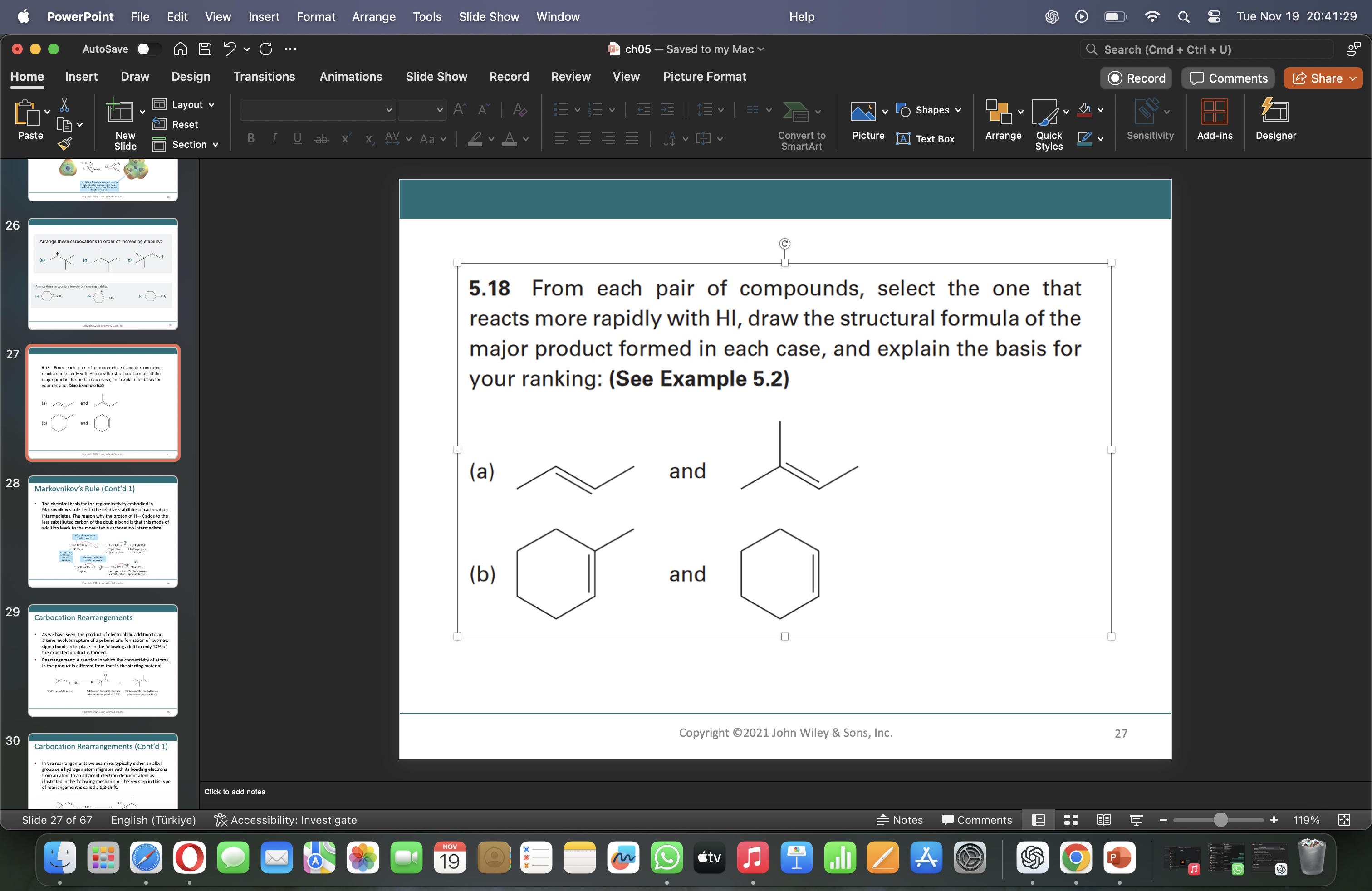
From each pair of compounds, select the one that reacts more rapidly with HI, draw the structural formula of the major product formed in each case, and explain the basis for your r... From each pair of compounds, select the one that reacts more rapidly with HI, draw the structural formula of the major product formed in each case, and explain the basis for your ranking.
Understand the Problem
The question asks to compare two pairs of compounds to determine which one reacts more rapidly with HI, to draw the structural formula of the major products formed, and to explain the ranking of reactivity based on the results. This involves understanding chemical reactivity and mechanisms.
Answer
(a) Right compound reacts faster. (b) Left compound reacts faster.
The final answer is:
(a) The compound with the more substituted double bond (right) reacts faster, forming 2-iodobutane.
(b) The secondary alkyl bromide (left) reacts faster, forming cyclohexane after substitution.
Answer for screen readers
The final answer is:
(a) The compound with the more substituted double bond (right) reacts faster, forming 2-iodobutane.
(b) The secondary alkyl bromide (left) reacts faster, forming cyclohexane after substitution.
More Information
Reactions with hydrogen iodide follow Markovnikov's rule, favoring more stable carbocations. More substituted alkenes generally react faster due to greater stability of the carbocation intermediate.
Tips
A common mistake is not evaluating the stability of carbocations correctly. Ensure comparison is based on substitution and resulting stability.
Sources
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information