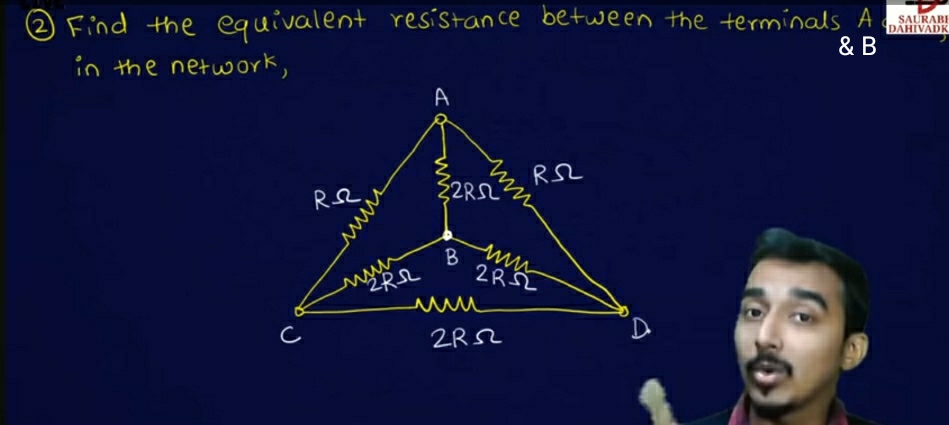
Find the equivalent resistance between the terminals A and B in the network.
Understand the Problem
The question is asking to determine the equivalent resistance between the terminals A and B in a given electrical network of resistors. This involves analyzing the circuit configuration and applying relevant electrical laws to find the total resistance.
Answer
The equivalent resistance between the terminals A and B is $$ \frac{9R}{5} \, \Omega $$.
Answer for screen readers
The equivalent resistance between the terminals A and B is $$ \frac{9R}{5} , \Omega $$.
Steps to Solve
-
Identify the resistors in the circuit
The circuit has four resistors with values R, 2R, 2R, and R arranged in a specific configuration between terminals A and B.
-
Simplify the resistors in series and parallel
Group the resistors to simplify the calculation:
- The two 2R resistors are in series with each other and can be combined: $$ R_{series} = 2R + 2R = 4R $$
-
Combine series and parallel resistors between A and B
Now we have:
- A resistor of R (between A and the point between series resistors)
- A parallel combination of R and 4R from the previous step:
The formula for equivalent resistance in parallel ($R_{eq}$) is: $$ \frac{1}{R_{eq}} = \frac{1}{R} + \frac{1}{4R} $$
-
Calculate the equivalent resistance
To find $R_{eq}$, we rearrange the previous equation: $$ R_{eq} = \frac{1}{\frac{1}{R} + \frac{1}{4R}} $$ Combine: $$ R_{eq} = \frac{1}{\frac{4 + 1}{4R}} = \frac{4R}{5} $$
-
Combine with the remaining resistor
Now, we have a resistor of $\frac{4R}{5}$ in series with the remaining R: $$ R_{total} = R + R_{eq} = R + \frac{4R}{5} = \frac{5R + 4R}{5} = \frac{9R}{5} $$
The equivalent resistance between the terminals A and B is $$ \frac{9R}{5} , \Omega $$.
More Information
This methodical approach allows us to accurately determine the equivalent resistance in a network of resistors, crucial for understanding circuit behavior in electrical engineering.
Tips
- Forgetting to correctly identify series and parallel configurations can lead to incorrect equivalent resistance calculations.
- Miscalculating the combined resistance when combining series or parallel resistors.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information