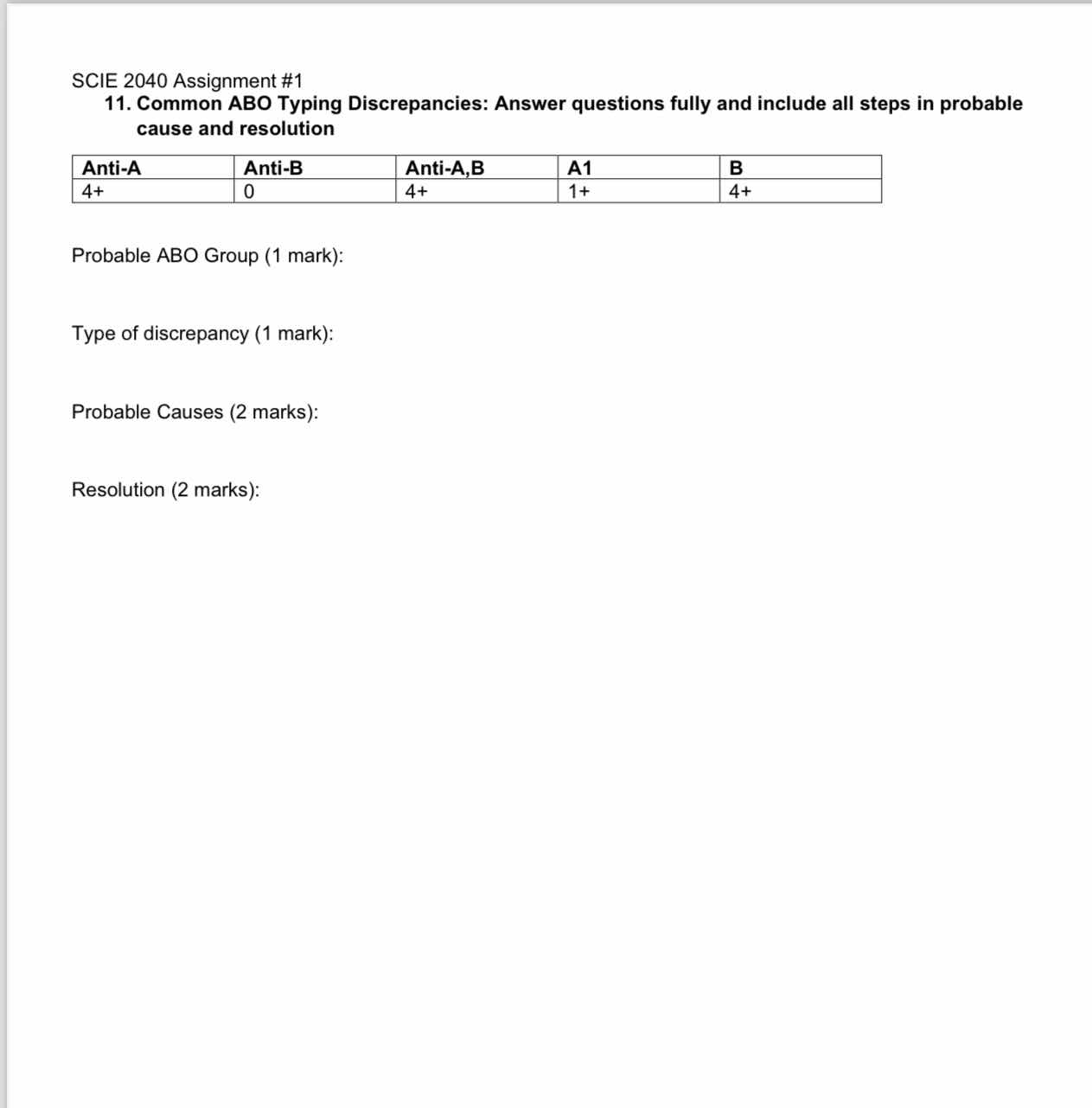
Common ABO typing discrepancies: Answer questions fully and include all steps in probable cause and resolution.
Understand the Problem
The question asks to analyze an ABO typing discrepancy with given test results, identifying the probable ABO group, type of discrepancy, probable causes, and resolution steps.
Answer
A2 blood group, weak reverse type discrepancy, A2 subgroup or technical error, use anti-A1 lectin or repeat test.
Probable ABO Group: A2. Type of discrepancy: Weak reverse type discrepancy. Probable Causes: A2 subgroup, technical error. Resolution: Test with anti-A1 lectin or repeat testing. The final answer is A2, weak reverse type discrepancy, A2 subgroup or technical error, test with anti-A1 or repeat testing.
Answer for screen readers
Probable ABO Group: A2. Type of discrepancy: Weak reverse type discrepancy. Probable Causes: A2 subgroup, technical error. Resolution: Test with anti-A1 lectin or repeat testing. The final answer is A2, weak reverse type discrepancy, A2 subgroup or technical error, test with anti-A1 or repeat testing.
More Information
ABO discrepancies often arise from subgroups, technical errors, or patient-specific factors like recent transfusions. Addressing these discrepancies is crucial for accurate blood typing and patient safety.
Tips
Common mistakes include misidentifying subgroups or overlooking technical errors in testing. Use confirmatory testing for accurate results.
Sources
- ABO Typing Discrepancies - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf - ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- Resolution of ABO Discrepancies - ARUP Laboratories - arup.utah.edu
- Help! I've Acquired a B! - Blood Bank Guy - bbguy.org
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information