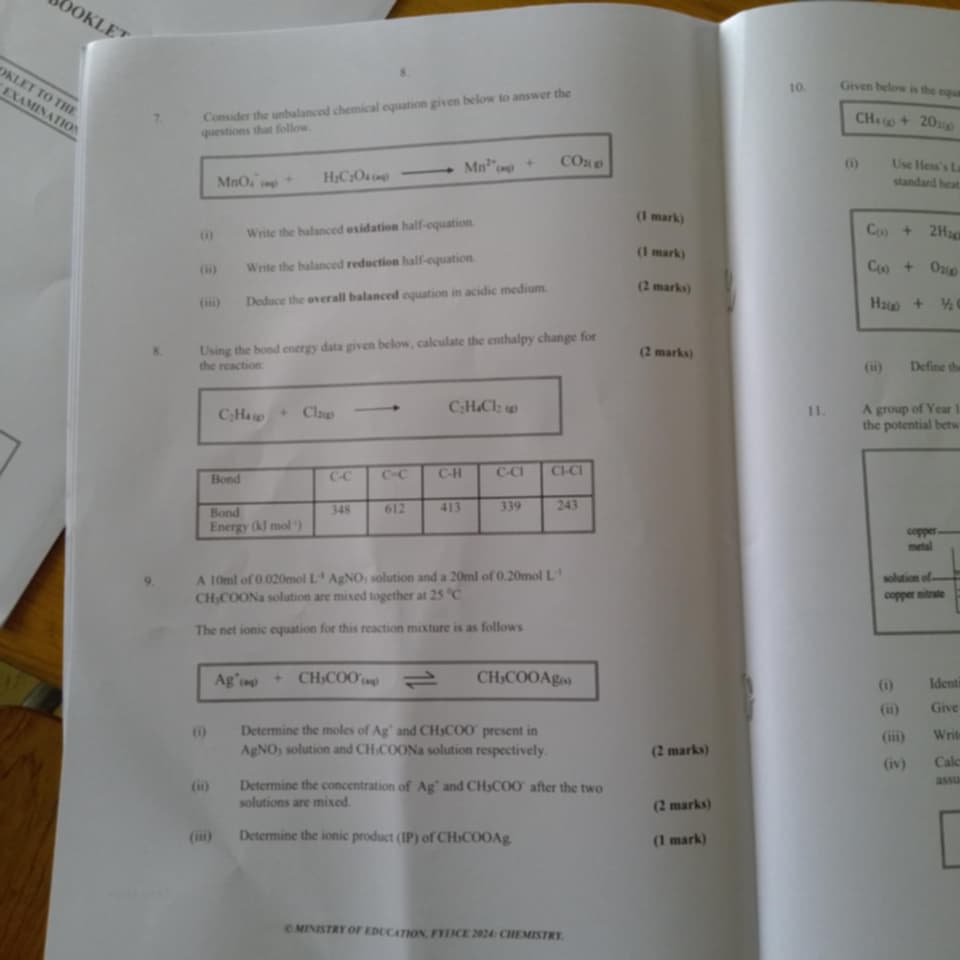
Consider the unbalanced chemical equation given below to answer the following questions. Write the balanced oxidation half-equation. Write the balanced reduction half-equation. Ded... Consider the unbalanced chemical equation given below to answer the following questions. Write the balanced oxidation half-equation. Write the balanced reduction half-equation. Deduce the overall balanced equation in acidic medium. Using the bond energy data given below, calculate the enthalpy change for the reaction: C2H4(g) + Cl2(g) → C2H4Cl2(g). A 10ml of 0.020mol L-1 AgNO3 solution and a 20ml of 0.20mol L-1 CH3COONa solution are mixed together at 25°C. Determine the moles of Ag+ and CH3COO- present in AgNO3 and CH3COONa solution respectively. Determine the concentration of Ag+ and CH3COO- after the two solutions are mixed. Determine the ionic product (IP) of CH3COOAg.
Understand the Problem
The question involves several tasks related to chemical equations, enthalpy calculation using bond energies, and ion concentrations in reactions. It is aimed at understanding redox reactions, thermochemistry, and solution chemistry.
Answer
Balanced equations: Oxidation: MnO4⁻ → Mn²⁺, Reduction: H2C2O4 → CO2. Enthalpy: +120.5 kJ/mol. Ag+ moles: 0.0002, CH3COO- moles: 0.004. Final [Ag+]: 0.00667 mol/L, [CH3COO-]: 0.133 mol/L. IP: 8.88 × 10⁻⁴ mol²/L².
Oxidation half-equation: MnO4⁻ → Mn²⁺. Reduction half-equation: H2C2O4 → CO2. Overall balanced equation: 2MnO4⁻ + 5H2C2O4 + 6H⁺ → 2Mn²⁺ + 10CO2 + 8H2O. Enthalpy change: +120.5 kJ/mol. Moles of Ag+: 0.0002 mol, CH3COO-: 0.004 mol. Final concentrations: [Ag+] = 0.00667 mol/L, [CH3COO-] = 0.133 mol/L. IP of CH3COOAg = 8.88 × 10⁻⁴ mol²/L².
Answer for screen readers
Oxidation half-equation: MnO4⁻ → Mn²⁺. Reduction half-equation: H2C2O4 → CO2. Overall balanced equation: 2MnO4⁻ + 5H2C2O4 + 6H⁺ → 2Mn²⁺ + 10CO2 + 8H2O. Enthalpy change: +120.5 kJ/mol. Moles of Ag+: 0.0002 mol, CH3COO-: 0.004 mol. Final concentrations: [Ag+] = 0.00667 mol/L, [CH3COO-] = 0.133 mol/L. IP of CH3COOAg = 8.88 × 10⁻⁴ mol²/L².
More Information
Balancing half-reactions in acidic mediums involves adding H+ ions and water to balance elements and charges. Enthalpy calculations use the principle that energy is required to break bonds and released when bonds are formed.
Tips
Ensure all atoms and charges are balanced in half-reactions. Watch for errors when calculating moles and concentrations after mixing solutions.
Sources
- Balancing Redox Reactions - Chemistry LibreTexts - chem.libretexts.org
- Worked example: Balancing a redox equation in acidic solution - khanacademy.org
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information