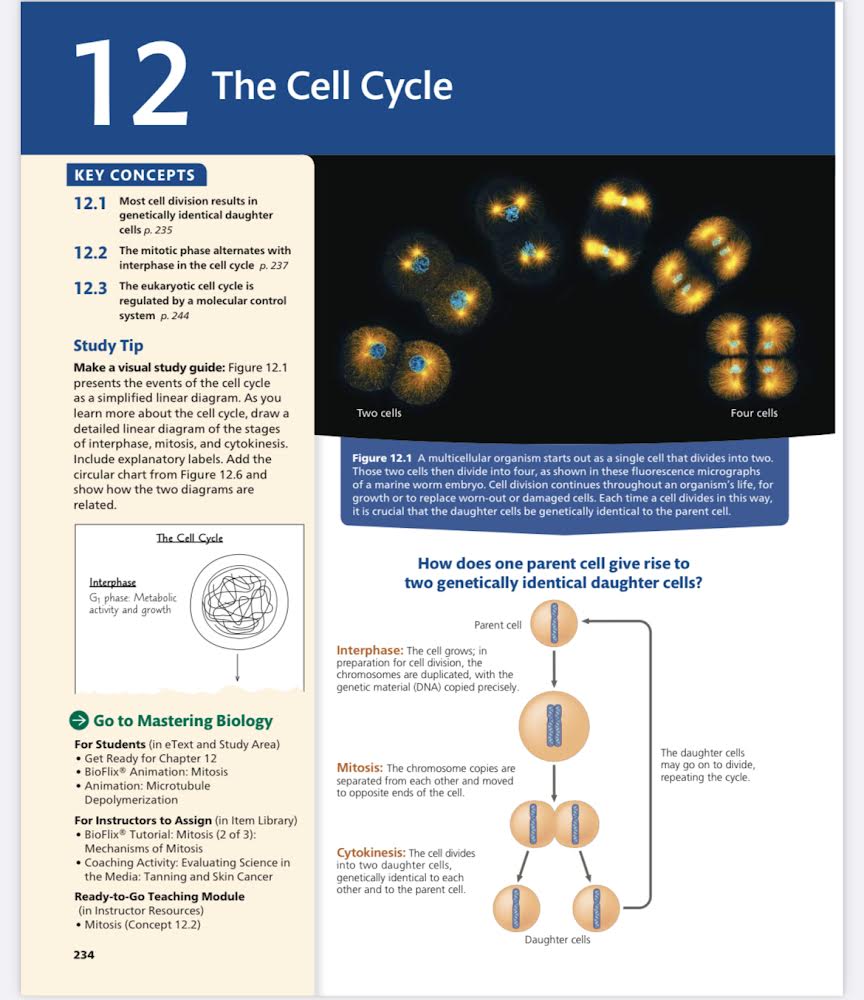
How does one parent cell give rise to two genetically identical daughter cells?
Understand the Problem
The question is asking how a single parent cell divides to produce two genetically identical daughter cells. This involves understanding the processes of interphase, mitosis, and cytokinesis involved in the cell cycle.
Answer
Mitosis duplicates DNA and divides the parent cell into two identical daughter cells.
The process of mitosis involves the duplication of the parent cell's contents, including DNA, followed by division into two identical daughter cells.
Answer for screen readers
The process of mitosis involves the duplication of the parent cell's contents, including DNA, followed by division into two identical daughter cells.
More Information
Mitosis is crucial for growth, repair, and asexual reproduction. It ensures that each daughter cell receives an exact copy of the parent cell's DNA, maintaining genetic consistency.
Tips
A common mistake is confusing mitosis with meiosis. Mitosis produces identical cells, while meiosis produces genetically different cells for sexual reproduction.
Sources
- How genes work - Cells divide - medlineplus.gov
- Phases of mitosis | Mitosis | Biology (article) - Khan Academy - khanacademy.org
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information