Create a quiz based on the comparison of Type 1, Type 2, and MODY diabetes.
Understand the Problem
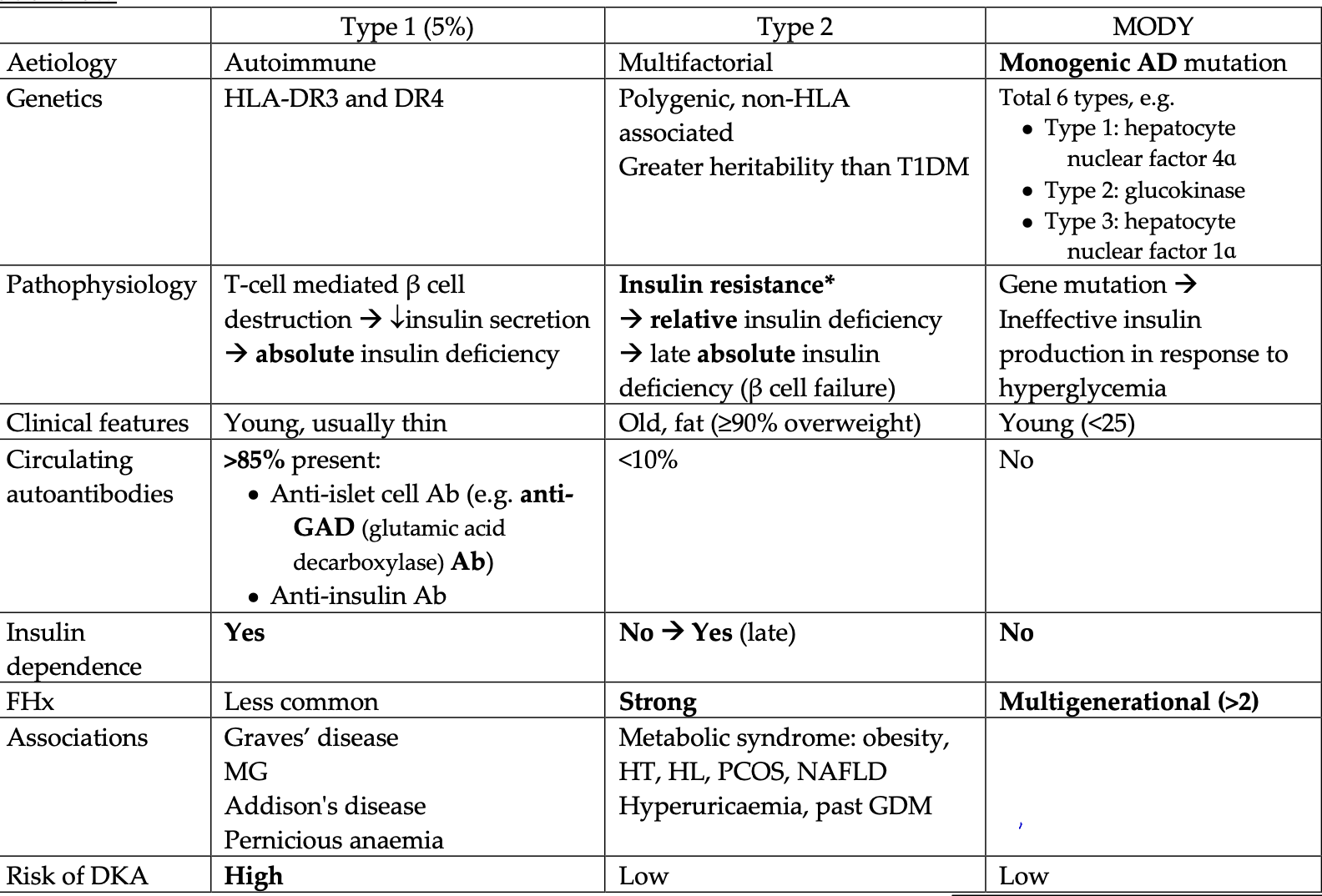
The question appears to request the creation of a quiz based on the table provided, which compares different types of diabetes mellitus (Type 1, Type 2, and MODY) along various factors such as aetiology, genetics, pathophysiology, clinical features, and others. The quiz will include questions related to these comparisons and details.
Answer
1. Type 1 is autoimmune, high DKA risk; Type 2 is multifactorial, late insulin dependence; MODY is monogenic. 2. Type 1 affects young, thin; Type 2 affects older, overweight; MODY affects under 25. 3. Type 2 is polygenic; MODY involves specific mutations.
- Type 1 diabetes is autoimmune with high DKA risk. Type 2 is multifactorial with late insulin dependence. MODY is monogenic with ineffective insulin response.
- Type 1 affects young, thin individuals. Type 2 is common in older, overweight individuals. MODY affects those under 25.
- Type 2 diabetes is polygenic, while MODY involves autosomal dominant mutations.
Answer for screen readers
- Type 1 diabetes is autoimmune with high DKA risk. Type 2 is multifactorial with late insulin dependence. MODY is monogenic with ineffective insulin response.
- Type 1 affects young, thin individuals. Type 2 is common in older, overweight individuals. MODY affects those under 25.
- Type 2 diabetes is polygenic, while MODY involves autosomal dominant mutations.
More Information
Type 1 diabetes often appears in childhood and is linked with antibodies. Type 2 typically develops in adults with obesity, while MODY is a rare form with specific genetic mutations and occurs in familial clusters.
Tips
Confusing MODY with Type 2 diabetes due to similar presentations can occur. Genetic testing can help differentiate MODY.
Sources
- Differentiating Among Type 1, Type 2 Diabetes, and MODY - pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- Maturity onset diabetes of the young (MODY) - diabetes.org.uk
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information