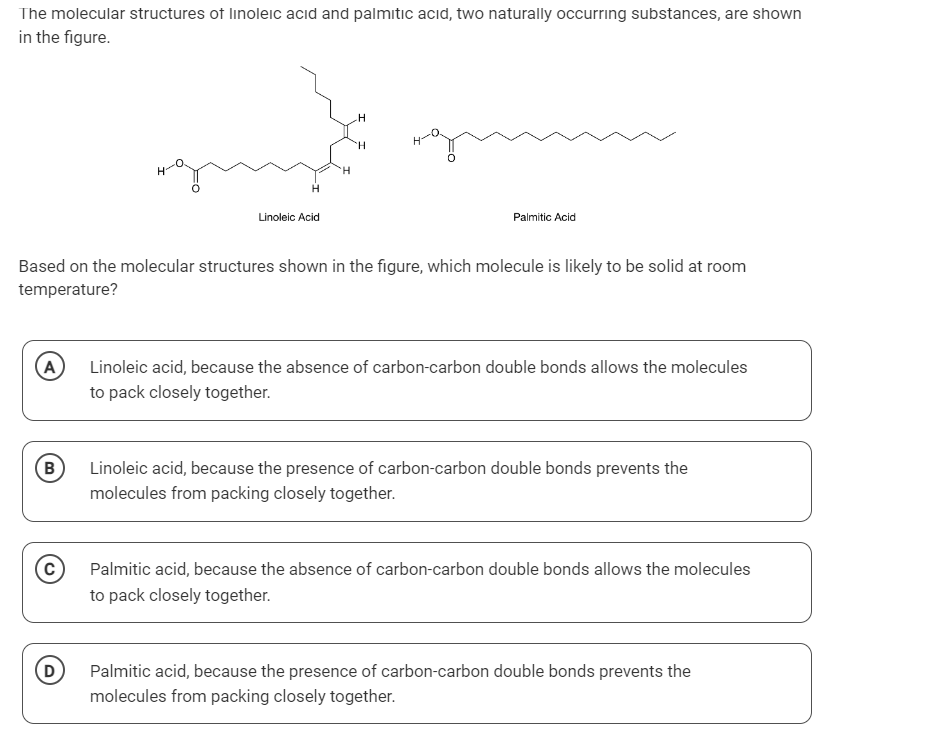
Based on the molecular structures shown in the figure, which molecule is likely to be solid at room temperature?
Understand the Problem
The question is asking to determine which of the two fatty acids, linoleic acid or palmitic acid, is likely to be solid at room temperature based on their molecular structures. It revolves around the concept of saturation in fatty acids and how the presence or absence of double bonds affects their physical state.
Answer
C
Palmitic acid, because the absence of carbon-carbon double bonds allows the molecules to pack closely together.
Answer for screen readers
Palmitic acid, because the absence of carbon-carbon double bonds allows the molecules to pack closely together.
More Information
Palmitic acid, a saturated fatty acid without double bonds, allows molecules to pack closely together, leading to a solid form at room temperature. In contrast, linoleic acid has double bonds, causing kinks and preventing tight packing, making it liquid at room temperature.
Tips
A common mistake is to overlook the presence or absence of double bonds. Saturated fatty acids (no double bonds) pack tightly and are solid at room temperature, while unsaturated fatty acids (with double bonds) do not pack as tightly and are liquid.
Sources
- Based on the molecular structures shown in the figure, which molecule is likely to be solid at room temperature? - brainscape.com
- Solved: 15. The molecular structures of linoleic acid and... | Chegg.com - chegg.com
- The molecular structures of linoleic acid and palmitic acid, two... - cliffsnotes.com
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information